* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the brachial plexus
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
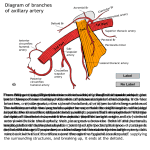
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) • supraclavicular branch • innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae BRACHIAL PLEXUS SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE • supraclavicular branch • supplies the diaphragm C 3, 4, 5 KEEPS THE DIAPHRAGM ALIVE BRACHIAL PLEXUS SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS LONG THORACIC NERVE (C5, C6, C7) • supraclavicular branch • innervates serratus anterior BRACHIAL PLEXUS SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE (C5, C6) • supraclavicular branch • innervates supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles (Rotator Cuff Muscles) and shoulder joint SUBCLAVIAN NERVE (C5, C6) – nerve to subclavius • supraclavicular branch • innervates subclavius and sternoclavicular joint THE SUPERIOR TRUNK is the ONLY trunk to give off branches THE DIVISIONS don’t have any BRANCHES BRACHIAL PLEXUS SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE LATERAL CORD: • Lateral pectoral n. • Musculocutaneous n. • Median n. BRACHIAL PLEXUS SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS LATERAL PECTORAL NERVE (C5-C7) • infraclavicular branch • innervates pectoralis major, pectoralis minor BRACHIAL PLEXUS SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE POSTERIOR CORD: STARS • Subscapular upper n. • Thoracodorsal n. • Axillary n. • Radial n. • Subscapular lower n. BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS UPPER SUBSCAPULAR NERVE (C5) • infraclavicular branch • innervates superior part of subscapularis (Rotator Cuff Muscles) LOWER SUBSCAPULAR NERVE (C6) • infraclavicular branch • innervates inferior part of subscapularis and teres minor (Rotator Cuff Muscles) THORACODORSAL NERVE (C6-C8) • infraclavicular branch • innervates la[ssimus dorsi BRACHIAL PLEXUS SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE MEDIAL CORD: • Ulnar n. • Median n. • Medial pectoral n. • Medial cutaneous n. of arm • Medial cutaneous n. of forearm Think MEDIAL – think ULNAR the rest begin with M… BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS MEDIAL PECTORAL NERVE (C8-T1) • infraclavicular branch • innervates pectoralis minor and sternocostal part of pectoris major MEDIAL CUTANEOUS NERVE OF ARM (C8-T1) • infraclavicular branch • innervates skin of the medial side of the arm, as far distal as medial epicondyle of humerus and olecranon of ulna MEDIAL CUTANEOUS NERVE OF FOREAM (C8-T1) • infraclavicular branch • innervates skin of the medial side of the forearm, as far distal as wrist BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS LESIONS OF THE PLEXUS BRACHIAL PLEXUS BRACHIAL PLEXUS LESIONS OF THE PLEXUS Mechanisms of Injury: A. Percussion B. Traction C. Cervical nerve compression BRACHIAL PLEXUS ERB-DUCHENNE PALSY (SUPERIOR TRUNK lesion (C5-C6) BRACHIAL PLEXUS ERB-DUCHENNE PALSY • is a SUPERIOR TRUNK lesion (C5-C6) • caused by trauma (violent stretch between the head and shoulder) or trauma[c birth – excessive increase in the angle between the head and the shoulder MUSCULOCUTANEOUS + SUPRASCAPULAR + SUBCLAVIAN+ PHRENIC NERVES LESION FINDINGS: • upper limb with an adducted shoulder • medially rotated arm • extended elbow • deformity of the affected wrist (waiter’s [p hand) • lateral aspect of the forearm also experiences some loss of sensa[on. A superior brachial plexus injury may produce muscle spasms and severe disability in hikers (backpacker’s palsy) who carry heavy backpacks for long periods. BRACHIAL PLEXUS KLUMPKE’S PALSY (INFERIOR TRUNK lesion (C8-T1) BRACHIAL PLEXUS KLUMPKE’S PALSY (INFERIOR TRUNK lesion (C8-T1) KLUMPKE’S PALSY is the most infrequent pahern and manifests as isolated hand paralysis. Inferior brachial plexus injuries may occur when the upper limb is suddenly pulled superiorly (for example, when a person grasps something to break a fall or a baby’s upper limb is pulled excessively during delivery). MEDIAN + RADIAL + ULNAR NERVES LESION FINDINGS: • loss of all lumbricals • all fingers are clawed CAUSE: • Pancoast tumor • trauma[c birth • loss of flexors and extensors ARTERIAL SUPPLY ARTERIAL SUPPLY SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY extends from the arch of the aorta to the lateral border of the first rib. The subclavian artery gives off the following branches: 1. Internal thoracic artery is con[nuous with the superior epigastric artery, which anastomoses with the inferior epigastric artery (a branch of the external iliac artery). This may provide a route of collateral circula[on if the abdominal aorta is blocked. 2. Vertebral artery 3. Thyrocervical trunk has three branches: • suprascapular artery, which par[cipates in collateral circula[on around the shoulder • transverse cervical artery, which par[cipates in collateral circula[on around the shoulder • inferior thyroid artery ARTERIAL SUPPLY AXILLARY ARTERY is a con[nua[on of the subclavian artery and extends from the lateral border of the first rib to the inferior border of the teres major muscle. The tendon of the pectoralis minor muscle crosses the axillary artery anteriorly and divides the axillary artery into three dis[nct parts (i.e., the first part is medial, the second part is posterior, and the third part lateral to the muscle). The axillary artery gives off the following branches: 1. First Part • superior thoracic artery 2. Second Part • thoracoacromial artery is a short, wide trunk that divides into four branches: acromial, deltoid, pectoral, and clavicular. • lateral thoracic artery 3. Third Part • anterior humeral circumflex artery • posterior humeral circumflex artery • subscapular artery, which gives off the circumflex scapular artery and the thoracodorsal artery ARTERIAL SUPPLY AXILLARY ARTERY A. Superior or Supreme Thoracic Artery Supplies the intercostal muscles in the first and second anterior intercostal spaces and adjacent muscles. B. Thoracoacromial Artery Is a short trunk from the first or second part of the axillary artery and has pectoral, clavicular, acromial, and deltoid branches. Pierces the costocoracoid membrane (or clavipectoral fascia). C. Lateral Thoracic Artery Runs along the lateral border of the pectoralis minor muscle. Supplies the pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, and serratus anterior muscles and the axillary lymph nodes and gives rise to lateral mammary branches. ARTERIAL SUPPLY AXILLARY ARTERY D. Subscapular Artery Is the largest branch of the axillary artery, arises at the lower border of the subscapularis muscle, and descends along the axillary border of the scapula. Divides into the thoracodorsal and circumflex scapular arteries: • Thoracodorsal Artery accompanies the thoracodorsal nerve and supplies the la[ssimus dorsi muscle and the lateral thoracic wall. • Circumflex Scapular Artery passes posteriorly into the triangular space bounded by the subscapularis muscle and the teres minor muscle above, the teres major muscle below, and the long head of the triceps brachii laterally. Ramifies in the infraspinous fossa and anastomoses with branches of the dorsal scapular and suprascapular arteries. ARTERIAL SUPPLY AXILLARY ARTERY E. Anterior Humeral Circumflex Artery Passes anteriorly around the surgical neck of the humerus. Anastomoses with the posterior humeral circumflex artery. F. Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery Runs posteriorly with the axillary nerve through the quadrangular space bounded by the teres minor and teres major muscles, the long head of the triceps brachii, and the humerus. Anastomoses with the anterior humeral circumflex artery and an ascending branch of the profunda brachii artery and also sends a branch to the acromial rete. ARTERIAL SUPPLY BRACHIAL ARTERY is a con[nua[on of the axillary artery and extends from the inferior border of the teres major muscle to the cubital fossa, where it ends in the cubital fossa opposite the neck of the radius. The brachial artery gives off the following branches: 1. Profunda brachii (deep brachial) artery • a fracture of the humerus at midshao may damage the deep brachial artery and radial nerve as they travel together on the posterior aspect of the humerus in the radial groove. • the deep brachial artery ends by dividing into the middle collateral artery and radial collateral artery. 2. Superior ulnar collateral artery runs with the ulnar nerve posterior to the medial epicondyle and anastomoses with the posterior ulnar recurrent artery to par[cipate in collateral circula[on around the elbow. 3. Inferior ulnar collateral artery anastomoses with the anterior ulnar recurrent artery to par[cipate in collateral circula[on around the elbow. ARTERIAL SUPPLY BRACHIAL ARTERY 4. Radial artery arises as the smaller lateral branch of the brachial artery in the cubital fossa and descends laterally under cover of the brachioradialis muscle, with the superficial radial nerve on its lateral side, on the supinator and flexor pollicis longus muscles. Curves over the radial side of the carpal bones beneath the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus muscle, the extensor pollicis longus and brevis muscles, and over the surface of the scaphoid and trapezium bones. Runs through the anatomic snupox. Divides into the princeps pollicis artery and the deep palmar arch. Accounts for the radial pulse, which can be felt proximal to the wrist between the tendons of the brachioradialis and flexor carpi radialis muscles. ARTERIAL SUPPLY BRACHIAL ARTERY Radial artery gives off the following branches: • recurrent radial artery anastomoses with the radial collateral artery. • palmar carpal branch • dorsal carpal branch • superficial palmar branch completes the superficial palmar arch. • princeps pollicis artery divides into two proper digital arteries for each side of the thumb. • radialis indicis artery • deep palmar arch is the main termina[on of the radial artery and anastomoses with the deep palmar branch of the ulnar artery. It gives rise to three palmar metacarpal arteries, which join the common palmar digital arteries from the superficial arch. ARTERIAL SUPPLY BRACHIAL ARTERY 5. Ulnar artery is the larger medial branch of the brachial artery in the cubital fossa. Descends behind the ulnar head of the pronator teres muscle and lies between the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus muscles. Enters the hand anterior to the flexor re[naculum, lateral to the pisiform bone, and medial to the hook of the hamate bone. Divides into the superficial palmar arch and the deep palmar branch. Accounts for the ulnar pulse, which is palpable just to the radial side of the inser[on of the flexor carpi ulnaris into the pisiform bone. ARTERIAL SUPPLY BRACHIAL ARTERY 5. Ulnar artery gives off the following branches: • anterior ulnar recurrent artery • posterior ulnar recurrent artery • common interosseous artery, which divides into the anterior interosseous artery and posterior interosseous artery. The posterior interosseous artery gives rise to the recurrent interosseous artery. • palmar carpal branch • dorsal carpal branch • deep palmar branch completes the deep palmar arch. • superficial palmar arch is the main termina[on of the ulnar artery and anastomoses with the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery. It gives rise to three common palmar digital arteries, each of which divides into proper palmar