* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Price Elasticities of Demand (PED) Inferior Goods
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Pricing science wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
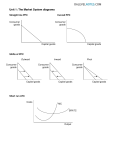
Price Elasticities of Demand (PED) Price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded changes in relation to a change in price. This is important for entrepreneurs as they want to know: - the impact a change in price would have on their revenue & ultimately profit. - how sucessfull puttng products on sale is likely to be. - whether they should absorb cost increases themselves or pass them onto the consumer through higher prices To calculate it: i-study.co.uk sample page PED= Price % change in quantity demanded % change in price Elastic demand P P1 Elastic demand This is when a change in price results in a larger % change in the quantity demanded. D Q Q1 If substitutes exist then a product is likely to have elastic demand (coca cola & pepsi). Luxury goods also tend to have elastic demand (since they are not essential). Quantity i-study.co.uk sample page Price Inelastic Demand This is when a change in price results in smaller % change in the quantity demanded of a product. P Low value goods such as sugar & salt are likely to be inelastic. P1 Goods that are necessary such as shampoo & soap tend to be inelastic since people have to purchase them. Inelastic demand Q Q1 D Quantity Price inelastic Price elastic * luxury good * very cheap * neccesity for food * no substitutes * lots of substitute goods * lots of competitors i-study.co.uk sample page Inferior Goods * These are products that people actually buy less of as they have more disposable income. * In this example, as comsumers have more money, they are likely to buy less cheap disposable razors and buy a more expensive, high quality version instead.