* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 212 HW17 - University of St. Thomas
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
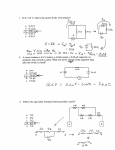
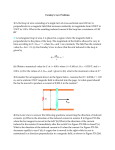
physics 112 hw21 /6 due Friday, 7 November 2014 1. A small circular ring is inside a larger loop that is connected to a battery and a switch, as shown in the figure at right. When the switch is closed, a current suddenly goes through the outer ring, suddenly creating a magnetic field in the middle. What is the direction of the Faraday’s Law current in the small ring a) just as the switch is closed, b) after the switch has been closed a long time, and c) just as the switch is reopened after being closed a long time. 2. A magnetic field is given by B = Bo (x/xo)2 k, where Bo and xo are constants. Find an expression for the magnetic flux through a square of side 2xo that lies in the x-y plane with one corner at the origin and two sides coinciding with the positive x and y axes. You will have to integrate! 3. “The Shrinking Loop” A circular loop of flexible iron wire has an initial circumference of 165.0 cm, but its circumference is decreasing at a constant rate of 12.0 cm/s due to a tangential pull on the wire. The loop is in a constant, uniform magnetic field oriented perpendicular to the plane of the loop and with magnitude 0.500 T. HINT: Determine the area of the loop as a function of circumference and thus time. a) Find the emf (voltage) induced in the loop at the instant when 9.0 seconds have passed. b) Find the direction of the induced current in the loop as viewed looking along the direction of the magnetic field. 4. A generator consists of a rectangular coil 75 cm by 1.3 m, spinning in a 0.14 T magnetic field. If it is to produce a 60-Hz alternating emf (i.e., V = Vo sin 2πft, where f = 60 Hz) with peak value 6.7 kV, how many turns must it have? 5. A long, straight solenoid with a cross-sectional area of 8.00 cm2 is wound with 90 turns of wire per centimeter, and the windings carry a current of 0.350 A. A second winding of 12 turns encircles the solenoid at its center. The current in the big solenoid goes (linearly) from 0.350 A to 0 A in 0.0400 seconds. What is the induced voltage in the second winding during this time? 6. A rectangular conducting loop of resistance R, mass m, and width w falls into a uniform magnetic field B as shown in the figure at right. If the loop is long enough and the field region has great enough vertical extent, the loop will reach a terminal speed. a) Why? b) Find an expression for the terminal speed. c) Indicate the direction of the loop current as it enters the field. w