* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multi Stage Amplifiers
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Naim Audio amplification wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
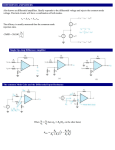
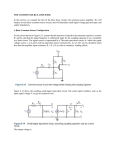
Chapter 3 : Multistage Amplifiers Q 1. What do you understand by multi-stage transistor amplifier? Mention its need. OR What are multi-stage amplifiers? Ans. A transistor circuit in which a number of amplifier stages are connected one after another is called as multistage transistor amplifier. When the output of one amplifier acts as an input to the next amplifier with suitable coupling device and so on then it is called as cascaded amplifier. The voltage gain of a multistage amplifier is equal to the product of the gains of the individual stages. If and A1 ar&thjrhaLt guins,stLpzi iaiagaini1inei then overall voltage gain is given by: Thus if we want to increase the voltage gain., current gain or power gain we need multistage transistor amplifiers. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 1 Q 2. A single stage amplifier has a gain of 60. The collector load and the input impedance is Calculate the over all gain when two such stages are cascaded through R-C coupling. Ans. When two such amplifiers are cascaded, the loading effect of input impedance of the second stage will reduce the gain of first amplifier but the gain of second stage will not be affected. Q 3. Define the unit decibel for expressing: J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 2 (i) voltage (ii) current and (iii) power. Ans. (i) Decibel for expressing voltage : It is 20 times the common logarithm of voltage gain (ii) Decibel for expressing current : It is 20 time.s the common logarithm of current gain (iii) Decibel for power: It is 10 times of the common logarithm of power gain Q 4. Explain in brief the function of a tank circuit in a tuned-voltage amplifier. Ans. Tuned voltage amplifier amplify a seleted frequency signal. In this tank circuit very high impedance at resonant frequency (i.e. XL = Xc) and very small impedance at er frequencies. The resonant frequency of tank circuit can be selected by adjusting the of variable capacitor connected in the circuit. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 3 Q 5. State what will happen to the voltage gain of an amplifier if the by passitor is open circuited. Ans. If the by pass capacitor is not put in the circuit, a.c. emitter current will flow through using an ac voltage drop across it. This voltage produce a feedback effect and there by tie output voltage. Thus for proper amplification, an emitter bypass capacitor is essential. Q 6. A multistage amplifier consists of two stages. The voltage gain of the s are 30 and 80. Calculate the overall voltage gain in dB. Ans. Voltage gain of one stage = 20 log10 30 and Voltage gain of seôond stage = 20 log10 80 Overall voltage gain is 201og10 30 + 20 tog10 80, Q 7. Which configuration of bipolar transistor is called as emitter follower r why for what purpose is it used? Ans. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 4 Common collector amplifier configuration is called as emitter follower 1 this circuit the output voltage developed across the emitter resistor just follows voltage . Hence the name emitter follower and it can be redrawn to form collector as terminal. Hence the circuit i.also called a common collector amplifier. The voltage gain of this circuit is one, but input impedance is very high impedance is very low. Therefore, this circuit is basically employed for imJeud1I(. IIIdL Q 8. What are the different types of configurations used in multistage am circuits? Ans. Different types of configurations used in multistage amplitude circuits are 1.Class-A 2.Class-B 3. Class-C 4.Class-D Q 9. What is the advantages of slagger tuner amplifier? J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 5 Ans. Stagger tuner amplifier have high selectivity, high gain and desirable band Q 10. Explain the statement : The cut-off frequencies of single stage amp are influenced by R-C combinations. . Ans. The cut-off frequecies of single stage amplifiers are influnced by R-C combinatic because : The first cut off frequency lies in low frequency range, in which the impedance by coupling capacitor Cc is comparable to the collector resistance Rc. Thus it largely the current amplification. The second cut-off frequency lies in the high frequency range where the area offered by coupling capacitor C is very small and it may be considered as a short circui Thus with increase in input frequency the magnitude of voltage gain, falls off. Q 11. State the factors to be considered while designing a biasing circuit t good transistor voltage amplifier Ans. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 6 (i) It should ensure proper zero signal collector current and VCE. (ii) It should ensure that .VCE does not fall ihe.required limits i.e. 1V for Si and 0.5 V. (iii) It should ensure the stabilisation of collector current against temperature variatic (iv) It should ensure to make the operating point independent of transistor parameters Q. 12. What are half-power frequencies? OR What is meant by frequency response of an ‘amplifier? What are halfpower frequencies? Ans. As the signal frequency varies the voltage gain of an amplifier also varies due to capacitive reactances of the circuit. The curve drawn between the signal frequency and voltage gain of an amplifier is called• as frequency response of an amplifier. The low frequency and high frequency at which the gain falls by 3 db are known as half‘r frequencies or 3-db points. It is termed as half power because the power output is 3db from its normal level. