* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
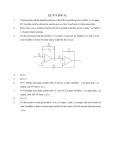
In practice, it is often required to make or break an electric al circuit in many operations. In some applications, it is desirable that this make and break should be very quick and without sparking. The mechanical switches or electric-mechanical switches (i.e. relays) cannot be used for the purpose due to two main reasons. First, these switches have a high inertia which limits their speed of operation which limits their speed of operation. Second, there is sparking at the contacts during breaking operation which result in the burning of contacts. Modern researches have revealed that tubes and transistors can serve as the switching devices. They can turn ON or OFF power in an electrical circuit as a very high speed without sparking. Such switches are called electronic switches. The electronic square, rectangular and saw tooth waves. A transistor with proper associated circuitry can be used as switch to turn ON or OFF current in electrical circuit. Transistor switches have become popular because of their high speed of operation and absence of sparking. When a transistor is used as a switch, it is so arranged in the circuit that either maximum current (called collector saturation current) flows through the load or minimum current (called collector leakage current) flows through the load. In other words, a switching transistor has two states viz. ON state or when collector saturation current flows through the load OFF state or when collector leakage current flows through the load. Is an electronic circuit that generates square waves (or other-non-sinusoidal waves such as rectangular, sawtooth waves). It is switching circuit which depends for operation on the positive feedback. It is basically a twostage amplifier with output of one fed back to the input of the other. A multivibrator operates in two states (viz. ON and OFF) controlled by circuit conditions. Each amplifier stage supplies feedback to the other in such a manner that will drive the transistor of one stage to saturation (ON state) and the other to cut off (OFF state). Depending upon the manner in which the two states interchange their states, multivibrators are classified as: Astable or free running multivibrator Monostable or one-shot multivibrator Bistable or flip-flop multivibrator The astable multivibrator has no state stable. It switches back and forth automatically from one state to the other, remaining in each for a time determined by circuit constant. Thus it is just as an oscillator since it requires no external pulse for its operation. A monostable multivibrator has only one state stable and one quasi-stable (i.e. half-stable). The application of input pulse triggers the circuit into quasi-stable state in which it remains for a period determined by circuit conditions. After this period of time, the circuit returns to its initial stable state, the process is repeated upon the application of each trigger pulse. The bistable multivibrator has both the state stable. It requires the applications of an external triggering pulse to change the operation from either one state to the other. Thus one impulse is used to generate half-cycle of square wave. It is called flip-flop because of the two possible state it can assume. A circuit in which output voltage is directly proportional to the derivative of the input is known as a differentiating circuit. A differentiating circuit is a simple RC series circuit output taken across R. It is important to note that merely using voltage across R does not make the circuit a differentiator; it is necessary to proportion the time constant of the circuit properly. The RC product should be many times smaller than the time period of the input wave. A ratio of 1 to 10 is usually sufficient to provide good differentiation. The output waveform from differentiating circuit depends upon the time constant and shape of the input wave. Thus if a d.c. or constant input is applied to such a circuit, the output will be zero. Similarly, when the input is a square wave, the output will consist of sharp narrow pulses. A circuit in which output voltage is directly proportional to the integral of the input is known as an integrating circuit. An integrating circuit is a simple RC series circuit with output taken across C. The circuit is suitably designed so the RC product is many times greater than the time period of the input wave. A ratio of 1 to 10 usually provides good integration. The output waveform from an integration circuit depends upon the time-constant and shape of the input wave. Thus, if the input fed to an integrating circuit is a square wave, its output will be a triangular wave. Similarly, if the input is a rectangular wave, then the output will be a saw-tooth wave. The circuit with which the waveform is shaped by removing (or clipping) a portion of the applied wave is known as a clipping circuit. The clippers can remove signal voltages above or below a specified level. In the operation of certain electronic circuits, it is essential to have some particular waveform. For, example we require square waves for using in television,digital and other electronic system. The desired square wave can be produced either by reshaping the existing signals or by generating them directly by multivibrators. A clipper does the job of reshaping the existing signal. Thus a sine wave can be converted into a square wave by removing the positive and negative peaks of sine waves through the use of diodes. It may be noted that in order to get a perfect square wave, the peak value of the sine wave should be very much greater than the required square wave. A circuit that adds d.c. component to a signal is known as clamping circuit. It shifts the signal as a whole, lining up either positive or negative peaks to any desired potential For example, suppose the input signal is a sine wave with peak-topeak value 20 V. if a clamper adds 10 V d.c component to it, the signal will be shifted either vertically upward or downward by 10 V, depending upward, it is called a positive clamper. On the other hand, if the clamper shifts the signal vertically downward, it is called negative clamper. A clamping circuit is frequency used to store d.c. component of a pulse which has been passed through an a.c. amplifier or through any other circuit which does not pass d.c. Thus if a pulse having a d.c. component is passed through a transformer or an a.c. amplifier, the d.c. component of the pulse can be restored by using a clamping circuit. D.c. restoration is often applied in Television recievers. POWER ELECTRONICS INTRODUCTION Since 1950’s there has been a great upsurge in the development and application of semiconductor devices. Today, there are well over 100 million semiconductor devices manufactured in a year. These figures alone indicate how important semiconductor devices have become to the electrical industry. One major field of application of semiconductor devices in the recent years has been to control large blocks of power in a system. This has led to the development of a new branch of engineering called power electronics. Power electronics essentially deals with the control of 50Hzpower flow in a system. The most important semiconductor devices which form the core of power electronics are SCR, Triac, Diac, and UJT. These devices can act as controlled switches and can perform the duties of rectification, inversion and regulation of power flow in a load. TRIAC –a triac is a 3 terminal semiconductor switching device which can control alternating current in a load. Triac is an abbreviation for triode a.c. switch. ‘Tri’ indicates that the device has three terminals and ‘a.c’ means that the device controls the alternating current or can conduct current in either direction. . One major difference between an SCR and triac is that whereas SCR is a unidirectional switch and can conduct in one direction only, a triac is a bidirectional switch and can conduct in either direction. The triac is often considered analogous to two SCRs connected in parallel but oriented in opposite directions ( inverse-parallel connection).