* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Markets with Asymmetric Information
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
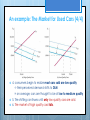
Markets with Asymmetric Information Presented by Jiajie Xu (Majoring in mathematical economics, Class 2011) 2014/10/17 Agenda Introduction An example: The Market for Used Cars Implications Possible of Asymmetric Information solutions Introduction Asymmetric information When some economic participants have better information than others, markets may fail to allocate goods efficiently or may not even exist. An important issue to be discussed in economic studies: The Nobel Price in Economic Sciences 1982, 1996, 2001, 2007are all related to the economics of information. An example: The Market for Used Cars (1/4) Types of used cars: Market price : high-quality cars low-quality cars. high-quality cars is $10,000 low-quality cars $5000 50,000 cars of each type are sold. Information: the seller knows much more about its quality than a buyer does. An example: The Market for Used Cars (2/4) High quality market: 1. the demand curve for highquality cars is DH 2. buyers lower their expectations about the average quality, demand shifts to DM 3. quantity of high-quality cars sold falls from 50,000 to 25,000, buyers with higher quality demand exit the market An example: The Market for Used Cars (3/4) Low quality market: 1. the demand curve for low-quality cars is DL 2. buyers raise their expectations about the average quality, demand shifts to DM 3. quantity of low-quality cars sold falls from 50,000 to 75,000 An example: The Market for Used Cars (4/4) 4. consumers begin to realize most cars sold are low quality -> their perceived demand shifts to DLM -> on average, cars are thought to be of low to medium quality 5. The shifting continues until only low-quality cars are sold. 6. The market of high quality cars fails. Implications of Asymmetric Information Adverse selection Form of market failure resulting when products of different qualities are sold at a single price because of asymmetric information, so that too much of the lowquality product and too little of the high-quality product are sold. Eg. the market for health insurance Firms can’t determine the health conditions of their client and charges the average price Healthy people exit the market Firms raise the price Eg. the online market Durable goods and luxury goods are sold much less than ordinary commodities in the online market Solutions to asymmetric information Maket signaling Process by which sellers send signals to buyers conveying information about product quality. Eg. Certificates/ product illustration Reputation Eg. Comments given by previous consumers Third party and regulations Eg. The functions of Ali Pay Thanks for listening! Markets with Asymmetric Information Presented by Jiajie Xu (Majoring in mathematical economics, Class 2011) 2014/10/17