* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Market Forces PPT - Mr. Chumley FHCI
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Supply chain management wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
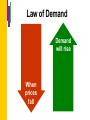
Economic Systems and Market Forces What goods and services will a country produce? Scarcity All economies are based on the principle of “scarcity”: All people and countries have limited resources that can not satisfy unlimited wants. An Economic System An economic system is a method used by a society to produce and distribute goods and services. There are three key questions addressed by every economic system: What goods and services will be produced? How will these goods and services be produced? Who will consume these goods and services? Types of Economic Systems There are three pure types of economic systems: • Traditional • Command • Free-Market 1-5 Copyright © 2008 A Traditional Economy In a traditional economy, people live and work as their ancestors lived and worked. In a traditional economy, we produce what our ancestors produced. produce it the way our ancestors did. distribute it the way our ancestors did. Traditional Economy In a traditional economy, elders answer the economic questions based on traditions. In Canada, some Inuit still maintain a traditional economy. Command Economy In a command economy, the national government makes all the economic decisions. Everyone in the country shares limited resources. Features government ownership of land and capital government control of labour government control of all economic activity Market Economy In a market economy, individuals make economic decisions. Individuals decide: what to produce how to produce it who gets the products Mixed Economies There are no pure command or pure market economies. Most modern economies are mixed economies: An economy where both government and individuals are involved in making economic decisions. Market Forces How do the right products get to the right places, in the right quantities, and at the right prices? Market Forces at Work A market economy is also called a free market economy because market forces are free to influence economic decisions. Three main market forces supply and demand profit competition Supply and Demand Demand quantity of a product a consumer is willing and able to buy at a certain price Supply quantity of a product a supplier is willing to provide at a certain price (Continued) Supply and Demand Market demand sum of all individual demands for a specific product Market supply sum of all individual suppliers’ supply of a specific product (Continued) Effect of Price on Demand Law of demand when prices fall, demand will rise when prices rise, demand will fall Law of Demand Demand will rise When prices fall Law of Demand Consumers buy more (demand rises) when price is low. Consumers buy less (demand falls) when price is high. Changes in Demand Changes in demand can be caused by changes in marketing campaigns the economic situation social trends These changes can interfere with the laws of supply and demand. Effect of Price on Supply Law of supply when prices are high, supply will rise when prices fall, supply will fall The law of supply is based on market supply. Law of Supply When prices are high Supply will rise Law of Supply Manufacturers will supply more of a product when its price is high because they will make more profit. Manufacturers will supply less of a product when the price falls because they will make less profit. Effect of Supply and Demand on Price Price affects supply and demand and gives us the laws of supply and demand. However, the level of supply and the level of demand interact to affect price. Effect of Demand on Supply and Price Demand Rises Consumers start buying lots of basketballs. Supply Falls Suppliers can’t keep up with the rapid sale of basketballs. Price Rises Suppliers raise the price of basketballs. Consumers pay the higher price. Effect of Demand on Supply and Price Demand Falls Consumers are not buying soccer balls. Supply Rises Soccer balls pile up in the suppliers’ warehouses. Price Falls Suppliers lower the price to sell the soccer balls. Effect of Supply on Price and Demand Supply Rises Strawberries are in season. The berries are spoiling before consumers purchase them. Price Falls The suppliers want to sell their product before it spoils. They lower the price of strawberries. Demand Rises The reduction in price increases consumers’ demand for strawberries. Profit Profit motive is the drive to earn more profit. Sales Costs and Expenses Profit Profit What is your profit if your store sells $100 worth of merchandise and your costs are $75? Sales – Costs= Profit $100 – $75 = $25 Your profit is $25. (Continued) Profit Three main ways to increase profit decrease costs or expenses increase productivity (the amount of product a worker produces per hour) increase sales (Continued) Competition Competition businesses competing with each other to get customers Competition results in better products better quality more services lower prices Role of the Consumer Consumers (as a group) have a large impact on a market economy through the forces of supply and demand. (Continued)