* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mobile IP version 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
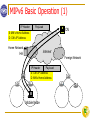
Mobility Support in IPv6 (MIPv6) Chun-Chuan Yang Dept. Computer Science & Info. Eng. National Chi Nan University 1 Outline MIPv6 Features MIPv6 Basic Operations MIPv6 Security MIPv6 vs. MIPv4 2 Mobile IPv6 Features (1) IPv6 Mobility is based on core features of IPv6 The base IPv6 was designed to support Mobility Mobility is not an “Add-on” features All IPv6 Networks are IPv6-Mobile Ready All IPv6 nodes are IPv6-Mobile Ready All IPv6 LANs/Subnets are IPv6 Mobile Ready IPv6 Neighbor Discovery and Address Autoconfiguration allow hosts to operate in any location without any special support 3 Mobile IPv6 Features (2) No Foreign Agent In Mobile IPv4, an MN registers to a foreign node and borrows its’ address to build an IP tunnel so that the HA can deliver the packets to the MN. But in Mobile IPv6, the MN can get a new IPv6 address, which can be only used by the MN and thus the FA no longer exists IPv6 Address auto-configuration: MN can obtain a CoA in foreign network without any help of foreign agent More Scalable : Better Performance Less traffic through Home Link Less redirection/re-routing (Traffic Optimization) 4 Mobile IPv6 Features (3) Bi-directional tunneling mode Does not require for the CN to support Mobile IPv6 Use of Reverse tunneling (for ingress filtering) Route Optimization (RO) mode Requires to register the MN’s current binding at the CN Uses a new type of IPv6 routing header Type-2 routing header = home address (Dest Addr = MN’s CoA) Shortest communications path Eliminates congestion at the MN’s HA and home link Impact of any possible failure of the HA or networks on the path to or from it is reduced 5 Mobile IPv6 Features (4) Dynamic Home Agent Address Discovery Allows a MN to dynamically discover the IP address of a home agent on its home link ICMP Home Agent Address Discovery Request Message Destination address: Home Agent anycast address for its own home subnet prefix Reply message HA list (with preferences) in the home link Each HA maintains the home agent lists 6 New IPv6 Protocol (1) Mobility Header Home Test Init, Home Test, Care-of Test Init, Care-of Test Perform the return routability procedure from MN to CN for ensuring authorization of subsequent Binding Updates Binding Binding Binding Binding Update Acknowledgement Refresh Request Error 7 New IPv6 Protocol (2) New IPv6 Destination Option Home Address destination option Type-2 Routing header: route optimization New ICMPv6 Messages Home Agent Address Discovery Request Home Agent Address Discovery Reply Mobile Prefix Solicitation Mobile Prefix Advertisement 8 Mobility Header Payload Proto: Same as IPv6 Next Header MH Type: Identifies the particular mobility message Message Data: the data specific to the indicated MH type 9 Binding Update Message MH Type=5 Message Data: A: Acknowledge H: Home Registration L: Link-Local Address Compatibility K: Key Management Mobility Capability 10 Binding Acknowledgement Message MH Type=6 Message Data: K:Key Management Mobility Capability 11 MIPv6 Basic Operation (1) IP Header PayLoad CN S: MN’s Home Address D: CN’s IP Address Home Network Internet HA Foreign Network IP Header PayLoad S: CN’s IP Address D: MN’s Home Address Mobile Node 12 MIPv6 Basic Operation (2) CN Home Network IP Header Mobility Header Internet PayLoad MH=5 Foreign Network HA IP Header Mobility Header MH=6 PayLoad Binding Update Binding Ack Mobile Node 13 MIPv6 Basic Operation (3) IP Header S: CN’s IP Address D: MN’s Home Address PayLoad CN Internet Home Network HA Tunneled packets New IP Header Old IP Header PayLoad S: HA’s Address D: MN’s COA Mobile Node 14 MIPv6 Basic Operation (4) CN Home Network Internet HA IP Header Mobility Header PayLoad MH=5 Binding Ack IP Header Mobility Header Binding Update PayLoad MH=6 Mobile Node 15 MIPv6 Basic Operation (5) CN Home Network Internet S: CN’s Address D: MN’s COA IP Header Routing Header HA (Type 2, MN’s Home Address) S: MN’s COA D: CN’s Address IP Header HA Dest Opt Payload Payload (includes MN’s Home Address) Mobile Node 16 Movement Movement Detection: Detect L3 handovers Neighbor Unreachability Detection (NUD) Default router is no longer bi-directionally reachable Router Discovery: select a new default router Prefix Discovery: form new care-of address Home registration Correspondent registration 17 Home Registration (1) Set H-bit & A-bit in the Binding Updates sent to the HA MN’s home address in Home Address destination option Source address = Care-of address Set L-bit if the MN’s link-local address (for the new careof-address) has the same interface ID as the home address Set K-bit if the IPsec SAs between the MN and the HA have been established dynamically, and the mobile node has the capability to update its endpoint in the used key management protocol to the new care-of address every time it moves 18 Home Registration (2) Sequence # Used by the receiving node to sequence BUs and by the sending node to match a returned BACK with this BU Lifetime The number of time units remaining before the binding must be considered expired One time unit is 4 seconds 19 Correspondent Registration (1) Allowing the CN to cache the MN’s current care-of address Return Routability procedure + registration After home registration, the MN should initiate a correspondent registration for each node that already appears in the MN’s Binding Update List The initiated procedures can be used to either update or delete binding information in the CN In addition, MN initiate the registration in response to receiving a packet tunneled using IPv6 encapsulation 20 Correspondent Registration (2) A Binding