* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
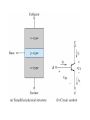
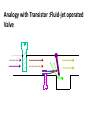
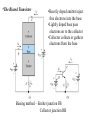
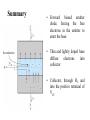
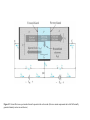
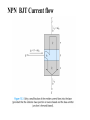
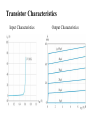
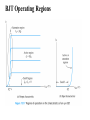
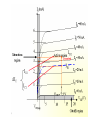
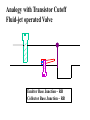
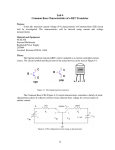
Electronic Principles 7th Edition Albert Malvino & David J Bates Ref. Books 1) Electronic devices and circuit theory – Robert Boylestad 2) Basic Electronics – A. P. Godse & U. A. Bakshi Rizwan H. Alad & Vasim A. Vohra Part 1 Syllabus • • • • • • • • Chap. 6 Bipolar Junction Transistors Chap. 7 Transistor Fundamentals Chap. 8 Transistor Biasing Chap. 9 Transistor AC Models Chap. 10 Voltage Amplifiers Chap. 11 CC and CB Amplifiers Chap. 12 Power Amplifiers Chap. 23 Oscillators Transistor • Three doped regions • Emitter, Base and Collector • Base region is much thinner as compared to the collector and emitter • npn and pnp • Emitter is heavily doped, Base is lightly and collector is intermediate • Collector regions is physically largest Before Diffusion After Diffusion Each of Dep. Layer barrier potential app. 0.7 V at 25o C Unbiased transistor is like two back-to-back diodes Bipolar Junction Transistors • A bipolar transistor essentially consists of a pair of PN Junction diodes that are joined back-to-back. • There are therefore two kinds of BJT, the NPN and PNP varieties. • The three layers of the sandwich are conventionally called the Collector, Base, and Emitter. Modern Transistors NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor •One N-P (Base Collector) diode one P-N (Base Emitter) diode PNP Bipolar Junction Transistor •One P-N (Base Collector) diode one N-P (Base Emitter) diode Analogy with Transistor :Fluid-jet operated Valve *The Biased Transistor •Heavily doped emitter inject free electrons into the base •Lightly doped base pass electrons on to the collector •Collector collects or gathers electrons from the base Biasing method – Emitter junction FB Collector junction RB Summary • Forward biased emitter diode, forcing the free electrons in the emitter to enter the base • Thin and lightly doped base diffuse electrons into collector • Collector, through RC and into the positive terminal of VCC Figure 5.3 Current flow in an npn transistor biased to operate in the active mode. (Reverse current components due to drift of thermally generated minority carriers are not shown.) Transistor Currents • IE – Largest emitter current • Emitter electrons flow to the collector, IC ≈ IE • IB ≤ 0.01 IC • KCL, IE = IC + IB BJT and •From the previous figure IE = IB + IC •Define dc = IC / IE • DC alpha is slightly less than 1 • Low power transistor αdc > 0.99 and High power transistor αdc > 0.95 •Define dc = IC / IB - known as a current gain BJT and •Then dc = IC / (IE –IC) = dc /(1- dc) •Assignment – Derive dc = dc /(1+ dc) •Then IC = dc IE & IB = (1-dc) IE Solved Example 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 NPN BJT Current flow The CE connection • CE, CC and CB • CE because emitter is common to both VBB and VCC • Left loop – Base loop • Right loop – collector loop The CE connection • Base Loop, VBB source and RB – current limiting resistor • Changing VBB or RB, change base current and IB Change than IC change • IB controls IC Notation Double Subscripts Single Subscripts • Voltage source – VBB and VCC • Used for Node voltages • VB – voltage between base and ground • VC and VE • VBE – voltage between points B and E • VCE = VC – VE • VCE – voltage between points C and E • VCB and VBE The Base Curve / Input Characteristics • Graph IB versus VBE • Like ordinary diode • Ohm’s low to Base loop VBB VBE IB RB • Ideal diode VBE = 0 and second app. VBE = 0.7 V I Collector Curve / output Characteristics • Graph IC versus VCE • Ohm’s low to Collector loop VCC VCE IC RC • Fixed value of based current, vary VCC and measure IC and VCE I Transistor Characteristics Input Characteristics Output Characteristics Active Region, Constant collector current • After collector diode reverse biased, it collect all the electrons that reach its deplation layer • Further increased VCE cannot increased IC • Collector can collect only those free electrons that emitter injects • VCE > VCE(max), collector diode break down • Power Dissipation PD = VCEIC • PD < PD(max) Operating Region of Transistor • Active region, middle region – normal operation of transistor Emitter diode – FB and Collector diode – RB • Breakdown region – transistor will be destroyed • Saturation region – rising part of curve, VCE between zero and few tenth of volt Collector diode has insufficient positive voltage to collect all the free electrons injected into the base Operating Region of Transistor • Cut off region – IB = 0 but still small collector current Because collector diode RB – Reverse minority carrier + Surface leakage current BJT Operating Regions Analogy with Transistor in Active Region: Fluid-jet operated Valve In active region this stopper does not really have noticeable effect on the flow rate Emitter Base Junction – FB Collector Base Junction – RB Analogy with Transistor Cutoff Fluid-jet operated Valve Emitter Base Junction – RB Collector Base Junction – RB Analogy with Transistor Saturation Fluid-jet operated Valve The valve is wide open; changing valve position a little bit does not have much influence on the flow rate. E-B Junction – FB C-B Junction – FB