* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ceteris Paribus
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
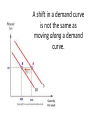
Ceteris Paribus • “All other things held constant” • Demand curves are accurate as long as there are no other changes than PRICE • Price causes movement ALONG the demand curve • Other factors cause the demand curve to SHIFT A shift in a demand curve is not the same as moving along a demand curve. Normal v. Inferior Goods • Most goods are normal goods- goods we demand more of when our income increases – Ex. new cars, HDTV • Inferior goods are those you would buy in smaller quantities if income increased – Ex. generic products, used cars What causes a shift? Income • Inferior goods are purchased when income drops Consumer Expectations • Expectations of higher or lower prices in the future can cause demand to increase or decrease What causes a shift? Population • Rise in population creates higher demand for housing, food, utilities, etc. Consumer Taste/Advertising • Advertising & publicity often play a role in creating fads & social trends Complements v. Substitutes • Complements are two goods that are bought and used together – Examples? • Substitutes are goods used in place of one another – Examples? We can sum up these factors as: • • • • • T R I P E Tastes & preferences Related goods Income Population Expected pricing Complete demand scenarios worksheet on your own.