Update is created as follows 1. Source address of the IPv6 header = the current care-of address 2. Destination address = the address of the CN 3. Mobility header with MH type = 5, including the Binding Authorization Data and the Nonce Indices mobility options 4. Home Address destination option = MN’s home address 21 Conceptual Data Structures CN: Binding Cache HA: Binding Cache and Home Agents List When sending a packet, the Binding Cache is searched before the Neighbor Discovery conceptual Destination Cache The Home Agents List is used by the dynamic home agent address discovery mechanism MN: Binding Update List It records information for each BU sent by this MN, in which the lifetime of the binding has not yet expired The Binding Update List includes all bindings sent by the MN either to its HA or CNs 22 MIPv6 Security Binding Updates to HA IPsec and ESP between MN and HA Key Distribution (IKE, Internet Key Exchange) Binding Updates to CN Return Routability Procedure to assure that the right MN is sending the message Binding management key (Kbm) for integrity and authenticity of the BU messages 23 IPsec Security Association An SA is a cryptographically protected connection There MUST be a SA between the MN and HA Provides integrity and autentication of BU and BACK An SA is defined by: <SPI, destination adress, flag> One SA per home-address IPsec Authentication Header (authentication only service) 24 Encapsulating Security Payload ESP: authentication + encryption 25 IPsec: AH vs. ESP 26 Binding Updates to CN Return Routability Procedure It enables CN to obtain some reasonable assurance that MN is in fact addressable at its claimed care-of address as well as at its home address Done by testing whether packets addressed to the two claimed addresses are routed to MN MN can pass the test only if it is able to supply proof that it received certain data (the “keygen tokens”) which CN sends to those addresses. These data are combined by MN into Kbm 27 Return Routability Procedure 28 RR Procedure Terminology (1) Node Key: a secret key (20 octets), Kcn, at CN Nonce: CN also generates nonces at regular intervals Cookie: Random number used by MN Home init cookie To prevent spoofing by a bogus CN in the RR procedure A cookie sent to the CN in the Home Test Init message, to be returned in the Home Test message Care-of init cookie A cookie sent to the CN in the Care-of Test Init message, to be returned in the Care-of Test message 29 RR Procedure Terminology (2) Keygen Token Number supplied by CN to enable MN to compute the necessary binding management key for authorizing a BU Care-of keygen token: Care-of Test message Home keygen token: Home Test message Cryptographic Functions SHA: Secure Hash Standard HMAC_SHA1: Keyed-Hashing for Message Authentication MAC: Message Authentication Codes 30 Return Routability Test: step 1 Secret Key: <Kcn> Temporary Nonces: 1 - <nonce1> Correspondent Node 2 - <nonce2> ... <home keygen token> = HMAC_SHA1Kcn (<home-address> | <nonce1> | 0) [1:64] <home init cookie> <Correspondent Address> Home Agent Home Test: src=<correspondent address> dst=<home address> <home init cookie> <home keygen token> home nonce index: 1 Home Test Init: src=<home address> dst=<correspondent address> <home init cookie> <Care-Of Address> Cookies: <home init cookie> <home keygen token> home nonce index: 1 Mobile Node 31 Return Routability Test: step 2 Secret Key: <Kcn> Temporary Nonces: 1 - <nonce1> Correspondent Node 2 - <nonce2> ... <care-of keygen token> = HMAC_SHA1Kcn (<care-of-address> | <nonce1> | 1) [1:64] <care-of init cookie> <Correspondent Address> Home Agent Care-of Test Init: src=<care-of address> dst=<correspondent address> <care-of init cookie> Care-of Test: src=<correspondent address> dst=<care-of address> <care-of init cookie> <care-of keygen token> care-of nonce index: 1 <Care-Of Address> Cookies: <care-of init cookie> <care-of keygen token> care-of nonce index: 1 Mobile Node 32 Secure Binding Update to CN Secret Key: <Kcn> Temporary Nonces: 1 - <nonce1> Correspondent Node 2 - <nonce2> ... <home keygen token> = HMAC_SHA1Kcn (<home-address> | <nonce1> | 0) [1:64] <care-of keygen token> = HMAC_SHA1Kcn (<care-of-address> | <nonce1> | 1) [1:64] <Correspondent Address> Once the correspondent node has verified the MAC, it can create a Binding Cache entry for the mobile. Kbm = SHA1 (<home-keygen-token> | <care-of keygen token>) MAC = HMAC_SHA1Kbm(<care-of-address>|<correspondent address>|BU) [1:96] Binding Update src=<care-of address> dst=<correspondent address> option: Home Address = <home address> <sequence number> <home nonce index = 1> <care-of nonce index = 1> <MAC> Cookies: <Care-Of Address> <care-of init cookie> <care-of keygen token> care-of nonce index: 1 <home init cookie> <home keygen token> home nonce index: 1 Mobile Node 33 Mobile IPv4 vs. Mobile IPv6 Mobile IPv4 Mobile IPv6 Mobile node, home agent, home link, foreign link (same) Mobile node’s home address Globally routable home address and link-local home address Foreign agent Collocated care-of address A “plain” IPv6 router on the foreign link (foreign agent no longer exists) Care-of address obtained via Agent Discovery, DHCP, or manually Care-of address obtained via Stateless Address Autoconfiguration, DHCP, or manually Agent Discovery Router Discovery Authenticated registration with home agent Authenticated notification of home agent and other correspondent nodes Routing to mobile nodes via tunneling Routing to mobile nodes via tunneling and source routing Route optimization via separate protocol specification Integrated support for route optimization 34 MIPv6 References RFC 3775: Mobility Support in IPv6 RFC 4443: ICMPv6 RFC 3776: Using IPsec for MIPv6 RFC 2408: The Internet Key Exchange 35