* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
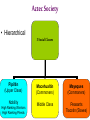
Aztec Society Aztec Society • Highly Structured • Based on agriculture, trade and guided by religion. • Aztec societies dominated by Pyramids topped with temples where human sacrifices provided the Gods with the human blood. Tower devoted to the Gods Sacrifice Throwing victims down the stairs Aztec Society • Hierarchical 3 Social Classes Pipiltin (Upper Class) Macehualtin (Commoners) Mayeques (Commoners) Nobility Middle Class Peasants Tlacotin (Slaves) High Ranking Warriors High Ranking Priests Nobility • The Ruling class • Top positions in government, army and priesthood • Emperor was Number 1 • Expected to conduct themselves exemplary • Punished more severely if they were disobedient Commoners • Middle Class (Macehualtin) • Could improve status by gaining recognition in the military, becoming a priest, merchant, artisan or trader. • Warriors were seen as equals to the Nobility. Commoners • Peasants (Mayeques) Worked land of the nobles Built and maintained temples Paid taxes and tribute. They were allowed to keep what was left over Commoners Tlacotin (Slaves) - Lowest of the low - Nobody born a slave – sold self if they could not afford to pay debts - Owners only owned the work they did - Slaves could buy back freedom Priests • Boys from all classes could study to become priests • Top Ranking positions reserved for the Pipiltin • Most important job is to offer Human Sacrifice to the Gods • Men in priesthood did not marry • Women Priests received specific jobs worshiping Goddesses Gender Roles Women - Cared for household and family - Could not have a position of power - Could do crafts, run businesses and control their own property - Received legal protection from marital abuse - If marriage ended women had automatic custody of children Gender Roles Men Did physical work and were forced to join the army when soldiers were needed. Children Start work at roughly age 5 Girls married in mid-teens Boy married in late teens/ early twenties Education • Free for all • Separate schools for nobles and the Macehualtin • Schooled from early teens till marriage • Taught religious rituals, singing dancing and music - Passed traditions from one generation to the next - Most information passed through stories Gender Roles in education • Boys and Girls were taught separately! Boys Learned Girls learned Occupational skills History Religious practices Characteristics of good citizenship Elements of warfare How to be a warrior To manage households for their spouses Spinning and weaving Morality Religion History Traditions