* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Josephson junction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
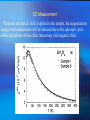
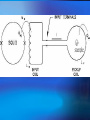
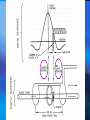
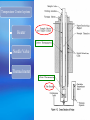
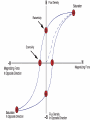
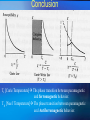
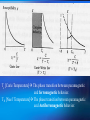
Superconducting Quantum Interference Device SQUID C. P. Sun National Sun Yat Sen University Department of Physics Outline Essential mechanism of SQUID The way to measure Temperature control system AC RSO Josephson Junction DC Introduction ● Essential Mechanism Josephson junction A Josephson junction is an superconductor-insulatorsuperconductor (SIS) layer structure placed between two electrodes DC Josephson : A dc current flows across the junction in the absence of any electric or magnetic field. AC Josephson : A dc voltage applied across the junction causes rf current oscillations across the junction. This effect has been utilized in a precision determination of the value of / e Further, an rf voltage applied with the dc voltage can then cause a dc current across the junction. Macroscopic long-range quantum interference: A dc magnetic field applied through a superconducting circuit containing two junctions causes the maximum supercurrent to show interference effect as a function of magnetic field intensity. Magnetometer DC Measurement When the external dc field is applied to the sample, the magnetization changed with temperature will be obtained due to the spin-spin, spinorbital and orbital-orbital effect interacting with magnetic field. AC Measurement: An oscillating AC magnetic field is applied to the sample. The change in flux seen by the detection circuitry is caused only by the magnetic moment of the sample as it responses the applied AC field. Xac= dM/dH obtained from these measurement is described as having both real and imaginary components X’ and X’’ , where the imaginary component is proportional to the energy losses in the sample. What can be derived from AC Measurement? Structure details of materials, resonance phenomena, electrical conductivity by induced currents, relaxation processes such as flux creep in SC and energy exchange between magnetic spins and the lattice in the paramagnetic materials. Advantage of MPMS AC System Conventional AC suceptometers measure the voltage induced in an inductive detection coil by an oscillating AC magnetic moment. The most common systems use mutual inductance bridge to measure the voltage induced. High pressure effect These systems measure only signals with frequencies at or very near the applied excitation. The natural constraint Voltage induced is proportional to the frequencies of the oscillating drive field How does MPMS solve it? ★ MPMS AC option combining an AC drive field with a SQUID-based detection system. ★The SQUID is an extremely sensitive flux-to-voltage converter that directly measures the change in flux as the sample moves through a superconducting detection coil coupled to the SQUID circuit. RSO Measurement (Reciprocating Sample Option) RSO measure a sample by moving it rapidly and sinusoidally through the SQUID pickup coil. The option’s use of a high-quality servo motor and a digital signal processor (DSP) allow rapid measurement. The servo motor, unlike the stepper motor performing DC measurements, doesn’t stop sample movement for each data reading. Lock-in techniques that use the DSP reduce the contribution of low-frequency noise to the measurement. Measure consideration of RSO ☆ Center position To ensure absolutely accurate measurements even when temperature drifts. To oscillate sample through most or all of pickup coils while taking a high number of readings. ☆Maximum slope To take measurements quickly. To move sample through small section of pickup coils. To perform hysteresis measurement. sensitive to position Temperature Control system Heater Needle Valve Thermal meter Thank you for attention Sun 2005.05.18 Conclusion Tc [Curie Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic and ferromagnetic behavior. TN [Neel’ Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic and Antiferromagnetic behavior. Collect More Data After More Experience More Experience can help us think more details The minimum value of magnetic flux (CGS) (SI) Fluxon 0 2c / 2e 2.0678 10 7 gauss cm 2 0 2 / 2e 2.0678 10 15 tesla m 2 Spin Glass Material exhibiting a high magnetic frustration and its magnetic structure is disordered even at low temperature. Tc [Curie Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic and ferromagnetic behavior. TN [Neel’ Temperature] Ths phase transition between paramagnetic and Antiferromagnetic behavior.