* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interstellar Cloud
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
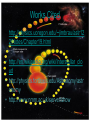
Stellar Birth Nikki B Karly B Interstellar Cloud An accumulation of dust, gas and plasma that is a denser-thanaverage region of the interstellar medium Collapsing Cloud Fragment The density of the cloud formed begins to decrease. Photons absorbed by the thin material of the fragment are radiated into space, so no temperature increase occurs. The fragments continue to contract until they become so dense that radiation can not escape the core of the star. Fragmentation Ceases Tens of thousands of years after the second stage, the fragment begins to collapse The center becomes opaque and the central temperature rises significantly A protostar appears at the center and the cloud shrinks to the size of our solar system Protostar A protostar is the center of the disc formed in the center of the interstellar gas cloud. Hotter than the gas it condensed, but cooler than a star. Further collapse occurs when the protostar reaches seven million Kelvin and nuclear reactions begin in the core. Protostar Evolution As the protostar moves beyond stage 4, it becomes a T Tauri star, moving toward the main sequence this path from stage 4 to 6 is known as the Hayashi track Characterized by violent surface activity and strong protostellar winds Central temperature is still not hot enough for thermonuclear fusion repulsion of two positively charged protons (Hydrogen nuclei) cannot be overcome Newborn Star After 100,000 years of formation, a newborn star is created. The temperature of the newborn star begins to increase, causing the fusion of hydrogen to create helium The remaining dust and gas surrounding the star disperses. Main Sequence The star contracts and comes into hydrostatic equilibrium Works Cited • http://physics.uoregon.edu/~jimbrau/astr12 2/Notes/Chapter19.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interstellar_clo ud • http://physics.fortlewis.edu/Astronomy/astr onomy • http://www.nmm.ac.uk/server/show