* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Common Problems of the Shoulder - UCSF
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
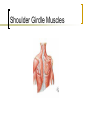
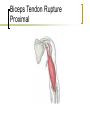
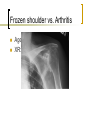
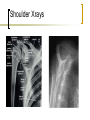
Common Problems of the Shoulder Part One Age >40 First, a little Anatomy Shoulder Girdle Muscles Shoulder Pain Rule out Extrinsic Sources Referred Abdomen: subdiaphragmatic Pulmonary disease: Pancoast tumor Radicular Cervical Spine Cervicogenic Pain Spondylosis: “degeneration” Ache into shoulders Pain reproduced with ROM Radiculopathy (weakness) C 4-5: 5 root, pain to shoulder, (deltoid) C 5-6: 6 root, lat forearm, thumb (biceps, ECRL) C 6-7: 7 root, middle finger (triceps) C 7-8: 8 root, small finger (finger flexion) C8-T1: T1 root, medial arm (finger abduction) Common Diagnoses Impingement Rotator cuff tear AC joint disease Frozen shoulder Rare: Glenohumeral arthritis, contusion, infection. Shoulder Pain Symptoms: Pain overhead Pain and weakness Pain with anything Duration of symptoms Duration of Symptoms If pain is acute (<12weeks), you can cure the patient with activity modification (no activity with elbow away from side), once a day stretch fully overhead, ice, and +/- NSAID or narcotic. Pain > 12weeks is harder. Pain > 6 months will need a miracle. Impingement The most common diagnosis Friction Overuse--rare to get it in the history Bursitis-->Tendinitis-->Rotator Cuff Tear Impingement Bursitis= pain but not when testing cuff Tendinitis=hurts when cuff muscles are tested Rotator cuff tear=weakness, frequently without pain Impingement/Bursitis Pain with overhead activity Pain felt at lateral shoulder Pain at night Can also be coming from the AC joint EXAM: Impingement Sign vs AC joint tenderness and Cross Arm Adduction Test Tests Impingement Sign Tests Cross Arm Adduction (pain must be at AC joint, not posterior capsule) AC Joint Tenderness directly over joint. Pain increased with adduction, overhead activity Treat like arthritis anywhere else. Injections are frequently helpful diagnostically and therapeutically. AC Joint Arthritis Impingement Treatment Activity modification: no activity with elbow away from side, in the gym, or at the computer. Once a day stretch fully overhead. NSAID and Ice Injection in 3-6 wks prn. Physical Therapy: After pain subsides: Regain ROM, strengthen rotator cuff Keeping shoulder healthy Once pain subsides, start rotator cuff strengthening. Continue cuff program at the gym and at home. BOTH shoulders. Pain and Weakness Does this mean a Rotator Cuff Tear? Can’t assess rotator cuff when there is pain Treat pain first: NSAID, PT, ice, rest-4 wks Cortisone shot (once) if above doesn’t work Test cuff when pain subsides. Refer after 6 weeks of treatment, not Rotator Cuff Tests Best single test is External Rotation Strength (Infraspinatus and Teres Minor). Can get extra credit testing Supraspinatus Advanced placement if massive tear picked up testing Subscapularis (hand push off test with hand dorsum resting on low back) Tests Rotator Cuff External Rotation Tests Rotator Cuff Supraspinatus Rotator Cuff Treatment Cuff tear is rare in age<50. Autopsy and MRI studies show most males over have RC tear and never had symptoms Beware of the Repeat Injectee who has weakness. Surgery decision is based on pain Biceps Tendon Rupture Proximal Special Case: Rupture of long head of Biceps Usually occurs without much trauma Rupture of attrition (like a rope rubbing over a rock), remember long (lateral) head is intra-articular and part of the cuff. Problem is the shoulder, not the tendon Some supination power lost, not elbow flexion Pain with Anything Usually severe symptoms, not acute Motion usually very restricted, passive and active (really can’t examine patient) Frozen vs. “freezing” shoulder PT, PT, PT (pain isn’t harmful) Lots of support needed, injection might help. Frozen Shoulder Not an “-itis”, more like Dupuytrens contracture in the hand. DDx: Shoulder joint infection (GH joint), Shoulder joint arthritis (DX with XR) Best Dx test: no passive external rotation. Frozen shoulder vs. Arthritis Age XR: Shoulder Infection Red, angry looking shoulder=septic arthritis of AC joint, not glenohumeral joint. Aspirate point of maximal angriness (over superior AC joint), get labs, xray, and refer Glenohumeral Joint Infection Very rare Increased incidence in diabetics, immuno-compromised patients. Shoulder looks normal, just bigger. SEVERE pain. Any motion hurts. Often a fever. Get labs (CBC, blood cultures, ESR, CRP), XR, then: Get a consult. Who needs an Xray? 1st visit, routine Hx/PE: No No improvement after Tx: Yes Odd Hx or PE, h/o fracture or injury: Yes Pre-referral: Yes Recommended XR: AP/outlet views Shoulder Xrays What about a MRI? If it will change what you do, order it. False positives Helpful if cervical spine is bemuddling. Some orthopedists like it prior to referral; doesn’t hurt to check for local customs. Shoulder MRI