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 7 Q 13. Why is coupling capacitor provided in RC coupled amplifier also called locking capacitor? OR Explain the effect of coupling capacitor on low frequency response of BJT amplifiers. Ans. The first stage of RC coupled amplifies is coupled to the base of the second stage rough the coupling-capacitor Cc. The coupling capacitor C blocks thç dc voltage and aows the ac signal to reach the base of the second stage. Thus, the coupling capacitor Cc is also known as blocking capacitor. Q 14. Discuss briefly the choice of transistor configuration in a cascade amplifier ? Ans. In a cascade amplifier the most commonly used configuration is common emitter (CE) because the voltage gain of common emitter amplifier is greater than unity while common collector (CC) configuration has voltage cain less than unity as well as the voltage gain of common base (CB) is also less than unity. Q 15. What are the requirements for efficient coupling in a multistage J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 8 amplifier? Ans. The requirements for efficient coupling in a multistage amplifier is (i) There should be proper impedance matching. (ii) Distortion should be removedduring coupling. Q 16. Give applications for transformer coupled amplifier. Ans. (i) It provide impedance matching due to which maximum power can be transferred. (ii) It keeps the dc power small. Due to following reasons transformer coupled amplifier isused in public address systems to drive speakers and to drive other power devices. Q 17. What is the function of tank circuit in tuned voltage amplifier? Ans. The tank circuit is parallel combination of L and C. It is used to select a particular audio frequency for amplification. The selected frequency depends upon the resonance frequency of the tank circuit In this case the impedance Z, is high and thus current 1r is S J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 9 which reduces the power loss, Q 18. Draw and label the frequency response of an RC coupled amplifier? Ans. The frequency response of an RC coupled amplifier is as shown:- Q 19. What are the limitations of single tuned voltage aplifIers? Ans Limitations of single tuned voltaged amplifiers: (i) Single tuned voltage amplifier reauces the bandwidth to large extent to get higher 10 factor. (ii) This results in poor reproduction. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 10 Q 20. A tuned circuit has a resonant frequency of 1600 kHz and bandwidth.What is the value of Q factor ? Ans. Q 21. A transformer coupling is used in the final stage of a multistage amplifier. If the output impedance of transistor is and the speaker has a resistance of , find the turn ratio of the transformer so that maximUm power is transferred to the load. Ans. According to maximum power transfer theorem the source impedance should be equal to load impedance. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 11 Q 22. State and explain atleast one typical application of each type of coupling. Ans. (i) RC coupling transistor amplifier : AC coupled amplifiers provide excellent audio fidelity over a wide range of frequencies. Therefore, they are Widely used as voltage amplifiers. The function of voltage amplifier is to raise the voltage level of the input signal. As R-C coupling has smaller size, smaller weight, lower cost and occupy less space therefore, it is preferred to couple various stages of voltage amplifiers by this coupling method as shown fig. below, J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 12 (ii) Transformer Coupling: Because of poor frequency response at lower frequencies (i e audio frequency -ange 50 Hz to 20 KHz) These amplifiers are not used for amplification of audio frequencies However these are widely used for amplification of radio frequency signals By putting suitable shunting capacitors across each winding of transformer it get resonance at any desired frequency where the gain is maximum Such amplifiers are called tuned voltage amplifiers fig shows below is a tuned amplifier (iii) Direct coupled amplifiers: When extremely low frequency (< 10 Hz) signals (such as photo electric current in film projector, thermo couple currents for temperature measurements etc) are required to be amplified, direct J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 13 coupling is used Q 23. Derive the equation for the overall voltage gain of multistage amplifier in terms of the individual voltage gains? Ans. Let us consider the block diagram for multistage amplifier as shown: J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 14 Q 24. A multistage amplifier consists of three stages. The voltage gain of stages are 60, 100 and 160. Calculate the overall gain in db. Ans. Voltage gain in db for 1st stage 20 log10 60 = 20 X 1.778 = 35.56db Voltage gain in db for 2nd stage = 20 log10 100-= 20 x 2 = 40db Voltage gain in 1b for 3rd stage = 20 log10 160 = 20 x 2.04 44.08 db The overall voltage gain in db = 35.56+ 40 + 44.08 Av(overat() = 119.64 db. Q 25. What is stagger tuning? Explain in brief OR Write note on Stagger tuned amplifier? Ans. Stagger tuned amplifier: It has been observed that if two or more tuned circuits, which are synchronously tuned are cascaded, the overall bandwidth decreases. However, if the different tuned circuits are cascaded, are tuned to slightly different frequencies, it is possible to obtain an increased bandwidth with a flat pass-band with steep sides. This technique is known as stagger-tuning Following fig shows a two stage tuned voltage amplifier The stagger tunning in this circuit, may be achieved by resonating the tuned circuits L1 C1 and L2 C2 to slightly different frequencies. