* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Excretory System basic
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
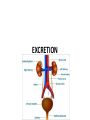
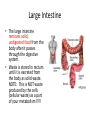
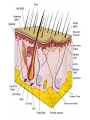
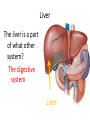
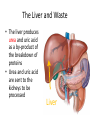
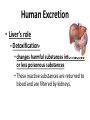
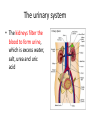
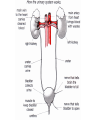
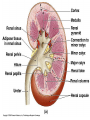
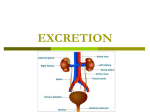
The Human Excretory System The function of the excretory system is the excrete (get rid of) wastes that are not helpful to the body. EXCRETION Excretion is: • removal of metabolic wastes • removal of excess heat Main Excretory organs involved are: • kidneys • liver • lungs • skin A Note About Metabolism • Metabolism • This is the series of activities that cells do in order to keep the organism alive. • Cellular activities usually involve chemical reactions that produce products necessary for life and bi-products (wastes) that are often toxic to cells. • Example: Cellular Respiration produces ATP energy for the cells but it also produces Carbon Dioxide, which is very harmful to the cells. Cellular Waste • Wastes that are removed include carbon dioxide, water, salt, urea and uric acid. • All excreted wastes travel at some time in the blood. Major Metabolic wastes: • carbon dioxide, water – CO2 and H2O are from cellular respiration • certain nitrogen compounds – Breakdown of amino acids from proteins produces nitrogen compounds • Urea • Ammonia • Uric acid • Mineral salts from metabolism – Sodium chloride (NaCl) – Potassium sulfate K2SO4 Structures of the Excretory System 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Skin Lungs Liver Urinary System Large Intestine Can you guess how these structures are a part of the excretory system? What makes the Large Intestine different from the rest? Large Intestine • The large intestine removes solid, undigested food from the body after it passes through the digestive system. • Waste is stored in rectum until it is excreted from the body as solid waste. NOTE: This is NOT waste produced by the cells (cellular waste) as a part of your metabolism!!!!! Skin Wastes such as excess water, salt, urea and uric acid are removed from the body in sweat. Skin 2. Excretion– Small amounts of urea and salts in sweat – Removal of excess heat (Major Function) • Blood vessels dilate bringing more warm blood to skin surface • Sweat is produced by sweat glands • Sweat absorbs body heat and evaporates to water vapor and body heat leaves the body in the water vapor • Body cools as a result of the evaporation Lungs Excess carbon dioxide waste is removed from the body when we exhale. CO2 Liver The liver is a part of what other system? The digestive system Liver The liver has many functions, including (but not limited to): 1. to produce substances that break down fats 2. produce urea (the main substance of urine) 3. make certain amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) 4. filter harmful substances from the blood (such as alcohol) 5. The liver is also responsible for producing cholesterol. It produces about 80% of the cholesterol in your body. The Liver and Waste • The liver produces urea and uric acid as a by-product of the breakdown of proteins • Urea and uric acid are sent to the kidneys to be processed Liver Formation of Urea in Liver: • Amino acids are broken down. 1) amino group, NH2→ changed to ammonia, NH3 → changed to urea (less poisonous) • Finally: Urea diffuses back into bloodstream and is filtered out by the kidneys. Human Excretion • Liver’s role –Detoxification• changes harmful substances into inactive or less poisonous substances • These inactive substances are returned to blood and are filtered by kidneys. The urinary system • The kidneys filter the blood to form urine, which is excess water, salt, urea and uric acid Urinary System Kidneys-> ureter-> urinary bladder-> urethra Kidneys 2 main functions 1. Remove wastes from cellular metabolism 2. Regulate the concentrations of substances found in the body fluids *****If kidneys cannot perform these functions a person will die.***** Kidney structure 3 layers of the kidney • Cortex- outer layer blood is filtered to remove waste and excess substances • Medulla- middle layer made up of tubes called collecting ducts that carry the filtered substances (filtrate) to the innermost layer of the kidney • Pelvis- cavity that collects the filtrate and connects the kidney to the ureter which exits the kidney Nephron Nephron- waste filtering unit of the kidney found in the cortex and the medulla • 1.25 million nephrons in each kidney Filtration in Nephron 1. Blood enters kidney through renal artery, 2. Small substances (water, salts and minerals) and wastes (urea) diffuse from the capillaries into the nephron of the kidneys. 3. Urea, excess water and excess substances travel to the renal pelvis to form urine. 4. Water and some dissolved substances are reabsorbed into the blood through the capillaries. 5. Clean blood leaves the kidney through the renal vein. Urine- final waste fluid excreted • Made up of water, urea and various salts. • 1-1.5 liters of urine are produced every 24 hours Structures Involved in Getting Rid of Urine! Ureter- tube connects kidney to urinary bladder •Function –conducts urine from kidney to bladder Urinary Bladder- collects and stores urine for Excretion Urethra- during urination urine travels from the bladder to the outside of the body