* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry 1st Semester Test * Ch
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
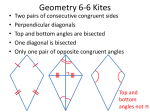
Geometry 1st Semester review Name__________________ 1. What are the next three numbers in this sequence? 0, 3, 9, 18, … j For Exercises 2 – 4, refer to the figure to the right. k Q R 2. Name the point(s) collinear to points H and I. H L G n I M O 3. Name all the point(s) coplanar to line j. N F m J K P 4. Name three noncollinear points. S 5. Find DF if DE = 23, EF = 48, and E is between D and F. For Exercises 6 – 7, refer to the given information and the figure below. 6. Find the length of CE . A B D C A 7. Find the length of BD . B C D E Given: AE = 30, AB = 5, AB = BC, CD = DE 8. Point Y is between X and Z. Find the length of XY if XY = 5x + 2, YZ= 7x + 8, and XZ = 70. 9. Use points M(4, 2), N(4, 7), P(-1, 3) and Q(5, -2) to find each of the following. MN = ___________ NP = ______________ PQ = _________ MQ = _____________ E For Exercises 10 – 11, refer to the figure to the right. V W 10. Find m Ð WUY. X Given: m Ð VUW = 20o m Ð YUX = 50o m Ð XUW = 55o 11. Find m Ð TUV. T Y U 12. Find the midpoint of a segment with endpoints X(11, -5) and Y(8, -14). 13. BD bisects Ð ABC. If m Ð ABD = 63o, what is m Ð ABC? V For Exercises 14 – 16, refer to the figure to the right. X 14. Name two pairs of angles that form a linear pair? Which angles are supplementary? 2 1 T 15. Which angles are vertical angles? 5 3 4 16. If m Ð 1 = (6x – 20)o, m Ð 5 = (7y + 12)o, and m Ð 4 = (3x + 7)o, Find the value of y. 17. Two angles are complementary. One angle has a measure that is twice the other angle. What is the measure of the smaller angle? 18. Two angles are supplementary. One angle is 5 times the other angle. What is the larger angle? 19. Classify the transformation as a rotation, reflection, or translation. a) b) 20. Consider the translation that is defined by the coordinate notation (x, y)(x – 4, y+ 4). What are the coordinates of the image of each of the following: a) A(2, -2) b) B(-1, 3) c) C(5, 7) Y 21. Sketch the image of A(-2, 7) after a composition using the following transformations. a) Reflection: in the x-axis Rotation: 90o clockwise about the origin b) Reflection: in the y-axis Translation: (x, y) (x – 2, y – 4) c) Rotation: 90o clockwise about the origin Translation: (x, y) (x – 5, y + 3) 22. What is the if-then form of “A group is a dozen if it has 12 objects?” 23. What is the inverse of “If it rains, then sidewalk is wet?” 24. What is the contrapositive of “If x = 7, then 3x + 3 = 24?” 25. What is the biconditional form of the statement “All dogs bark?” 26. Write each statement below as a biconditional statement, if possible a) If two lines do not intersect, then they are parallel. b) If two angles are complementary, then they add up to 90. c) If two angles are a linear pair, then they are supplementary. 27. Identify the conclusion that can be reached and tell which law of logic allows the conclusion to be made given the true statements #1 and #2 below? a) Statement #1: If two lines are perpendicular, then they form right angles. Statement #2: If two lines form right angles, then the angles are 90. Conclusion: ________________________________________________________. Law of Logic ______________________________________ b) Statement #1: If you study for the test, then you will get a good grade. Statement #2: Art studied for the test. Conclusion: ________________________________________________________ Law of Logic ______________________________________________ 28. Which property of equality matches each conditional statement: a) If x = 15, then x + 3 = 18. _______________________________ b) If x = 12, then 5x = 60 ________________________________ c) If x + y = 14, then 14 = x + y _____________________________ d) If x = n and n = 7, then x = 7 ______________________________ 29. In the figure to the right, WX @ YZ . Find the length of XZ . 