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 15 Q 29. Draw the circuit diagram of a tuned amplifier Discuss its operation How are current gain and voltage gain given in this cases Name various types of tuned amplifiers Ans. Tuned amplifiers are those amplifiers which amplify a selected frequency or a selected band of frequencies Circuit diagram of a single tuned amplifier is as J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 16 shown Operation: When high frequency signal is applied at the input terminals the resonant frequency of parallel tuned circuit select and amplifiers the resonant frequency by changing the value of C. Only a particular frequency is selected and others are rejected by the tuned J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 17 Q 30. Find gain in dB for voltage gain = 40. Ans. Voltage gain in dB = 20 log10 40 = 20 x 1.602 = 32.04 J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 18 Q 31. A multi stage amplifier consists of three stages as voltage gain in dB 33, 36,40 dB respectively. Then calculate the overall voltage gain in dB. Ans. Overall voltage, gain in dB = 33 + 36 + 40 = 109 dB. falls Q. 32. In an amplifier the maximum voltage gain is 2000 and occurs at 10 KHz. It to 1414 at 20 KHz and 30 Hz. Determine (i) lower cut off frequency (ii) upper cut-off frequency. Ans. The frequency response curve is shown in figure. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 19 Thus, lower cut off frequency = 30 Hz and upper cut off frequency = 20 KHz. Q 33. From 032 find bandwidth Ans. Bandwidth = 30 Hz to 20 KHz = (30 - 20) KHz = 10 KHz Q 34. Calculate voltage gain of single stage if it having and J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 20 Q 35. In two stage RC coupled amplifier and for each stage Find (i) voltage gain of second stage (ii) Overall voltage gain. Ans. (i) As no load is for, second stage Voltage gain of second stage J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 21 Q 36. Two stage amplifier stages coupled by coupling transformer. f output impedance of first stage is and input impedance of second stage is .Calculate the inductance of primary and secondary of transformer for perfect matching at frequency = J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 22 Q 38. Draw cascode connection as tuned amplifier. Ans. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 23 Q 39. Explain the features of class B push-pull operation Ans 1. Greater power output 2. Higher power efficiency 3. No power loss at zero signal 4. With signal the DC current increases Q 40. Use of cascading amplifiers. Ans. Cascading amplifiers means the output of one amplifier acts as an input to the similar stage and so on. The use of cascading amplifiers is to increase the strength of the signal by a large value. If input to an amplifier is 5V and it gives output 5 times, then the output of cascading amplifiers having two stages is given by Thus, larger outputs are obtaining if number of amplifier stages increases. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 24 Q 41. Differentiate between tuned and untuned amplifiers. Ans. The main difference between tuned and untuned amplifiers is that the, tuned amplifiers are designed for specific, usually narrow bandwidth but untuned are not designed by such specifications. Q 42. Why R-C coupling is the most widely used coupling between the two stages cascaded amplifier? Ans. R-C coupling gives excellent frequency response i.e. a constant gain over the audio-frequency range. Thus, are useful for speech and music. Also R-C coupling is cheaper in cost because of low cost of resistors and capacitors used in the circuit. By using R-C coupling with circuit becomes very compact because of its components are very light and small. Q 43. Compare the characteristics of single, double and stagger tuned amplifiers. Give typical circuits and list their important applications. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 25 Ans. 1. Single tuned voltage amplifier: 2. Double tuned voltage amplifier: 3. Stagger tuned voltage amplifier J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 26 Application of tuned voltage amplifiers 1. Tuned voitage amplifiers are used in the wireless communication systems. 2. These are used in communication transmitters to transmit the signals. 3 These are used in communication receivers to: receive the desired signals. Q 44. Write shrt note on: Single turned amplifier. Ans. Single tuned amplifier is consists of ransistor amplifier with a parallel tuned circuit as the collector load. The values of capacitance and inductance- ot the tuned circuit are so selected that the frequency to be amplified is equal to its resonant frequency. It is as shown in fig. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 27 The output of the single tuned amplifier can be obtained by using either a coupling capacitor C or by using a secondary coil at the output stage. J Srinivasa Rao-Multi Stage Transistor Amplifiers Page 28