* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Snubber Circuits
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
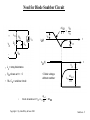
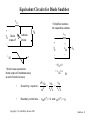
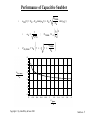
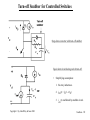
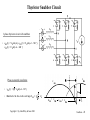
Lecture Notes Snubber Circuits Outline A. Overview of Snubber Circuits B. Diode Snubbers C. Turn-off Snubbers D. Overvoltage Snubbers E. Turn-on Snubbers F. Thyristor Snubbers Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 1 Overview of Snubber Circuits for Hard-Switched Converters Function: Protect semiconductor devices by: • Limiting device voltages during turn-off transients • Limiting device currents during turn-on transients • Limiting the rate-of-rise (di/dt) of currents through the semiconductor device at device turn-on • Limiting the rate-of-rise (dv/dt) of voltages across the semiconductor device at device turn-off • Shaping the switching trajectory of the device as it turns on/off Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Types of Snubber Circuits 1. Unpolarized series R-C snubbers • Used to protect diodes and thyristors 2. Polarized R-C snubbers • Used as turn-off snubbers to shape the turn-on switching trajectory of controlled switches. • Used as overvoltage snubbers to clamp voltages applied to controlled switches to safe values. • Limit dv/dt during device turn-off 3. Polarized L-R snubbers • Used as turn-on snubbers to shape the turn-off switching trajectory of controlled switches. • Limit di/dt during device turn-on Snubbers - 2 Need for Diode Snubber Circuit d i Df + V d - L Rs Io Df Cs Io d t Vd = L t i Df(t) I rr Sw v t (t) Df Vd • L = stray inductance • Sw closes at t = 0 • Rs - Cs = snubber circuit • • Diode voltage without snubber diL Diode breakdown i f V d + L dt Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 L di L d t > BV BD Snubbers - 3 Equivalent Circuits for Diode Snubber L • Simplified snubber the capacitive snubber + Vd Rs cathode Diode snap-off L anode + - + v Cs - V d i Df - t • Rs = 0 • Worst case assumptiondiode snaps off instantaneously at end of diode recovery •v d 2 v Cs v Cs = -v Cs Df Vd • Governing equat ion - • Boundary cond it ions - v Cs(0 + ) = 0 and iL(0 + ) = I rr Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Cs dt 2 + LCs = LCs Snubbers - 4 Performance of Capacitive Snubber • v Cs( t ) = V d - V d cos( o t ) + V d • • Cbase sin( o t ) Cs o = 1 ; L Cs V cs,max = V d 1 I 2 rr C base = L V d Cbase 1 + Cs + 5 4 V Cs,max 3 Vd 2 1 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 C base Cs Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 5 Effect of Adding Snubber Resistance Snubber Equivalent Circuit • Governing equat ion L • Boun dary con dition s i( 0 + ) = I rr and d2 i di i + Rs + = 0 2 dt C dt s V d - I rr Rs di(0 + ) = dt L Diode voltage as a function of time Vdf Vd (t) = - 1 a = o e-t sin(at - + ) ; Rs Š 2 Rb cos() Rs 2 1- (/ o) ; = 2 L ; o = 1 (2-x) -1 ; = tan LCs 4 - x2 L [Irr]2 Cs Rs Vd = C ; x = R ; Rb = I ; Cb = ; = tan-1(/a) 2 b b rr Vd Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 6 Performance of R-C Snubber 3 • • • • At t = t m v Df ( t ) = V max t an-1 ( a/ ) - tm = + •0 a a V max Vd = = 1 + Cs Cbase 1+ and -1 - x x= R s,opt C s= C base R = 1.3 base 2 V max exp( -t m ) V d 1 Rs Rbase R sI rr • Ls I rr 2 Cbase = Vd2 and Rbase = Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 V Vd Irr d 0 0 1 Rs R base 2 Snubbers - 7 Diode Snubber Design Nomogram Wtot 2 L s I rr/2 3 WR 2 L s I rr/2 0 2 0 V max Vd 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 for R = R s s,opt 0 0 R s,op R base 0 0 Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 1 C s / C base 2 3 Snubbers - 8 Need