* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seed Characteristics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
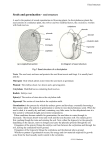
Seed Characteristics Plant Propagation 3 Basic Parts Embryo Food Storage Tissues Coverings Embryo Living part of the seed. Produced by the fusion of male and female gametes. Young Seedling Epicotyl: means “above the cotyledons”. It becomes the above-ground shoot. Hypocotyl: means “below the cotyledons”. It becomes the below-ground root system. Epigeous vs. Hypogeous Germination First true leaves Epigeous Germination Hypogeous Germination Cotyledons Food Storage Tissues Endosperm in monocots. Cotyledons in dicots. Coverings Seed coat ( formed from integuments). In some cases the Pericarp (ovary wall). Sunflower Seed Germination Requirements of Seed Moisture Favorable Oxygen temperatures Light and Seed Germination May be required for germination in some species: Small-seeded annual plants Photo-dormant weed seeds Seed Dormancy A seed is said to be dormant when it is unable to germinate even though the proper conditions for germination are all present. Viable vs. Non-viable Seed Viable: the embryo is alive and capable of germinating. Non-viable: the embryo is dead and cannot germinate. Viability Tests #1 Place the seed in a bucket of water. #2 Tetrazolium test. #3 Cut test. #4 Germination test. Seeds Treated with Tetrazolium Stages of Seed Germination #1 Activation #2 Nutrient digestion and translocation #3 Seedling growth Activation of water – physical process Increased enzyme activity Cell elongation/enlargement Radicle emergence Imbibition Radicle Emergence in Corn Corn Seed Radicle Nutrient Digestion and Translocation Stored food converted from starches to simpler forms (sugars). Sugars absorbed by cotyledons and translocated to the embryo. Seedling Growth Epicotyl emergence. Continued development of the radicle. Seed Provenance Refers to the geographical region from which the seed is collected. Cold hardiness Growth rate Drought tolerance, etc… USDA Forest Service “Super Trees”. The End