* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Leptospirosis
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
IgA nephropathy wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
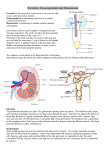
Leptospirosis Canine typhus or infectious jaundice Definition It is peracute, acute or chronic water born contagious disease of dogs caused by leptospira interrogans spp., characterized by pyrexia, anorexia, depression and signs of renal and hepatic failure Etiology Leptospira interrogans servoars as: L. Icterohaemorrhagica L. Conicola L. Grippotyphosa All serovars are antigenically distinct It is flexible filamentous, motile spirochete Infected dogs may excrete leptospira in urine intermittently for months or even years Epidemiology Distribution The disease is worldwide and present in Egypt Animal susceptibility Dogs of all ages are susceptible but cats appears to be resistant Mode of transmissions Source of infection Clinically infected or carrier dogs shed the organisms in urine for months or even years Mode of transmission Direct contact through penetration of mucosa of mouth or conjunctiva or abraded skin Ingestion of contaminated materials as infected meats Indirect transmission through exposure to contaminated fomites Transplacental or venereal and bite wound transmission Pathogenesis After infection Organism Localized and replicate in Kidney and liver Replicate in nephron cause nephritis and renal damage and shedding in urine for long time Injury and damage to hepatocytes in liver causing hepatic fibrosis The organism cause meningitis, Uveitis and transplacental infection cause abortion Clinical signs IP 1-2 w, morbidity rate is variable and mortality rate is low Peracute fever, depression and anorexia Abdominal and renal pain and reluctance to move Vascular injury with hematemesis, melena, epistaxis and petechiation Terminally, hypothermia, shock and death Subacute and chronic form Fever, depression, anorexia, abdominal pain and vomition Paraspinal hyperesthia due to muscular, meningeal and renal inflammation Peticheal and echymotic hemorrhage Deterioration in renal function as anuria or oliguria and frequent urination Uremic breath due to chronic nephritis Scanty feces with melena Signs of hepatitis as change of fecal color from brown to gray and icterus Occasionally, abortion, uveitis and meningitis may be occur Postmortem lesions Carcass show icteric mm with diffuse petechiation Respiratory tract is edematous and lung is congested Liver is enlarged with yellow brown discoloration Kidney is enlarged, pale or yellow in color and have subcapsular hemorrhage Swelling and focal white spotting in renal cortex Diagnosis Field diagnosis It depends on epidemiology, clinical signs and PM lesions of the disease Diagnosis Laboratory diagnosis Samples: Urine, Kidney and liver from recently dead animal, blood and serum Laboratory procedures 1. Demonstration of organism by dark field microscope 2. Urine anlanysis, proteinuria, hyperbilurinuria 3. Hematological examination, leukopenia then leukocytosis and thrombocytopenia 4. Serological test as agglutination test or ELISA 5. Culture is difficult because of the organism is fastidious and slow growth Differential diagnosis The disease misdiagnosed with diseases cause hepatic or renal damage as: 1. Infectious hepatitis 2. Canine disptemper Treatment Specific antibiotic Penecillin G sodium 25.000- 40.000 IU/kg I/V or I/M Dihyderostreptomycin 15 mg/kg IM every 12 hr Supportive treatment Fluid therapy, tonics Diuretic as furosemide Control Management Isolation and treated the infected animal Hygienic disposal of infected materials Detection and elimination od carriers and all known shedders Prevent contact between dogs and their urine Cleaning and disinfectant all infected premises Vaccination Bivalent leptospira bacterin (L. canicola & L. icterohaemorrhagica) It gives at 9, 12 and 15 week of age Repeated annually The immunization reduce severity and incidence of the disease but it does not prevent the carrier