for Snubbers with Controlled Switches Step-down converter L L1 V d L2 i L3 Switch current and voltage waveforms sw Sw Io i I rr sw I + vsw - di dt L o I V d o vsw to • di dt t t 1 t 3 4 t5 t 6 L1 , L , L = stray inductances 2 3 Switching trajectory of switch • L = L1 + L + L 2 3 idealized s witching loci i sw t 5 t6 turn-off to t1 turn-on • Overvoltage at turn-off due to stray inductance • Overcurrent at turn-on due to diode reverse recovery t 4 t3 vsw Vd Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 9 Turn-off Snubber for Controlled Switches Step-down converter with turn-off snubber Equivalent circuit during switch turn-off. • Simplifying assumptions 1. No stray inductance. 2. isw(t) = Io(1 - t/tfi) 3. isw(t) uneffected by snubber circuit. Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 10 Turn-off Snubber Operation • Capac ito r v olt age and current for 0 < t < • Io t t f i i Cs( t ) = t fi and v (t) = Cs Io t 2 2C t s fi Io t f i For Cs = Cs1 , v Cs = V d at t = t f i yiel ding C s1 = 2 Vd Circuit waveforms for var yin g values of Cs Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 11 Benefits of Snubber Resistance at Switch Turn-on v sw • Ds shorts out Rs during Sw turn-off. • During Sw turn-on, Ds reverse-biased and Cs discharges thru Rs. i D t rr I rr f i sw Io Vd Rs I rr • Turn-on with Rs > 0 • Turn-on with Rs = 0 • Energy stored on Cs dissipated in Sw. • Energy stored on Cs dissipated in Rs rather than in Sw. • Voltage fall time kept quite short. • Extra energy dissipation in Sw because of lengthened voltage fall time. Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 12 Effect of Turn-off Snubber Capacitance Energy dissipation WR = d issipat ion in resistor WT = d issipat ion in switc h Sw Io t f i Cs1 = 2 Vd Wtota l = W R + W T i sw Io Wbase = 0 .5 V d Io t f i Cs < Cs1 RBSOA Switching trajectory Cs = Cs1 Cs > Cs1 V Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 d v sw Snubbers - 13 Turn-off Snubber Design Procedure Selection of Cs • Minimize energy dissipation (WT) in BJT at turn-on • Minimize WR + WT • Keep switching lo cus within RBSOA • Reasonable value is Cs = Cs1 Snubber recovery time (BJT in on-state) • Capacitor voltage = Vd exp(-t/RsCs) • Time for vCs to drop to 0.1V d is 2.3 RsCs Selection of Rs • BJT must remain on for a time of 2.3 R sCs Vd • Limit icap(0+) = R < Irr s Vd • Usually designer specifies Irr < 0.2 I o so R = 0.2 I o s Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 14 Overvoltage Snubber • Step-down converter with overvoltage snubber comprised of Dov, Cov, and Rov. • Overvoltage snubber limits overvoltage (due to stray I nductance) across Sw as it turns off. • Swit ch Sw wavefor ms w it hout overvolta ge snubb er • t f i = s wit ch cur rent fall t ime ; kV d = overvo lta ge o n Sw diL Io • kV d = L = L dt t fi • L = Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 kV d t f i Io Snubbers - 15 Operation of Overvoltage Snubber š • Dov on f or 0 < t < š • t f i << LCov 2 LCov 2 • Dov,Cov provide alternate path for inductor current as Sw turns off. • Switch current can fall to zero much faster than Ls current. • Df forced to be on (approximating a short ckt) by Io after Swis off. • Equivalent circuit after turn-off of Sw. Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 16 Overvoltage Snubber Design • Cov = • • ( v sw,max ) 2 Limi t v sw,max t o 0 .1 V d kV d t f i Using L s = Io • Cov = • L s Io 2 kV d t f iIo 2 Io (0 .1 V d ) 2 in equat ion for Cov yiel ds = 1 0 0k t f i Io Vd Cov = 20 0 k Cs1 wh ere Cs1 = t f iIo 2 Vd which is u sed in t ur n-off snubbe r • Recovery t ime of Cov ( 2. 