* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phylum Playthelminthes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
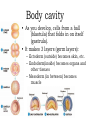
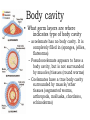
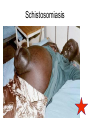
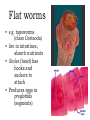
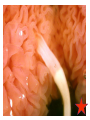
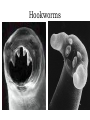
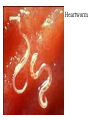
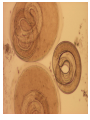
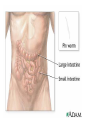
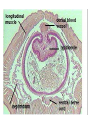
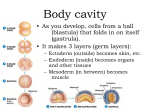
Body cavity • As you develop, cells from a ball (blastula) that folds in on itself (gastrula). • It makes 3 layers (germ layers): – Ectoderm (outside) becomes skin, etc. – Endoderm(inside) becomes organs and other tissues – Mesoderm (in between) becomes muscle Body cavity • What germ layers are where indicates type of body cavity – acoelemate has no body cavity. It is completely filled in (sponges, jellies, flatworms) – Pseudocoelemate appears to have a body cavity, but is not surrounded by muscles/tissues (round worms) – Coelemates have a true body cavity surrounded by muscle/other tissues (segmented worms, arthropods, mollusks, chordates, echinoderms) Platyhelminthes • Flat worms • Bilateral symmetry • Exchange O2/CO2 through skin (diffusion) • No circulatory system • Incomplete digestive system (1 opening … gut) • Cephalized (sensory organs at “head”) • Pseudocoelemate…2 layers with fluid in between • Many are parasites • e.g. Planaria (Class Turbellaria) • Scavenge for food, taken in through pharynx • Water excreted through flame cells • Cerebral ganglia collection of nerves (“brain”) • Fission/sexual repro. (herm, exchange sperm) • Eye spots sense light Flat worms Flat worms • • • • • e.g. Flukes (Class Trematoda) Live blood, intestines, lungs, liver… Suckers to attach, draw in body fluids Hermaphroditic Life cycle with more than 1 host • E.g. schistosomiasis Schistosome • Big one is female, little one is male • Spread by snails! • Causes enlargement of liver/spleen Schistosomiasis Flat worms • e.g. tapeworms (class Cestaoda) • live in intestines, absorb nutrients • Scolex (head) has hooks and suckers to attach • Produces eggs in proglottids (segments) Tapeworm Marine Flatworm Marine Flatworm Nematoda • Round worms • Bilateral symmetry • Pseudocoelemate…2 layers with fluid in between • Complete digestive system (2 openings)…specialized organs with specific functions • Seperate sexes • Many are parasites Roundworms • Ascaris – Live in intestines block them • Hookworms – Live in intestinal wall, feed on blood anemia • Trichinella – Live in muscle pain, stiffness, death • Pinworms – Live in mesentaries of intestine, crawl out at night to lay eggs • Filarial worms – Live in lymph system – Elephantiasis – Heartworms Ascaris Worms Hookworms Heartworm Trichinella Pinworm G Pinworm Filarial worms Filarial Worms Elephantiasis • Even once the worms are removed, it will stay like this the rest of their life • Often infects genitalia/anal • Often gets other infections that kill the person Annelida • “little rings”… segmented worms • bilaterally symmetrical • complete digestive tract • true coelem … 2 layers, space between, allows body to expand/contract in parts • segments allow worm to survive when some parts are damaged Segmented worms • Earthworms – Moves via setae, and 2 sets of muscles (circular and longitudinal) • Squeeze circular muscle, and worm anterior moves forward, plants setae, squeeze longitudinal muscles to bring posterior up – Complete digestive system (mouth, pharynx, crop, gizzard, intestine, anus) – Closed circulatory system (blood moves posterior on dorsal side, anterior in ventral side) Segmented worms – breathe through skin (why you see them on sidewalk when it rains) – ventral nerve cord and cerebral ganglia (“brain”) – nephridia (primitive kidney) in each segment – hermaphroditic, but exchange sperm to reproduce, then lay eggs – clitellum secretes mucus to hold them together Earthworm Leeches • No setae…sucker at each end • Secrete an anesthetic, so you don’t feel them, and a anticoagulent to keep blood from clotting • Will fall off when “full,” otherwise pull them off (don’t cut or burn!) • Used for reattachment surgery! Class Hirudinea OK…to end on a peaceful note, these, too, are segmented worms…. They’re marine worms called feather dusters…