6x + 3 8x - 5 W 27 X Y Z 30. Two angles, Ð 1 and Ð 2, are complementary. If m Ð 1 = 54 , what is m Ð 2? o 31. Use the figure to the right to find m Ð 2 if m Ð 1 = 41o. 2 1 For Exercises 32 – 33, refer to the figure to the right. 32. Find m Ð 2 if m Ð 3 = 115o. 1 For Exercises 34 – 37, refer to the figure to the right. 34. 3 2 33. Solve for x if m Ð 4 = (4x + 5)o and m Ð 3 = (6x + 15)o 4 G F AB and FG are ________________. E 35. Which lines are skew to BC ? 36. BC and H D BH are ___________________. C A B 37. Name a line parallel to EG . ______________ For Exercises 38 and 39, refer to the figure to the right. 38. Find the value of x. 39. Find the value of y. 41° y x 40. Use the figure below to determine the type angles shown and what is true when x || y. z a) Ð1 and Ð3; Ð6 and Ð8 ___________________________________ 1 8 b) mÐ2 and mÐ3 x 2 ___________________________________ c) mÐ1 and mÐ5 ___________________________________ y d) mÐ2 and mÐ6 ___________________________________ 7 79° 46° I 4 5 M J 41. Use the figure to the right to determine which line segments are parallel. 6 3 80° 45° 79° K L N 42. Use the figure to the right to find the value of x that makes x || y . 110° x (4x + 30)° y c 43. Which theorem or postulate proves a || b in the figure to the right? a b 44. Use the figure below to determine the value of x that makes a || b. c 3x (4x + 40) a b 45. Write the equation of the line has a y-intercept of 3 and is parallel to the line with 1 equation y = - x + 91. 3 46. Identify each pair of lines as perpendicular, parallel, or neither? a) y = y= 1 x + 7; 3 1 x–7 3 ______________ b) y = 7x + 3: y = 8x + 3 _________________ c) y = y= 3 x–7 5 1 x+8 2 1 y x2 2 d) y = 5 x – 23 3 _____________ ______________ 47. Given l || m, m Ð 4 = 108o and mÐ10 = 64, use the figure to the right to find the measure of each angle. 1 = _______ 2 = _______ 3 = _______ l m 1 2 5 6 4 = _______ 5 = _______ 6 = _______ 10 7 = _______ 8 = _______ 9 = _______ 10 = _______ 11 = _______ 12 = _______ 13 = _______ 14 = _______ 15 = _______ 16 = _______ 9 13 14 3 4 7 8 p 11 12 n 15 16 48. Find the slope of any line that is perpendicular to the line through (-2, 7) and (4, -11). 49. Use the figure to the right to find the value of x. (4x + 10)° 88° 50. Use the figure to the right to find the value of x. 5x + 5 2x + 14 8x - 17 51. Name the type of triangle described below. a) At least two congruent sides and an obtuse angle. ___________________ b) three congruent sides. __________________________ c) a right angle and two congruent sides. ___________________________ d) three acute angles and no congruent sides is __________________. A D C B 52. Given AD^ BD , AC^ BC , and BD @ AC , which postulate or theorem can be used to prove ACB @ BDA ? 53. Find the measure of Ð1 in the figure to the right. 135 Ð1 54. An isosceles triangle has a perimeter of 64 cm. The lengths of the legs of the triangle are represented by (4x – 5) and (7x – 26). Find the length of the base of the triangle. For Exercises 55 and 56, refer to the figure to the right. 55. Given ÐA @ ÐD and ÐB @ ÐE, find the value of x. A 30° B E 50° C 56. Find mÐC. (5x + 30)° F D 57. In MNO and XYZ, MN @ XY and NO @ YZ . If the two triangles are congruent, what else must be true to prove the triangles congruent by SAS? E 58. Use the figure to the right to determine which postulate or theorem can be used to prove EFH @ GHF? H G F 59. Given that ÐA @ ÐD and ÐB @ ÐE, what is the 3rd congruence needed to prove that ABC @ DEF by ASA? 60. Tell which postulate or theorem can be used to prove that the triangles are congruent and give the congruence correspondence of the triangles? K L a) b) I ______________________ J _____________________ 41° 61. What are the values of x and y in the figure at the right? 