3 Rov Cov ) must be le ss th an of f -t ime d ura t ion, t off , o f th e swit ch Sw. • Rov - t off 2 .3 C ov Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 17 Turn-on Snubber Step-down converter with turn-on snubber • Snubber reduces Vsw at switch turn-on due drop across inductor Ls. • Will limit rate-of-rise of switch current if Ls is sufficiently large. Switching trajectory with and without turn-on snubber. Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 18 Turn-on Snubber Operating Waveforms Small v alues o f snu bber in ductan ce (L s < L s1 ) • • • • • disw con t rol led b y s wit ch S w dt and dr ive circui t . v sw = LsIo t ri Large values o f snu bber induc t anc e (L s > L s1 ) Vd Io limit ed by c ircu it to < Ls t ri disw dt Ls1 = V d t ri Io Irr reduc ed wh en L s > L s1 b ecause Irr proport iona l to Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 disw dt Snubbers - 19 Turn-on Snubber Recovery at Switch Turn-off I o RLs exp(-R Ls t/L s ) Io R Ls is w v s w V d Io t rv • Switch waveforms at turn-off with turn-on snubber in circuit. • Assume switch current fall time tri = 0. • Inductor current must discharge thru DLs- RLs series segment. • Overvoltage smaller if tfi smaller. • Time of 2.3 L s/RLs required for inductor current to decay to 0.1 I o • Off-time of switch must be > 2.3 Ls/RLs Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 20 Turn-on Snubber Design Trade-offs Selection of indu cto r • Larger L s decreases energy dissipation in switch at turn-on • Wsw = WB (1 + Irr/Io)2 [1 - Ls/Ls1] • WB = VdIotfi/2 and Ls1 = Vdtfi/Io • Ls > Ls1 Wsw = 0 • Larger L s increases energy dissipation in R Ls • WR = WB Ls / Ls1 • Ls > Ls1 reduces magnitude of reverse recovery current Irr • Inductor must carry current Io when switch is on - makes inductor expensive and hence turn-on snubber seldom used Selection o f resistor RLs • Smaller values of RLs reduce switch overvoltage Io RLs at turn-off • Limiting overvoltage to 0.1V d yields RLs = 0.1 V d/Io • Larger values of RLs shortens minimum switch off-time of 2.3 L s/RLs Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 21 Thyristor Snubber Circuit 3-phase thyristor circuit with snubbers • v an( t ) = V ssin( t ) , v bn ( t ) = V ssin( t - 120 ) , v cn ( t ) = V ssin( t - 240 ) Phase-to-neutral waveforms v an v bn 3 V ssin( t - 60 ) • v LL ( t ) = • Maximum r ms lin e-t o-lin e vol t age V LL = Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 3 Vs 2 v LL = v bn v an = v ba t1 Snubbers - 22 Equivalent Circuit for SCR Snubber Calculations Assumptions • Trigger angl e = 90 so tha t v LL ( t ) = ma ximum = 2 V LL Equivalent circuit after T1 reverse recovery • Reve rse r ecove ry t ime t rr << perio d of a c w avefo rm so t hat v LL ( t ) equals a cons t ant valu e of v ba( t 1 ) = • • • i 2 V LL Worst c ase st ray induc t anc e L g ive s rise to react anc e equal to o r less th an 5 % o f line imped ance. Line imped anc e = Vs 2 Ia1 = 2 V LL 6 Ia1 = V LL 2L + V ( t)1 ba 3 Ia1 L P T1 after recovery Cs i - T 3 (on) T1 Rs A wh ere Ia1 = rms value of f undame nt al co mp onent o f th e line cu rrent . V LL L = 0.05 3 Ia1 Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 Snubbers - 23 Component Values for Thyristor Snubber • • Use s ame d esign as f or diode snubb er bu t adapt th e f or m ulas to th e th y risto r cir cui t not ation Snub b er capacit or Cs = Cbase = L • Fro m s nubb er eq uiv alent ci r cui t 2 • Ir r = diL dt t rr 2 V LL = L diL 0.05 2 3 I a1 Vd = • Cs = Cbase = • Snub b er resist anc e Rs = 1.3 Rbase = 1.3 2 V LL 0.05 • 2 V LL t r r = 25 Ia1 t r r V LL • • = dt 2 V LL t rr = 2 L I 2 rr V d Rs = V LL 3 I a1 1.3 25 2 V LL 25 Ia1 t r r 2 Ia1 t r r = 2 V LL 0.07 = 8.7 Ia1 t r r V LL Vd Irr V LL Ia1 t rr Ene r gy dissipat ed pe r c y cle in snubb er re sist ance = W R • WR = L Ir r 2 2 Copyright © by John Wiley & Sons 2003 + CsV d 2 2 = 18 Ia1 V LL ( t rr ) 2 Snubbers - 24