* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download U2D3-Classifying Triangles
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
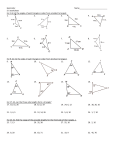
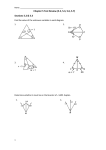
MPM2DW Classifying Triangles Triangles can be classified by the lengths of their sides, or by their angles. For the purpose of this lesson, we will mainly focus on the side-length classifications: Scalene – Isosceles – All sides are different lengths (all angles are different). The triangle has two identical side lengths (angles at the base of those sides are identical) Equilateral – The triangle has three identical side lengths (all three angles are the same) If you are given the three vertices of a triangle, you can find the lengths of the sides by using the length of a line segment formula. l x2 x1 2 y2 y1 2 Ex.1. ∆DEF has vertices D(1, 7), E(3, 4) and F(6, 6). a. Classify the triangle by side length b. Determine the perimeter of the triangle, to the nearest tenth of a unit. Triangles can also be classified by angles Acute Triangle – Three angles less than 90 degrees. Obtuse Triangle – One angle greater than 90 degrees. Right Triangle – One angle equal to 90 degrees. For now, we won’t worry about acute or obtuse triangles. However, we can tell if a triangle is a right triangle based on the slopes of the line segments that make up the triangle. If two of the line segments are perpendicular (slopes are negative reciprocals), then it is a right triangle. Ex.2. ∆ABC has vertices A(1, 7), B(3, 4) and C(6, 6). a) Show whether or not it is a right-angled triangle by using the slopes of the line segments. b) Calculate the side lengths. Do they fulfil the Pythagorean relation? c) Find the area of the triangle Homework – Pg. 72. Q. 5,7,8,9,10