* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prof: URVISH MEVADA
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
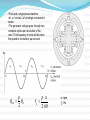
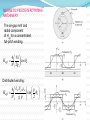
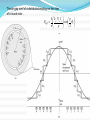
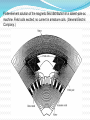
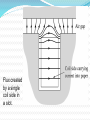
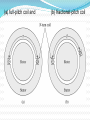
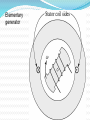
TITLE OF CONCEPT AC MACHINE WINDING DESIGN. PREAPED BY : 140023109007 140023109008 140023109009 140023109011 140023109012 140023109013 140023109014 140023109015 GUIDED BY: Prof: URVISH MEVADA ELEMENTARY CONCEPT Electromechanical energy conversion occurs when changes in the flux linkages λ resulting from mechanical motio Magnetic Field Horizontal axis d e(t ) dt e(t) Armature winding: AC current carrying winding Synchronous machine Induction machine Armature winding is stator winding (stationary) Synchronous machine Field winding is on the rotor INTRODUCTION TO AC MACHINES AC Machines: Synchronous Machines and Induction Machines Synchronous Machines: •Two-pole, single phase machine •Rotor rotates with a constant speed •Constraction is made such that air-gap flux density is sinusoidal •Sinusoidal flux distribution results with sinusoidal induced voltage (a) Space distribution of flux density and (b) corresponding waveform of the generated voltage for the single-phase generator. •Four-pole, single phase machine •a1,-a1 and a2,-a2 windings connected in series •The generator voltage goes through two complete cycles per revolution of the rotor. The frequency in hertz will be twice the speed in revolutions per second. p ae a 2 p n fe 2 60 n: rpm fe: Hz Field winding is a two-pole distributed winding Winding distributed in multiple slots and arranged to produce sinusoidal distributed air-gap flux. Elementary two-pole cylindricalrotor field winding. Schematic views of three-phase generators: (a) twopole, (b) four-pole, and (c) Y connection of the windings. Induction Machines: •The stator winding excited by ac current. The current produces a rotating magnetic field which in turn produces currents in rotor conductors due to induction. •These machines mostly used as motors. •Rotor windings are short circuited (electrically) and frequently have no external connections. •Stator and rotor fluxes rotate in synchronism with each other and that torque is related to the relative displacement between them. •Rotor does not rotate synchronously Typical induction-motor speed-torque characteristic. Inside View of An Induction Motor and Winding Windings placed in stator slots AC Machines: The mmf of one phase of a distributed two-pole, three-phase winding with full-pitch coils. 4 k N ph ia p cos a Fag1 p 2 k Winding factor (usually between 0.85 and 0.95) N ph Series turns per phase MAGNETIC FIELDS IN ROTATING MACHINERY The air-gap mmf and radial component of Hag for a concentrated full-pitch winding. 4 Ni H ag1 cos a 2g Distributed winding: 4 k w N ph ia p cos a H ag1 gp 2 The air-gap mmf of a distributed winding on the rotor of a round-rotor . Fag1 4 kr N r I r p cos r p 2 Finite-element solution of the magnetic field distribution in a salient-pole ac machine. Field coils excited; no current in armature coils. (General Electric Company.) Flux created by a single coil side in a slot. (a) full-pitch coil and (b) fractional-pitch coil Elementary generator Elementary cylindrical-rotor, two-phase synchronous machine