* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Map to the STAARs - Hanks World Geography
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
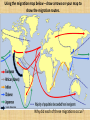
Map to the STAARs Bell Ringer # 1a Geographic Distributions Which of these states had the largest percentage of people from Germany? A. B. C. D. Pennsylvania New York Georgia Vermont Bell Ringer #1b Geographic Distributions According to the graph above, which part of Texas has the lowest elevation? A. East B. West C. North D. South World Geography EOC Review Below is an example of what your map will look like when we are complete. Your Map will include items on the back … We will process significant information on the back of your map. Day 1- 5 Themes Essential QuestionHow can maps be used to explain the division of land, including man-made and natural borders, into separate political units such as cities, states, or countries? Key Ideas Concepts• Location, Place, Human-Environment Interaction, Movement, Regions Vocabulary• Absolute Location, Distortion, Map Projection, Relative Location Verbs• Describe, Explain, Compare, Analyze, Identify, Evaluate Day 1 Map Perspectives Day 1 More Map Perspectives Day 1 Physical Features • Cut out maps and tape together starting with center pieces • You will begin to fill out physical features on each continent according to the physical features page of the resource packet. • Name, Period- Northeast corner • Glue key to Northwest corner of map • Draw compass in Southwest corner Day 1 Locations: GlobalEquator, Prime Meridian, 2 Tropics, 7 continents, 5 oceans North AmericaLand: The Rockies, Appalachians, Cascades, Canadian Shield Water: Mississippi R., St. Lawrence R., 5 Great Lakes South AmericaLand: Andes Mts., Isthmus of Panama, Panama Canal, Amazon Rainforest/Basin Water: Amazon R., Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico EuropeLand: Pyrenees Mts., Alps, Ural Mts., Iberian Peninsula, Scandinavian Peninsula Water: Mediterranean Sea, Rhine R., Strait of Gibraltar AfricaLand: Sahara D., Mt. Kilimanjaro, Great Rift Valley, Congo Rainforest/Basin Water: Lake Victoria, Nile R., Congo R. AsiaLand: Himalayas, Gobi D., Indus River Valley Water: Yellow R., Yangtze R., Ganges R., Indus R. Australia, Oceania, AntarcticaLand: Australian Outback Stop Water: Weddell Sea, Great Barrier Reef Day 1 Bell Ringer #2a Geographic Distributions Which statement about Houston’s climate is correct? A. It has more rain in winter than in summer. B. July is the wettest month. C. March is the driest month. D. September is the hottest month. Bell Ringer #2b Effects of Spatial Diffusion of a Phenomenon The introduction of sugar cane transformed the Caribbean region because… A. large numbers of African slaves were imported to work on sugar cane plantations. B. it radically changed the diet of the native inhabitants. C. the native people grew rich from the exportation of sugar cane. D. many Europeans migrated to the Caribbean region to work as laborers on the sugar cane plantation. Day 2- Physical Geography Essential Questions• How and why do geographers use tools to study the interactions between the physical and human landscapes of Earth? • How do physical forces cause change in the Earth’s landscape over time? How does this alter the human landscape and force adaptations and modifications to the environment? Can you think of any examples? Day 2 Key Ideas Concepts• Geographic Tools, Systems, Forces of Change, Physical Environment, Climate, Interdependence, Innovation, Human-Environmental Interaction, Physical and Human processes, Adaption, Modification, Region Vocabulary• Geography, Human-Environment interaction, Convection, Plate tectonics Verbs• Describe, Explain, Compare, Analyze, Identify, Evaluate Day 2 Locations: GlobalEquator, Prime Meridian, 2 Tropics, 7 continents, 5 oceans North AmericaLand: The Rockies, Appalachians, Cascades, Canadian Shield Water: Mississippi R., St. Lawrence R., 5 Great Lakes South AmericaLand: Andes Mts., Isthmus of Panama, Panama Canal, Amazon Rainforest/Basin Water: Amazon R., Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico EuropeLand: Pyrenees Mts., Alps, Ural Mts., Iberian Peninsula, Scandinavian Peninsula Water: Mediterranean Sea, Rhine R., Strait of Gibraltar AfricaLand: Sahara D., Mt. Kilimanjaro, Great Rift Valley, Congo Rainforest/Basin Water: Lake Victoria, Nile R., Congo R. AsiaLand: Himalayas, Gobi D., Indus River Valley Water: Yellow R., Yangtze R., Ganges R., Indus R. Australia, Oceania, AntarcticaLand: Australian Outback Water: Weddell Sea, Great Barrier Reef Day 2 Factors that Affect Climate Latitude (most important) Air Masses Continentality Elevation Mountain Barriers Ocean Currents Pressure & Wind Storm Tracks Weather vs. Climate List what you know about each climate region in the chart on the back of your map. How does climate affect how people live? Simple summary of climatic zones: Polar - very cold and dry all year Temperate - cold winters and mild summers Arid - dry, hot all year Tropical - hot and wet all year Mediterranean - mild winters, dry hot summers Mountains (tundra) very cold all year The classification is based on maximum and minimum temperatures and the temperature range as well as the total and seasonal distribution of precipitation. Weather 1. Complete your chart using your knowledge and classroom resources. 