* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protective or Reverse Precautions
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
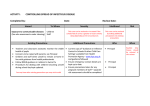
Precautions If it is wet and not yours, wear gloves! Precaution Type Protection From Standard & Contact Precautions (a.k.a. Universal All patient’s bodily fluids (Blood, Precautions) secretions, feces, This precaution is urine, mucous membranes, open designed for the care of all patients’ skin tears, lesions, regardless of their sputum .etc) diagnosis or presumed infection status. Droplet Precautions This layers on top of Standard Precautions. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves as a minimum. Use mask, gown, face shield as needed depending on the procedure and if there is a potential for fluids to splash, spray or squirt. Also, if there is a chance of your clothes to come in “contact” with contaminated areas which may transfer infectious germs, wear a gown. Heavy bacteria and viruses spread by coughing and sneezing. These Follow the Standard/Contact droplets are heavy Precautions with the addition of and fall to surfaces a surgical mask. rapidly, usually falling within 3 feet of the patient. Hardy and lightweight bacteria Airborne and viruses that can be suspended in the Precautions air for long periods Layers on top of the of time and may be above precautions. carried for long distances on air currents. Example Diagnoses M-Multi-drug resistant organisms R-Respiratory infection S-Skin Infection W-Wound infection E-Enteric (intestinal) or Eye infection H-Herpes simplex I-Impetigo P-Pediculosis (lice) S-Scabies S-treptococcal pharyngitis P-Pertussis I-Influenza D- Diphtheria E-Epiglottis R-Rubella M-Mumps A-Anthrax N-Neisseria meningitidis A step above Droplet My-Measles Precautions with a special mask ChickenChicken Pox or N95 respirator. Wear a gown to protect your clothes. Hez-Herpes The patient, if possible, should Zoster be in a room with special air TBflow ventilation. Tuberculosis T-Transplant Protective or Reverse Precautions Protection of the patient from To protect immuno- hospital or visitors’ Gloves, Mask and Gowns. compromised infective agents. patients; impaired resistance to infection. H-HIV AAutoimmune NNeutropenia (low neutrophil count) *These precaution guidelines and PPE may vary between facilities. As always consult your facility’s policy and Infection Control Manual for the most updated information for your institution. Always wash your hands prior to donning and after removing your PPE.