* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronics Class 2
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
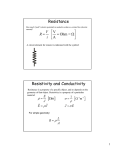
Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 1 Resistance • Resistance is an electrical property of a material that “resists” the flow of electrons. • The schematic symbol for a resistor is: • Common units for resistance are: – Ohms – Kilohm: 1K= 1000 ohms, 10K = 10,000 ohms – Megohm: 1M = 1,000,000 ohms • The units symbol for ohms is: Ω (ohms) 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 2 Current • • • • Current: Defined as “flow of electrons”. Current: Units of current is AMPS. Current: Electrical symbol for current is I. Common units for current are: – Amps – Milliamps (ma): 1 ma = .001 amp – Microamps (ua) : 1 ua = .000001 amp, or .001 ma – Nanoamps (na) : 1 na = .000000001 amp or .000001 ma, or .001 ua. 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 3 Voltage • Volts is the electrical force that causes electrons (current) to flow. • Units of volts is VOLTS. • The symbol of volts is E. • Common units for voltage are: – – – – Volts Millivolt (mv) : .001 volt. Microvolt (uv) : .000001 volt, or .001 mv Nanovolt (nv) : .000000001 volt, or .000001 mv, or .001 uv. 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 4 Power • Power is the measure of how much energy a circuit or appliance uses. • Power is measured in Watts (W). • The symbol for power is P. • Power is calculated by: P = E x I. • Typical units are watts, killowatts (1000 watts), megawatts (1,000,000) watts, etc. 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 5 Ohms Law • One of the most important laws in electronics/electricity. • E = I x R : Voltage = Current x Resistance • Volts is measure in VOLTS, current is measured in AMPS, and resistance is measured in OHMS. • 1 AMP, going through 1 OHM of resistance, generates a voltage drop of 1 VOLT. • 1 V = 1 A x 1 Ω. 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 6 More Ohm’s Law Different forms of Ohm’s Law: E = I x R : Voltage = Current X Resistance I = E / R : Current = Voltage / Resistance R = E / I : Resistance = Voltage / Current + 10V 1000 Ω 5/12/2017 Volts = 10. Resistance = 1000Ω Compute current. I=E/R I = 10 / 1000 = .01A .01A = 10ma Question: what would the current be if the voltage was 1 V? How about 1000 V? Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 7 Ohm’s Law Board • We will use the ohm’s law board to illustrate that ohm’s law really works. You will also learn how to use a meter. • The purpose of this board is to use ohm’s law to calculate the value of 3 resistors. • Also, we will calculate the amount of power two resistors dissipate, and notice the difference between the two. 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 8 Calibration of Ohm’s Law Board. Vin A J4 10V B 1 2 R1 GND 3 4 R2 R3 R_calibrate 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 5/12/2017 Turn on meter (->1) Dial meter to 2000u DCA (->2) Place meter lead (mA -> 3) to J4-A. Place meter lead (COM -> 4) to J4-B. Turn Board ON. Adjust R_Calibrate until meter reads 1000 ua (as close as you can get it.) You now know how much current goes through R1, R2 and R3. Write this down as I_cal on worksheet. NOTE: 1000 ua (microamp) = 1 ma (milliamp) = .001 A (amp). We will use .001 A when we calculate resistance. Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 9 Measure Voltage for R1, R2 and R3 Vin A J4 B 1 J2 10V J3 R1 GND 2 3 R2 100 ohm 50 ohm R3 GND R_calibrate 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 5/12/2017 Remove meter leads from J4-A and J4-B. Add jumper wire for J4. Dial meter to 20 DCV Place VΩmA lead (2) at top of R1. Place COM lead (3) at bottom of R1. Read the voltage from the meter and write it on worksheet for V_R1. Connect the meter to top and bottom of R2 and write down this voltage as V_R2. Do the same for R3. Write down the voltage as V_R3. Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 10 OHM’S LAW WORK SHEET Vin Calibration Current I_cal =__________ua J4 = ________A J2 10V J3 R1 GND R2 100 ohm 50 ohm R3 GND V_R1 = ________V R1 = ________Ω V_R2 = ________V R2 = ________Ω V_R3 = ________V R3 = ________Ω R_calibrate 5/12/2017 Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree OMHS LAW R = E/I 11 Power Measurement Vin 1 V+ J2 J3 3 4 GND 100 ohm 50 ohm GND 5/12/2017 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Connect wire across J2. Dial meter to 20 DCV (1) Connect meter VΩmA lead (3) to V+. Connect meter COM lead (4) to GND. Read the meter and write down the measured voltage. 6. Voltage measured at V+ = _________V. Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 12 Power Worksheet Vin V+ V+ J2 J3 GND 100 ohm 50 ohm GND 5/12/2017 = ________V 1. Calculate power across 100 ohm resistor. P = V x V / 100 ________W 2. Calculate power across 50 ohm resistor. P = V x V / 50 ________W 3. Touch 100 ohm and 50 ohm resistors quickly with your fingers. What is different between the 2? Why are they different? Electronics Merit Badge Class 2 - 2013 National Scout Jamboree 13