61 in 61 in x y 49 in 62. What is the value of x in the figure to the right? xo 63. Find the m Ð BCD in the figure to the right. C m m m D A CAB = 30o ABC = (4x + 10)o BCD = (6x + 20)o B Use the figure to the right for Exercises 64 – 65. 64. Given that F, G, and E are the midpoints of KL, LM ,and KM respectively, find FG. 4x - 5 L 6x + 2 F G K 65. Given that F, G, and E are the midpoints of KL, LM ,and KM respectively and m Ð EKF = 62o, find m Ð GFK. E 14x - 8 M 8 66. In NPR, points O, Q, and S are midpoints of the sides. Find the slope and the length of OQ 6 4 and NR in the figure to the right. P O 2 Q N -10 -5 5 S 10 R -2 -4 E 55° 67. Using the figure to the right, list the sides in order from shortest to longest. -6 42° F -8 G 68. A triangle has two sides that have lengths of 12 cm and 25 cm. Name two inequalities that could represent the length of the third side? 69. Tell if each set of measures will form a triangle? a) 2 cm, 3cm, 5 cm ______________ b) 20 in., 17 in., 40 in ______________ c) 8.3 ft., 4.3 ft., 4.9 ft._____________ d) 12 cm, 12 cm, 1.5 cm ____________ e) 30.5 in., 58.5 in., 26.5 in. __________ 70. In ABC, mÐA = (3x + 25)°, mÐB = (7x – 9)° , and mÐC = (2x + 20) °. List the sides of ABC in order from shortest to longest. 71. Use the diagram below to complete the statement. a) If x = 27 and y = 26, then mÐ1 _______mÐ6. b) If mÐ1 = 100and mÐ6 = 98 Then x ___________y 1 20 in 19 in 3 y 2 x 5 4 19 in 20 in 6 72. Use the figure to the right to choose the inequality that correctly describes the restriction on the value of x. 22 m 46° 48° 22 m x+3 2x - 11 73. Use the figure to the right to find the length of NK when MN = 10 cm and MK = 24 cm. N M K Geometry 1st Semester Proof Review Name ________________ 1. Given: BC || DE , ÐADE @ ÐAED Prove: ÐABC @ ÐACB A B C E D 2. Given: AB || CD, AD ^ DC , AB ^ BC Prove: ABC @ CDA A B D C H 3. Given: HL and JK bisect each other. Prove: ÐL @ ÐH K J M L P 4. Given: PQ @ PW , QR @ WV Prove: PR @ PV Q R v w 5. Given: PQ is an altitude and a median of OPR Prove: OPR is isosceles R O 6. Given: 3(2t + 9) = 30 Prove: t = ½ d c 7. Given: a || b; c || d Prove: Ð1 @ Ð12 1 a 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 b 8. Given: Ð AEC @ Ð DEB Prove: Ð AEB @ Ð DEC 10 11 9 12 A B C E D Geometry 1st Semester Review Name:___________________ Be able to define and understand all of the following terms and concepts. 1. Conjecture 26. Conditional Statements 2. Points 27. Hypothesis and Conclusion 3. Lines 28. Inductive Reasoning 4. Planes 29. Counterexample 5. Segments 30. Converse 6. Rays 31. Inverse 7. Length of a segment (AB) 32. Contrapositive 8. Collinear Points 33. Biconditional statement 9. Coplanar Points 34. Theorem 10. Opposite Rays 35. Law of Detachment 11. Intersection of two lines 36. Law of Syllogism 12. Intersection of two planes 37. Perpendicular Lines 13. Distance Formula 38. Line perpendicular to a plane 14. Midpoint Formula 39. Parallel Lines 15. Betweenness of points 40. Parallel Planes 16. Bisect 41. Transversal 17. Midpoint 42. Alternate Exterior Angles 18. Vertical Angles 43. Alternate Interior Angles 19. Linear Pair 44. Corresponding Angles 20. Complementary Angles 45. Consecutive Interior Angles 21. Supplementary Angles 22. Angle Addition postulate 23. Segment Addition Postulate 24. Angles – acute, right, obtuse 25. Adjacent Angles