* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nitrogen Cycling - MrPfancooksWIKI
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
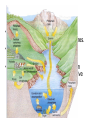
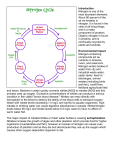
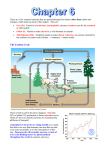
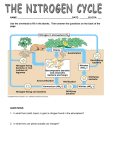
Nutrient Cycles NITROGEN MOLECULES TO KNOW N2 - Nitrogen Gas NO2 – Nitrite NO3 – Nitrate NH4 – Ammonia Nitrogen Cycling Nitrogen Fixation aka nitrification • To be useful to plant organisms nitrogen must be supplied in the form of the Nitrate ion NO3 – • NITROGEN FIXATION is a series of processes when Nitrogen gas from the atmosphere (N2) is converted into Nitrate ions • Nitrogen fixation can occur through lightning or through special bacteria Fixation by Lightning • Energy in lightning causes Nitrogen gas to combine with Oxygen gas to for Nitrates • The Nitrates dissolve in rain and move into plants through their roots • Plants use these nitrates to make amino acids (proteins) Nitrogen Fixation by Bacteria • Special bacteria are responsible for creating most of the Nitrates plants need. • Bacteria nodules form on the roots of legumes (beans, peas, alfalfa) to supply them with usable nitrogen • Excess nitrates move into the soil to help other plants Decomposing Nitrogen • When organisms die decomposers break Nitrogen containing molecules into simpler chemicals like ammonia (NH3) AMMONIFICATION • Some bacteria convert Ammonia into nitrites (Nitrification) Some bacteria can turn nitrites into nitrates (Nitrification) • With the right bacteria decaying matter like manure can be turned into usable nitrates Denitrification • When there is low oxygen in the soil bacteria can remove oxygen turning nitrates (NO3) back into nitrites (NO2) and then back into Nitrogen Gas (N2) • Denitrification usually occurs in bogs leaving the soil low in usable nitrogen. Phosphorous Cycle • Phosphorous is a key element in ATP, DNA and the Calcium Phosphate in bones. • Phosphorous is cycled between living organisms by decomposers • Phosphorous is also found in Bedrock in Phosphate ions. Phosphates can dissolve out of rocks and can be absorbed by plants Human Effects on Cycling • Fertilizers are materials used to restore nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorous that have been removed from the soil. • Runoff from fields carries extra nutrients into streams. This can cause Eutrophication • Eutrophication is the over concentration of nutrients in an ecosystem • Eutrophication can also be caused by municipal or industrial sewage deposit. Eutrophication (to much of a good thing) • Causes overgrowth of algae (Algal Bloom) which may block out sunlight • Nitrates in water are dangerous for animals that have hemoglobin in their blood • Increased numbers of decomposing algae and animals reduces the amount of oxygen in the water causing even more species death • Sea of Azov In Ukraine Caspian Sea