* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INTRODUCTION TO INFORMATION SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Bus (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
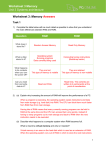
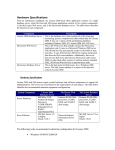
Review For Final (Fall 2009) © Abdou Illia 1 Computer Hardware 2 The Core Computer Components Four subsystems in a computer system: 1. Input subsystem 2. Processing subsystem 3. Output subsystem 4. I/O (Storage) subsystem Input/Output (storage) Input Process Output 3 Output Devices Monitors Cathode ray tube (CRTs) Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) Quality of display Resolution in pixels (e.g. 640 x 480) Dot pitch in millimeters (.26 to .28) Active-Matrix vs. Passive-Matrix display 4 Printers Speed and resolution Pages per minute (PPM) Inkjet: Dots per inch (DPI) Impact printers Number of ink dots to fill a square inch Higher DPI = greater page clarity Create image by striking paper and ribbon Dot-matrix printers = most common impact printers Non-impact printers Create image by spraying or rolling ink on the page 5 I/O or Secondary Storage devices Secondary compared to the main primary memory called RAM Nonvolatile1 storage of digital data Could be Magnetic or Optical Magnetic storage (i.e. data stored on magnetically coated surface) Examples: Magnetic tape, Hard disk, floppy disk Sequential access (e.g. tape) or direct access (e.g. HDD) Hard disk disks many standards: Parallel ATA (PATA) or IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) Serial ATA (SATA)2 SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) SCSI provides disk fault-tolerance by using RAID – Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks; that is multiple disks set together to provide continued service in case one disk fails. Disk speed: Transfer rate in MBps (Megabytes per second) Average Read Time (in milliseconds or ms) Platter rotation speed in RPM (5400/7200/10,000/15,000) 1. Means that the stored data wouldn’t disappear (or be deleted) in case of power shortage 2. In SATA and PATA, ATA stands for Advanced Technology Attachment 6 Measuring Storage Capacity 7 Processing subsystem Motherboard: chipset that all components connect to Two major components in processing subsys. CPU (Central Processing Unit) or Processor(s) Primary Storage: Random Access Memory (RAM) Read Only Memory (ROM) Other components on the Motherboard CPU Busses that transfer data Primary Storage 8 Central Processing Unit Processor Clock: generate time that synchronize other components ICU: Fetches instructions from RAM ALU: Execute instructions (arithmetic & logic operations) Registers: Store control information, data, intermediate results Clock Instruction Control Unit Arithmetic Logic Unit Registers 9 CPU speed Speed measured in hertz Hertz = # of instructions executed per second Megahertz = 1 million of instructions per second Gigahertz = 1 billion of instructions per second Major Processor manufacturers Intel - Celeron - Pentium 3, Pentium 4, Pentium 4 Xeon, Dual Core Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) - K6 series processors (which compete with Intel Pentium 3) - Athlon series (which compete with Intel Pentium 4) IBM - PowerPC 740, 750, 750FX, 750GL, 750GX 10 Primary Storage Computer’s memory stored on semiconductor chips Two categories: RAM (Random Access Memory) which is volatile Synchronous Dynamic RAM (SDRAM) Double Data Rate SDRAM or DDR SDRAM ROM (Read-Only Memory) which is non-volatile Capacity in Megabytes (MB) or Gigabytes (GB) Primary Storage RAM Program RAM holds running programs and the data they use ROM contains critical programs such as those that boot the computer Data ROM 11 Summary Questions Book Notes 1) Name two devices that could be used for both input and output. 2) What is the difference between: (a) a Kilobyte and a Gigabyte? (b) a Megabyte and a byte? 3) What is the function of the Instruction Control Unit or ICU found in the processing subsystem? 4) Explain the difference between RAM and ROM. 5) What is pixel? What is dot pitch 6) What is a byte? 7) What is a Hertz? 12 Network Technology 13 Computer Network Once connected to the network, the computer (or another device) becomes a network node An interconnection of computers and computing equipment using either wires or radio waves over small or large geographic distances GHI DEF ABC MNO “Connect to GHI” JKL 14 Physical Transmission Media Physical media Wireless Transmission media used to physically connect nodes in to the network Transmits electrical or optical signals Could be cooper wire or fiber optic cable 15 Transmission Media (Continued) Twisted Pair Category Use Signal Data rate Distance Problem Category 1 Telephone Analog/Digital <100Kbps 3-4 miles Security, noise Category 2 T1, ISDN Digital <2 Mbps 3-4 miles Security, noise Category 3 LANs Digital 10 Mbps 100 m Security, noise Category 4 LANs Digital 20 Mbps 100 m Security, noise Category 5 LANs Digital 100 Mhz 100 m Security, noise Category 6 LANs Digital 250 Mhz 100 m Security, noise Category 7 LANs Digital 600 Mhz 100 m Security, noise 16 Wireless Media Uses electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiation for data transmission Propagation through space, and indirectly, through solid objects Two kinds of wireless media used Radio waves (radio Frequency) Infrared light Affected by Multipath interference Highly vulnerable to snooping Limited distance Blocked by thick objects Close proximity and “line of sight” location required Laptop Comm. Tower 17 Network Topologies The configurations of network components How physically the network looks like How logically data is transferred on the network Widely used network topologies: Bus Star Ring (Mesh, not common in business setting) 18 Bus Network Topology Most simple network topology All devices connected to a common central cable called a “bus” Inexpensive If cable fails, the entire network will shut down 19 Star Network Topology Centered around central device called a hub or a switch All network nodes connect to the hub/switch Easy to install and update If hub fails, network fails 20 Ring Topology Node connected to a logical ring in a central device called MAU More reliable than bus or star Only one node sends at a time (no collisions) Expensive and limited speed 21 Network Architecture Defines how the processing takes place on the network Two primary types Client-server Peer-to-peer (P2P) 22 Summary Questions Malaga Notes 1) What is a node? 2) Name physical and wireless media used in networking 3) What transmission media is used for the telephone? 4) What are the main network topology? What are the differences between them? 5) Distinguish between Client-server and P2P networks 23 The Internet and eBusiness See Exam 3 Review (Part 2) PowerPoint notes in Final Review Section of course web site 24 Managing Security See Exam 3 Review (Part 2) PowerPoint notes in Final Review Section of course web site 25 Managing the Development and Purchase of IS See Exam 3 Review (Part 1) PowerPoint notes in Final Review Section of course web site 26