* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 Section 3
Geothermal energy wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Volcanic ash wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Types of volcanic eruptions wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
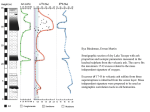
Chapter 8 Section 3 Negative Effects of Volcanic Eruptions • Volcanic explosions can have local and global effects. • In April 1815, Tambora volcano in Indonesia erupted explosively. • The pyroclastic flows and falling debris killed about 10,000 people in the area. • High in the atmosphere, ash and gas spread around Earth. • The average global temperature decreased by as much as 3°C for one to two years. • The lower temperature caused crop failures and starvation, particularly in New England and Europe. • The effects of lower temperatures led to the deaths of about 82,000 people. • Therefore, an estimated total of 92,000 people around the world lost their lives as a result of the Tambora eruption. Local Effects of Volcanic Eruptions • Volcanic eruptions can cause loss of human life and loss of wildlife habitat. • The blast from an explosive eruption can knock down trees, destroy buildings, and kill humans and animals. • Pyroclastic flows can burn everything in their path. • Hot volcanic materials can melt the snowcap on a mountain, causing devastating floods. • Volcanic ash can mix with water to form fast-moving mudflows called lahars. • The weight of falling ash can collapse structures, bury crops, and damage engines. • Volcanic ash can also cause respiratory problems in humans. Global Effects of Volcanic Eruptions • Large volcanic eruptions can affect Earth’s climate for several years. • During large eruptions, ash and sulfur-rich gases can be pushed into the stratosphere. • As the ash and gases spread around the planet, they absorb and scatter sunlight. • Enough sunlight may be absorbed or scattered to lower the average global temperature of Earth. • In 1991, after the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, the amount of sunlight to reach Earth’s surface decreased by 2-4%. • This decrease caused the average global temperature of Earth to decrease by several tenths of a degree for several years. Benefits of Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Soils • Volcanic soils are some of the most fertile soils on Earth. • Volcanic rocks are made of minerals that contain elements important to plant growth. • When volcanic rocks break down, they form soils that contain many nutrients that plants can use. Geothermal Energy • Magma heats the rocks that surround it. • These rocks often hold water that also becomes heated. • This heated water, called geothermal water, may reach temperatures of hundreds of degrees Celcius. • Geothermal water contains large amounts of heat energy. • This energy can be tapped by drilling wells to reach the hot water. • Water can also be pumped through heated rocks to obtain energy. • Geothermal water can be used to drive turbines that generate electricity. • It can also be used to heat homes, grow crops, or keep roads free of ice. • In Reykjavik, Iceland, 85% of all homes are heated with geothermal water. • Volcanic rocks are often used in construction. • As early as 300 BCE, Romans made concrete from volcanic ash and lime. • This material was used to build the Colosseum in Rome in 80 CE. The strength of this material has allowed the Colosseum to stand for nearly two thousand years. • As recently as the 20th century, volcanic ash was used to make concrete for dams in the United States. • Today, basalt and pumice are often used in the construction of roads and bridges, and the production of concrete. • Volcanic rocks have many other uses. • Volcanic ash absorbs moisture, so it is used in cat litter. • Because pumice is abrasive, it is used in facial scrubs, soaps, cleaners, and polishes. • Pumice is added to soil to allow air and water to circulate more easily through the soil. • Because metals in pumice are not water soluble, pumice is used alone or with silica sand to filter drinking water.