* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.1.2.A Flip Flop Applications
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
UML state machine wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Beam-index tube wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
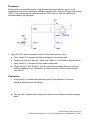
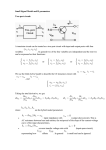
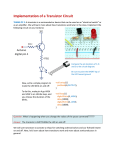
Activity 3.1.2 Flip-Flop Applications: Event Detection Introduction In this activity you will simulate an event detector circuit using a D flip-flop. This design will sound an alarm if a beam of light is disrupted on its photosensitive detector input. The circuit shown below is a photosensitive event detector. This circuit sounds an alarm if the beam of light between the 12-volt incandescent bulb and phototransistor is disrupted. This circuit would be used as part of a larger burglar alarm system. As the name implies, a phototransistor is a transistor that is sensitive to light. In the event detection circuit, the phototransistor acts as a switch. As long as the phototransistor is in the proximity of the incandescent bulb, the transistor will be on. This, in turn, will hold the CLK input of the flip-flop at a logic zero. If the beam of light is disrupted, the phototransistor will be turned off. When the transistor is off, the CLK input of the flip-flop will be pulled high through the 5.6 k resistor. This zero-to-one transition will toggle the Q output to a one, which will turn the buzzer on. The buzzer will remain on until the reset button is pressed. Equipment Circuit Design Software (CDS) © 2014 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Digital Electronics Activity 3.1.2 Flip-Flop Applications: Event Detection – Page 1 Procedure Shown below is a simplified version of the photosensitive event detector circuit. In this simplified version, the phototransistor has been replaced with a single pull single throw switch (SPST). This substitution was made because the CDS does not have the capability to simulate breaking the light beam. 1. Using the CDS, enter the simplified version of the event detector circuit. a. Close “Switch P” to simulate that the phototransistor is receiving light. b. Clear the flip-flop with “Switch C”. Make sure “Switch C” is left open as pictured above. c. Open “Switch P” to simulate the light beam being broken. d. Toggle “Switch P” and “Switch C” until the relationship between the event input and clear are apparent to you. Remember, the event detector holds the output until the user clears it. Conclusion 1. In this activity you studied event detection as a flip-flop application. List three additional applications of the flip-flop. 2. Can you think of another device that might utilize an event detector besides a burglar alarm? © 2014 Project Lead The Way, Inc. Digital Electronics Activity 3.1.2 Flip-Flop Applications: Event Detection – Page 2