* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Economics Environment of Business
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
American School (economics) wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
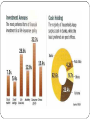
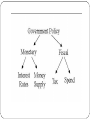
Economics Environment of Business Economics Environment The definition of economic environment is the environment in which businesses operate that is dependent on the sum total of economic factors. Economic factors include income, employment, inflation, interest rates, consumer behavior and distribution of wealth. All of the economic factors have effects on the economic environment, which in turn affects the business market. Economic factors affecting business At what stage of the business cycle is the economy Inflation rate Prevailing interest rates Unemployment level Labor costs Levels of disposable income and income distribution Taxes Tariffs The economic environment is constantly changing because of changes to economic factors. Economic factors are both controllable and uncontrollable. The controllable factors, such as price, income and interest rates are politically controlled. Uncontrollable factors, such as consumer wealth and distribution of wealth, fluctuate and vary, making them difficult to predict. Both the controllable and uncontrollable factors cause changes in the market and consumer demand. The failure to account for economic factors leads to financial consequences for businesses and the economy as a whole. The economic environment is divided into the macroeconomic environment and the microeconomic environment. The microeconomic environment is affected by factors like market size, supply and demand, which affects business actions and decision-making. The macroeconomic environment is affected by factors like exchange rates and taxes, which affects the entire economy on a broader level. Both divisions of the economic environment plays an important part in the success or failure of the market. Economics Systems 1)In the free market economy all resources are owned privately. The consumers and firms decide the allocation of resources. Government has no control over the economy. Consumer needs are met and necessity goods like education and health are not available for everyone. Eg. Cuba 2)In the command economy all resources are owned by the government. The government decides the allocation of resources; that is what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce. Firms are not very efficient as they do not earn profits. Eg. China 3)In the mixed economy resources are owned both privately and by the government. It is the combination of the above economies. Important sectors like health, medical, education are under the government and less important ones are under private ownership. Eg. India,Singapore etc. Most countries follow this economy system. Meaning of Privatization The transfer of ownership, property or business from the government to the private sector is termed privatization. The government ceases to be the owner of the entity or business Privatization is sought to be achieved through any or more of the four important routes: sale to outside owners, management-employee buyout, equal-access voucher privatization, and spontaneous. Nature of Privatization Privatization may be understood as the process whereby activities or enterprises that were once owned and operated by government and its employees are now performed, managed by private business and individuals, often with much better results in terms of cost and quality service. THE OBJECTIVE OF PRIVATIZATION Greater efficiency Revealing the true and full cost of the service provided Promotion of technological advancement Development of capital markets Broadening the wealth and achieving widespread private ownerships in society Curbing inflation Raising extra-revenues for the government Eliminating hidden unemployment and reducing thepower of public employee unions Privatization Routes Sale to Outside - disinvestment Management-Employee Buy Out Equal-access Voucher Privatization Spontaneous Privatization Economic Trends: Income Sr. No. Industry Percentage change over previous year at constant (2004-05 prices) at current prices 2011-12 3.6 2012-13 1.8 2011-12 12.2 2012-13 12.1 1 Agriculture, forestry & fishing 2 Mining & quarrying -0.6 0.4 2.5 11.7 3 4 Manufacturing Electricity, gas & water supply 2.7 6.5 1.9 4.9 11.2 10.5 7.7 18.3 5 6 Construction Trade, hotels, transport & communication 5.6 7.0 5.9 5.2 15.1 18.5 13.9 12.8 7 Financing, insurance, real estate & business services 11.7 8.6 18.7 17.3 8 Community, social & personal services 6.0 6.8 14.9 16.0 Total GDP 6.2 5.0 15.0 13.3 Economic Trends: Savings and Investments Trade and Balance of Payment Balance of Trade Balance of Payments Current Account Capital Account Money Monetary Policy The actions of a central bank, currency board or other regulatory committee that determine the size and rate of growth of the money supply, which in turn affects interest rates. Monetary policy is maintained through actions such as increasing the interest rate, or changing the amount of money banks need to keep in the vault (bank reserves). Fiscal policy Fiscal policy is how the government manages its budget. It collects revenue via taxation that it then spends on various programs