* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rh-Mediated Isoimmune Hemolytic Disease
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
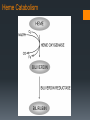
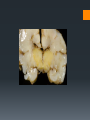
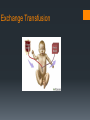
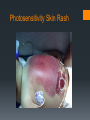
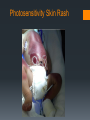
Rh-Mediated Isoimmune Hemolytic Disease Suzanne Reuter MD SDPA ~ Spearfish September 8, 2016 Objectives Understand heme catabolism Define Rh-isoimmune disease as it relates to a newborn Review abnormal indices in Rh-isoimmune disease Discuss therapies for hyperbilirubinemia Review complications of exchange transfusion Identify complications of phototherapy Day of Delivery 34 weeks gestation Maternal anti-D (1:64) and anti-C (1:8) 2240 grams (5 lb) Apgars 71, 85 Initial respiratory compromise necessitating use of: NIPPV NCPAP NC Day of Delivery Physical Exam notable for: Pallor Jaundice Mild subcostal retractions Grade II/VI systolic murmur Mildly hyperdynamic precordium Liver 4 cm below the right costal margin Palpable spleen Day of Delivery Initial lab results: Hematocrit: 22.6 % Platelets: 119,000 Reticulocyte count: 23% Unconjugated bilirubin: 9.1 Conjugated bilirubin: 0.1 Blood type: A+ (antibody +) Maternal blood type: A- (antibody + x2) 16 hours of age: Unconjugated bilirubin:18.8 What’s the concern? Heme Catabolism Kernicterus – Bilirubin-Induced Neurologic Dysfunction Bilirubin staining of the basal ganglia, hippocampus, substancia nigra, brainstem nuclei Neuronal necrosis Choreoathetosis cerebral palsy High-frequency hearing loss Paralysis of upward gaze Dental enamel hypoplasia Cognitive function intact Treatment Treatment Intravenous Immunoglobulin – A LOT! Threshold Bilirubin nomograms for 35 weeks and older Threshold Premature infants: Half the first 2 numbers in the weight 2240 grams = half of 22 = 11 Bilirubin/albumin ratio (term infants) B/A ratio > 7 →→→ All bilirubin binding sites on albumin are saturated Exchange Transfusion Exchange Transfusion - Effects Positive Unconjugated bilirubin decreases Negative Acidosis Hypernatremia Hypocalcemia Hypoglycemia Hyperkalemia Air embolus Infection Clots Arrhythmia BP instability Intraventricular hemorrhage (premature infants) Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) Increase in conjugated bilirubin (peak 0.7) s/p Exchange Transfusion Bilirubin rebounded to 16.3 and albumin dropped to 2.9 B/A ratio was 5.6 Complicating Factors… Maternal Drug Use Suboxone (buprenophine) – Treatment of narcotic addiction Withdrawal in babies following birth (usually peak at 3d): Hypertonia Tremors Agitation Myoclonic jerks Apnea Bradycardia Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Agitation, sneezing, jitteriness Treated with Fentanyl (narcotic), Phenobarbital (anti-seizure) Photosensitivity Skin Rash Photosensitivity Skin Rash Remaining hospital course… Struggled with nipple feeds Slowly weaned off Fentanyl and Phenobarbital Phototherapy rash completely resolved with no residual skin changes Questions