* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ip addressing
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
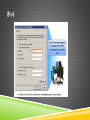
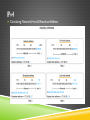
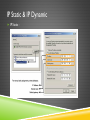
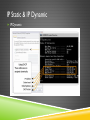
IP ADDRESSING Jarkom Dasar – Week 7 Aisyatul Karima, 2012 OUTLINE IPv4 IPv6 IP Public & IP Private IP Static & IP Dynamic IPv4 IPv4 Network Address 4 octet 32 bit Host Address IPv4 Convertion binary decimal IPv4 IPv4 IP Address Classes IPv4 Address Types in IPv4 IPv4 Calculating Network,Host & Broadcast Address IPv4 Types of communication in IPv4 network : Unicast - the process of sending a packet from one host to an individual host Broadcast - the process of sending a packet from one host to all hosts in the network Multicast - the process of sending a packet from one host to a selected group of hosts IPv6 Creating expanded addressing capabilities was the initial motivation for developing this new protocol. Other issues were also considered during the development of IPv6, such as: Improved packet handling Increased scalability and longevity QoS mechanisms Integrated security IPv6 To provide these features, IPv6 offers: 128-bit hierarchical addressing - to expand addressing capabilities Header format simplification - to improve packet handling Improved support for extensions and options - for increased scalability/longevity and improved packet handling Flow labeling capability - as QoS mechanisms Authentication and privacy capabilities - to integrate security IPv6 Overview IPv6 : IPv6 IP Public & IP Private Although most IPv4 host addresses are public addresses designated for use in networks that are accessible on the Internet, there are blocks of addresses that are used in networks that require limited or no Internet access. These addresses are called private addresses. IP Public & IP Private The private address blocks are: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 (10.0.0.0 /8) 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 (172.16.0.0 /12) 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 (192.168.0.0 /16) IP Public & IP Private IP Public & IP Private NAT (Network Address Translasion) : With services to translate private addresses to public addresses, hosts on a privately addressed network can have access to resources across the Internet. These services, called Network Address Translation (NAT), can be implemented on a device at the edge of the private network. NAT allows the hosts in the network to "borrow" a public address for communicating to outside networks. IP Public & IP Private IP Public : The vast majority of the addresses in the IPv4 unicast host range are public addresses. These addresses are designed to be used in the hosts that are publicly accessible from the Internet. IP Public & IP Private IP Static & IP Dynamic IP Static : IP Static & IP Dynamic IP Static : With a static assignment, the network administrator must manually configure the network information for a host. Advantages : they are useful for printers, servers, and other networking devices that need to be accessible to clients on the network. increased control of network resources. Disadvantage : it can be time-consuming to enter the information on each host. IP Static & IP Dynamic IP Dynamic IP Static & IP Dynamic IP dynamic : Because of the challenges associated with static address management, end user devices often have addresses dynamically assigned, using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). DHCP enables the automatic assignment of addressing information such as IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and other configuration information. Advantages : DHCP is generally the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks because it reduces the burden on network support staff and virtually eliminates entry errors. DHCP not permanently assigned to a host but is only "leased" for a period of time. EXERCISE 1. 2. Konversikan dari bentuk desimal ini menjadi biner : a) 192.168.33.45 b) 172.16.0.99 c) 10.11.45.7 d) 125.163.78.54 e) 67.80.5.36 Konversikan dari bentuk biner ini menjadi desimal : a) 11110000.10101111.00110100.10001101 b) 11000011.11001100.00110011.00001111 c) 11110111.01110111.10101011.11110101 d) 10111110.10101011.11000110.10110011 e) 11100111.10111011.10111101.00001111 EXERCISE 3. Tentukan network address,host address , broadcast address dan subnet mask dari blok IP address berikut ini : a) 172.16.4.0/24 b) 125.163.6.0/24 c) 192.168.3.0/25 d) 125.163.8.0/26 e) 172.18.9.0/29