* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cable-replacement
Low Pin Count wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Serial Peripheral Interface Bus wikipedia , lookup
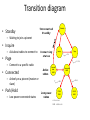
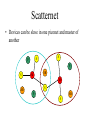
What is Bluetooth? • A cable-replacement technology that can be used to connect almost any device to any other device • Radio interface enabling electronic devices to communicate wirelessly via short range (10 meters) ad-hoc radio connections • a standard for a small , cheap radio chip to be plugged into computers, printers, mobile phones, etc Bluetooth is a standardized protocol for sending and receiving data via a 2.4GHz wireless link. It’s a secure protocol, and it’s perfect for shortrange, low-power, low-cost, wireless transmissions between electronic devices. What does Bluetooth do for you? Landline Cable Replacement Data/Voice Access Points Personal Ad-hoc Networks Modern Cordless Computer facilities Automatic Synchronization In the Office At Home The Bluetooth program overview Bluetooth Wireless Connections Made Easy Promise Bluetooth Freedom, Simplicity, Reliability, Values Versatility and Security Usage What the technology can do Scenarios Specification How to implement the usage scenarios Profiles Certification License free IP for adopters: product Testing testing to ensure interoperability; Interoperability protect the Bluetooth brand General Description • • • • • • • A cable replacement technology Operates in the unlicensed ISM band at 2.4 GHz Frequency Hopping scheme (1600 hops/sec) 1 Mb/s symbol rate Range 10+ meters Single chip radio + baseband Key features: • • • • Robustness low complexity low power, and low cost. General Description • Bluetooth supports – Synchronous & asynchronous data channels. • Three simultaneous synchronous voice channels, or • One channel, with asynchronous data and synchronous voice – Each voice channel supports 64 kb/s in each direction. – The channel can support maximal 723.2 kb/s asymmetric, or 433.9 kb/s symmetric. • Bluetooth provides – point-to-point connection (only two BlueTooth units involved), or – point-to-multipoint connection. Usage scenarios: Synchronization User benefits • Proximity synchronization • Easily maintained database • Common Sharing Common Data… Usage scenarios: Headset User benefits • Multiple device access • Cordless phone benefits • Hand’s free operation Wireless Freedom… Usage scenarios: Data access points PSTN, ISDN, LAN, WAN, xDSL User benefits • No more connectors • Easy internet access • Common connection experience Remote Connections... Power consciousness • Standby current < 0.3 mA – 3 months(*) • Voice mode 8-30 mA – 75 hours • Data mode average 5 mA (0.3-30mA, 20 kbps, 25%) – 120 hours • Low-power architecture – Programmable data length (else radio sleeps) – Hold and Park modes: 60 µA • Devices connected but not participating • Hold retains AMA (active member address) address, Park releases AMA, gets PMA address • Device can participate within 2 ms (*)Estimates calculated with 600 mAh battery and internal amplifier, power will vary with implementation Radio • Low Cost – Single chip radio (minimize external components) – Today’s technology – Time division duplex • Low Power – Standby modes – Sniff, Hold, Park – Low voltage RF • Robust Operation – Fast frequency hopping 1600 hops/sec – Strong interference protection • Fast ARQ • Robust access code • Forward header correction Piconet • is a computer network which links a wireless user group of devices using Bluetooth technology protocols. • consists of two or more devices occupying the same physical channel (synchronized to a common clock and hopping sequence). • It allows one master device to interconnect with up to seven active slave devices. • Up to 255 further slave devices can be inactive, or parked, which the master device can bring into active status at any time, but an active station must go into parked first. Piconet • One unit acts as the master of the Piconet, whereas the others act as slaves. • Up to seven slaves can be active. • More slaves can be synchronized & locked to the master in parked state. • The channel access for all the slaves in a piconet is controlled by the master. Connection Establishment States • Standby – State in which Bluetooth device is inactive, radio not switched on, enable low power operation. • Page – Master enters page state and starts transmitting paging messages to Slave using earlier gained access code and timing information. • Page Scan – Device periodically enters page state to allow paging devices to establish connections. Connection Establishment States • Inquiry – State in which device tries to discover all Bluetooth enabled devices in the close vicinity. • Inquiry scan – Most devices periodically enter the inquiry scan state to make themselves available to inquiring devices. Transition diagram • Standby Unconnected Standby Standby – Waiting to join a piconet • Inquire – Ask about radios to connect to • Page Connecting states Active states Transmit data AMA – Actively on a piconet (master or slave) • Park/Hold – Low-power connected states Page Ttpcl=2s Ttpcl=0.6s – Connect to a specific radio • Connected Inquiry Connected AMA Ttpcl=2ms Low-power states PARK PMA releases AMA address Ttpcl=2ms HOLD AMA Connection Setup Inquiry - scan protocol • to learn about the clock offset and device address of other nodes in proximity Piconet formation Page - scan protocol • to establish links with nodes in proximity Master Active Slave Parked Slave Standby Scatternet • Devices can be slave in one piconet and master of another S S P P S M SB M S SB P SB S The Bluetooth network topology • Radio designation – Connected radios can be master or slave – Radios are symmetric (same radio can be master or slave) S M P • Piconet – Master can connect to 7 simultaneous or 200+ active slaves per piconet sb S – Unique hopping pattern/ID S P P • Scatternet – High capacity system – Minimal impact with up to 10 piconets within range – Radios can share piconets! sb M S Summary • Bluetooth is a global, RF-based, short-range, connectivity technology & solution for portable, personal devices – it is not just a radio – create piconets on-the-fly • piconets may overlap in time and space for high aggregate bandwidth • The Bluetooth spec comprises – a HW & SW protocol specification