2. Using the symbols you created, draw the symbols on the front of your own map in the appropriate places for each phenomena. . Stop Bell Ringer #3a Critical Thinking Skills According to the graph, about what percent of Nigeria’s population are males between the ages of 5 and 9? A. B. C. D. 7% 8.5% 15% 17% Bell Ringer #3b Size and Distribution of Cities What conclusion can you draw from the graph of city populations? A. Cities are growing too fast for their governments to provide them with adequate services. B. One quarter of the world’s population lives in urban areas. C. The populations of Latin American cities will soon equal those of Asian cities. D. Population in Latin American cities are growing larger than Asian cities. Day 3- Human Geography Essential Questions- • How do social, political, and economic factors determine population trends and demographics in a region? • How do physical and human characteristics define places and regions and how and why do they often change over time? • Why do humans modify and adapt to the physical environment? Day 3 Key Ideas Concepts- Population, Demographics, Migration, Places, Regions, Character of a place, Human-Environmental Interaction, Impact Vocabulary• Region, Push/Pull Factors, Human Geography, Globalization Verbs• Describe, Explain, Analyze, Identify Day 3 Areas by Size Universe Solar System Planet Hemisphere Continent Region Country/Nation State/Territory County City Area Day 1 Using the pictures describe the difference between formal, functional, and perceptual regions. Write answer on back in Human Geography section. Regions Formal- Ex. Corn belt Functional- Ex. LA Freeway system Perceptual- Bible Belt Human Environment Interaction • In the section titled “Human Geography,” write a definition for Adapting and Modifying the Environment. • Give two examples for each Population • What do population pyramids tell us? Population Pyramids 1. Draw a line from the population pyramids to the appropriate country. You will have 6 of them. 2. Cut out the blocks of people and glue them in or near two highly populated countries. 3. Cut out the growth images and glue them on or near two fast growing countries. TOP TEN COUNTRIES WITH THE HIGHEST POPULATION # Country 2000 Population 2010 Population 2012 Population 2050 Expected Pop. 1 China 1,268,853,362 1,330,141,295 1,343,239,923 1,303,723,332 2 India 1,004,124,224 1,173,108,018 1,205,073,612 1,656,553,632 3 United States 282,338,631 310,232,863 313,847,465 439,010,253 4 Indonesia 213,829,469 242,968,342 248,645,008 313,020,847 5 Brazil 176,319,621 201,103,330 193,946,886 260,692,493 6 Pakistan 146,404,914 184,404,791 190,291,129 276,428,758 7 Bangladesh 130,406,594 156,118,464 161,083,804 233,587,279 8 Nigeria 123,178,818 152,217,341 170,123,740 264,262,405 9 Russia 146,709,971 139,390,205 142,517,670 109,187,353 10 Japan 126,729,223 126,804,433 127,368,088 93,673,826 TOP TEN Countries 3,618,894,827 4,016,489,082 4,096,137,325 4,950,140,178 Rest of the World 2,466,012,769 2,829,120,878 2,921,709,597 4,306,202,522 TOTAL World Population 6,084,907,596 6,845,609,960 7,017,846,922 9,256,342,700 Population Pyramids • How can we address problems facing fast growing populations? • What are the challenges facing shrinking populations? Your map should be starting to look like this one…. Exit slip • Choose two population graphs to analyze • Answer the following questions– Do they show positive, neutral, or negative growth? – Where are the population bulges? – What issues will they have to deal with in the future? Stop Bell Ringer #4a A Spatial Exchanges and their Influences on the Present What geographic feature prevented the Bantu from heading north? A. Central African Rainforest B. Lake Victoria C. Namib Desert D. Sahara Bell Ringer #4b Spatial Exchanges and their Influences on the Present According to the map, what geographic feature was essential for migrations to the Americas? A. The ice sheet. B. The Pacific Ocean. C. The Beringia land bridge. D. The isthmus of Panama. Bell Ringer #4c Effects of Spatial Diffusion of a Phenomenon Based on the map, which of the following statements correctly describes some of the consequences of the Columbian Exchange? A. It spread tomatoes and peppers to the Old World but disease to the Americas. B. It resulted in the distribution of pigs and other livestock to Europe and Africa. C. It brought pineapples, cacao, and coffee to Africa. D. It brought rice to the Americas but spread disease to Asia. Migration - complete the push/pull chart below in your resource packet. Using the migration map below – draw arrows on your map to show the migration routes. Latin America Why did each of these migrations occur? Net migrations – Why do these different regions fall into these different categories? JeopardyGeography Stop