* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download density-independent limiting factors
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
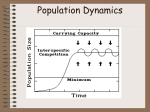
Ecology Population Growth $6,000,000.00 $5,000,000.00 Dollars ($) $4,000,000.00 $3,000,000.00 $2,000,000.00 $1,000,000.00 $0.00 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Day Population Growth – Any organism provided ideal growing conditions will experience rapid population growth – Larger it gets, faster it grows – exponential growth curve – Darwin calculated if all the offspring of 1 pair of elephants were to survive and reproduce, after 750 yrs there would be 19 million elephants Why doesn’t exponential growth happen for long? Sooner or later, you will run out of resources. Competition for resources – deer population for example Logistic Growth – Lets introduce a few animals to a new environment – at first the population begins to grow slowly – Soon the population grows rapidly –few die, many produced – Population growth begins to slow – growing still, but slower – why is this happening? Carrying Capacity Carrying Capacity The largest # of individuals an environment can support Logistic Growth – When birthrate and deathrate are equal, population growth stops – Steady state – population size stays the same (averages out) Logistic Growth – Draw a line through the middle of steady state – carrying capacity – Carrying capacity is the average of the steady state – Factors at this point keep the population from getting any bigger – food, overcrowding, competition Logistic Growth Occurs when resources become less available (Slows population growth rate) Slow population growth rate due to 1. Decrease in birthrate 2. Increase in deathrate 3. Immigration decreases 4. Emigration increases Density Dependent Limiting Factors – factors that control population size operate more strongly on large populations than small ones – Competition, predation, parasitism, and crowding Competition – struggle for food, water, & space Density Dependent Limiting Factors Predation – Just about every species serves as food for some other species – Predators vs. Prey Density Dependent Limiting Factors Prey – defenses –Poison chemicals –Shells –Poison skins –Camouflage –Behaviors such as mimicry Poison Batesian mimicry Monarch butterfly or viceroy butterfly? Mertensian mimicry (Warning coloration) Coral snake or King snake? Camouflage in nature Industrial melanism of the peppered moth Shells as Defense Slime as Defense Limiting Factors Growth of many species is controlled by density dependent and density independent limiting factors. Density Dependent Limiting Factors Counterdefenses – Monarch butterfly caterpillars have evolved the ability to avoid certain plant poisons – Predator population varies with prey population Large # of prey = large # predators = small # prey Density Dependent Limiting Factors Symbiosis means living together – Parasitism – one benefits, one is hurt – Commensalism – one benefits, one not affected – Mutualism - both benefit Density Dependent Limiting Factors Crowding and Stress – crowding helps parasites travel from host to host – Most animals have built in need for certain amount of space – hunting, nesting, territory (fish for example) – Increase fighting = decrease breeding Make Love Not War Limits to population growth Limiting Factor – causes population growth to decrease Density Dependent Limiting Factors Factors which work best with a large dense population Interspecific competition Intraspecific competition Predation Disease Parasitism Density Independent Limiting Factors Tornado, hurricane, drought, temperature Human disturbance (Clear-cutting forests or damming rivers) Competition Competitive exclusion principle No two species can occupy the same niche in the same habitat at the same time Interspecific competition occurs between two species for similar resources Intraspecific competition occurs within a species for similar resources Why Competition? Limited resources Food Water Space Shelter Mates Sunlight Density Independent Limiting Factors Because population size does not matter in these instances, these natural occurances are called densityindependent limiting factors. Density Independent Limiting Factors Long hot dry weather Frosts Happen regardless of how large the population is Density Independent Limiting Factors Boom and Bust Growth Curves – Populations grow exponentially then crash, then back again Aphids feed on plant buds that can be washed away in a rain storm Human Population Growth Exponential growth due to: Agriculture Industry Better healthcare / medicine Reduced death rate High birth rate Human Population Growth Human populations tend to increase over time – About 500 years ago, human population began growing exponentially. – Today, it has slowed in the US and parts of Europe, but not in most of the rest of the world – China, India, Africa, and Latin America Demography The scientific study of human populations Birthrates Deathrates Age structure U.S. Age Distribution South Africa Age Distribution South Africa and U.S.