* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Horizontal Distance Measurement
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
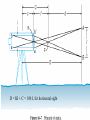
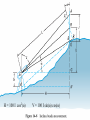
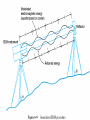
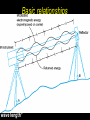
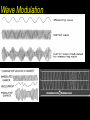
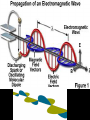
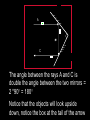
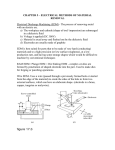
Horizontal Distance Measurement Tape Odometer Subtense Bar Stadia EDM Distance Measurement Devices and accuracy: • Older technologies “ quick look” • • • • • • Pacing : 1:50 Optical rangefinders: 1: 50 Odometers: 1:200 Tacheometry / stadia 1: 500 Subtense bar 1: 3000 Tapes: 1: 10,000 • Modern Technology: - Electronic Distance Measuring (EDM) devices: 2 +2 ppm Tape Measurement Accuracy and speed considerations for civil engineers. • Sources of Errors: • • Incorrect length of the tape • Temperature difference • Sag • Poor alignment • Tape not horizontal • Improper Plumbing Odometer and Subtense Bar • • The idea of an odometer. Subtense bar: a 2 m rod. • Distance H= cot(/2) m. Aiming Telescope –Subtense Bar –Distance H = cot(/2) m. L H L /2 tan ( /2) = (L/2) / H /2 H = (L/2) / tan( /2) If L = 2 m, then H = 1 / tan (/2) = cot (/2) Example: what is the horizontal distance between A and B if the angle was 2? • Chapter (16) • Principle of the Stadia: Stadia • Horizontal Distance = 100 rod intercept for a horizontal line of sight and a vertical rod • Symbols: • (I) rod intercept, or stadia interval • (i) spacing between stadia hair • (f/i) = k = 100: stadia interval factor • C = (c + f) approximately 0, Stadia constant D = KI + C = 100 I, for horizontal sight H = 100 I cos2(α) V = 100 I sin(α) cos(α) Electronic Distance Measurement • Early types: Transmit light, measure up to 25 miles • Transmit microwaves, measure up to 50 miles • Classification of EDM: • Electro-optical: laser or infra red reflected from passive prism or surfaces, the US has installed a prism on the moon. • Microwave: two positive units, GPS replaced them for most engineering applications such as hydrographic surveys • Electromagnetic Spectrum Distance Computation • • • We only measure the phase angle shift (change) , different signals of wave length: 10 100 1000 10,000 m are sent. Each fraction provides a digit(s). (Phase shift / 360)*wave length = non complete cycle length. Example: how a distance 3485.123 is measured. Electronic Distance Measurement EDM The Idea: To measure the distance between two points (A) and (B) the EDM on point (A) sends electromagnetic waves. The waves received at (B) are reflected back or resent to (A) by a •Knowing device onthe (B).speed of electromagnetic waves in the air, the EDM computes the distance by measuring the time difference or the shift of the wave phase angle (will be explained in details later). Concept of the fraction 90 0 180 270 Phase Angle Assume that = 2 m If 1 = 80, it corresponds to a distance = (80/360) * = 0.44 m If 2 = 135, it corresponds to a distance = (135/360) * = 0.75 m If 3 = 240, it corresponds to a distance = (80/360) * = 1.33 m Basic relationships u Distance = Velocity * Time = ((N *) + ) / 2 Where is a fraction of wave length = (/360) * N is the number of full cycles, ambiguity? Since is divided by 2, so is , we call /2 “effective wave length” Wave Modulation EDM Mounted on a theodolite A C The angle between the rays A and C is double the angle between the two mirrors = 2 *90 = 180 Notice that the objects will look upside down, notice the box at the tail of the arrow Aiming at a prism through the telescope of a total station in a zoo! Reflectors (Prisms) Fully rotating prism Prism and sighting target Pole and bipod • • A reflector might include a single prism or a group of prisms Reflectors can be a simple reflecting paper-sticker, they are called sheetprisms, paper prism, or reflective sheeting. Very instrumental in construction sites and deformation monitoring of structures. EDM Accuracy 3mm, and 3ppm is the most common. • Estimated error in distance = Ei2 + er2 + ec2 + (ppm X D)2 • Where: Ei and er are the centering errors of the instrument and the reflector, ec is the constant error of the EDM, and PPM is the scalar error of the EDM Example 6-5 page 156: if the estimates errors of centering the instrument and target were ± 3mm and ± 5mm respectively, the EDM had a specified error of ± (2mm +2ppm) what is the estimated error in measuring 827.329 m? Answer: ± 6.4 mm • •Prism constant consideration. •Total station Vs EDM. •Data collectors. •Prismless EDM: up to 100 m, can reach hard places, figure 6-14. Handheld laser measuring devices