* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comparing Religions DBQ: Buddhism and Hinduism Your task is to
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
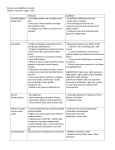
Comparing Religions DBQ: Buddhism and Hinduism Your task is to compare contrast Hinduism and Buddhism. You must explain how the two religions are similar and different in practice and beliefs. Source #1 -Buddhist Philosophic Beliefs THE MIDDLE WAY, (or Middle Path). Find the middle way between your extremes that is right for you. It is usually found by experiencing extremes. Buddha said, "Believe nothing until you have tried it out for yourself and found it to be true. Don't accept something just because I tell to." LETTING GO- Liberation comes in part through giving up attachments and letting go. This includes unhelpful ideas and beliefs and attachments in the material world. THE FOUR NOBLE TRUTHS 1. Suffering exists. It is part of the structure of existence. 2. Suffering has a cause. 3. There is a way to end (or greatly reduce) suffering. 4. A way to end (reduce) suffering is to follow the eightfold path. THE EIGHTFOLD PATH 1. Right Understanding- especially knowledge of the Four Noble Truths Source #2-Hindu Philosophic Beliefs Moksha The spiritual goal of a Hindu is to become one with Brahma. This freedom is referred to as moksha. Until moksha is achieved, a Hindu believes that he/she will be repeatedly reincarnated in order that he/she may work towards self-realization of the truth (the truth being that only Brahman exists, nothing else). Ways to achieve Moksha: 1) spiritual - acquire spiritual knowledge through yoga and meditation. 2) devotion to god 3) working selflessly for the good of society 4) respect for elders 5) karma through pure acts, knowledge and devotion. You can reincarnate to a higher level; the opposite achieves the contrary result. Source #3-Hinduism and Reincarnation Hindus believe in reincarnation - a belief that the soul is eternal and lives many lifetimes, in one body after another. The soul is sometimes born in a human body, 2. Right Motivation- the determination to remove animosity, malice, and hatred from our thinking, and also the determination to renounce worldly pleasures. 3. Right Speech- telling the truth and avoiding lies, harsh language, frivolous gossip, and any remarks which may cause others unnecessary hardship or pain. 4. Right Action-act in ways that honor rather than destroy life, stealing or action which would harm others or yourself. Let your acts create good karma. 5. Right Livelihood- find an occupation which suits your nature, contributes to the world positively, and does not cause damage, difficulty, or hardship to others. 6. Right Effort-directing your efforts toward faithfully following the Eightfold Path 7. Right Mindfulness-letting go of "I must have this," or "I must have that." Develop moment-by-moment awareness of, and sensitivity to, the effects of what we do in our lives and the world. Learn to perceive the world and others clearly, without judgment or envy. 8. Right Concentration-practicing meditative states lead in the direction of self-mastery and the middle path. sometimes in an animal body and sometimes in a plant body. Hindus believe that all forms of life contain a soul, and all souls have the chance to experience life in different forms. Samsara means going through the cycle of repeated births and deaths (reincarnation). Hindus believe that existence of this cycle is governed by karma. Source #4-Buddhism and Reincarnation Buddhists believe that human beings have the potential to become free from suffering by practicing meditation and cultivating a lifestyle prescribed by the Buddha. The wheel of life is a very important symbol in Buddhism because it depicts the cycle of life and death. Buddhists believe that after beings die, they are reborn or reincarnated into a new form. This new form could be a deity, human, animal, some lower creature like a hungry ghost or an inhabitant of hell. It is believed that all positive thoughts and actions cause good karma and may direct one into being reborn in a higher form. The consequences of one’s negative deeds, bad karma, may result in rebirth in a lower form. 1. Fill-out the chart below to help you organize the information from the packet to form main ideas and evidence that support your main ideas Unit 4, Page #______________ Comparing Religions DBQ: Buddhism and Hinduism Main Beliefs-what ideas are important (include reincarnation!) Buddhism Practices-what followers must do Hinduism Hinduism Buddhism 2. Now that you have some evidence in the table, you need to write a MEL-Con paragraph about the following: a. How are their beliefs similar? b. How are their practices similar? c. How are their practices and beliefs different? Main Idea: (Hint – use the question above as a guide in forming your main idea) Evidence 1: Evidence 2: Evidence 3: Link 1: Link 2: Link 3: Conclusion: Your mini-essay will be scored on the following rubric: 3 Points 2 Points 1 Point Writer has focused on one issue related to the assignment. Main idea is clear and well stated. Ample evidence is given to support topic statement (main idea). Examples are specific and explained in detail. Focus is somewhat vague; main idea sentence could be worded better, but there is a topic sentence. Evidence is somewhat vague and not specific enough or evidence is not closely related to the subject. Focus is unclear; what are you trying to prove here? Main idea sentence is not evident. Links Paragraph contains a statement after each piece of evidence that clearly links information to the main idea. Link explains how the evidence fits the main idea. Link is at least 2 sentences. Statement after each piece of evidence is related to the information in the main idea but not clearly linked. Link is at least 2 sentences. Links are missing throughout the paragraph; no real explanation of how the evidence supports the main idea. Link is only 1 sentence or is missing. Conclusion Writer uses a final statement that "wraps up" the paragraph, refers back to the main idea. Writer uses a concluding statement that sort of wraps up the paragraph; could be stronger, but okay. Writer fails to conclude the paragraph with a final statement to "wrap it up." Main Idea Evidence Evidence is basically opinion or does not relate to the main idea. No specific evidence described or evidence described is unrelated. Unit 4, Page #______________