* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Macroeconomic Environment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
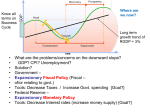
Macroeconomic Fundamentals ECO 473 - Money & Banking - Dr. D. Foster The Circular Flow of Income and Product The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) • Defined as: The total value of all final goods and services produced during a given period. Evaluated at market prices … sort of. Serves as a measure of an economy’s total output and of the total income generated (to individuals). Limitations of GDP • Excludes nonmarket production. • Measurement problems. • Welfare interpretations. • Country differences are difficult. Components of GDP • Consumption spending: Total household purchases of goods and services. • Investment spending: Purchases of new capital goods (fixed I), and Changes in business inventories. • Government spending: State/Local/Federal government expenditures. • Net export spending: Exports - Imports. Inflation Defined A continuous rise in the general price level. • • • • Not a rise in some prices. Not a one-time rise in prices. A rise in the “general price level.” Which is…? Measured by a price index; e.g. the CPI. Real versus Nominal values • Nominal GDP (aka “current dollar”) versus Real GDP (aka “constant dollar”). Problems Interpreting Inflation • Compared to the CPI . . . you don’t buy the same things you don’t buy the same proportions you make tradeoffs between goods • Lots of items are excluded from measurement: Used goods, land, stocks … The Costs of Inflation • If unexpected – effects on borrowers & lenders. • If expected – inconvenience, repricing & Fed actions. Unemployment • Measured rate depends on: the population, the civilian population, the civilian population over 16 yrs. old (&…), the labor force, and whether one is looking for work. Unemployment and the Business Cycle • Unemployment rate: The % of the civilian labor force that is unemployed. • Frictional unemployment: Workers are “between” jobs at any given time. • Structural unemployment: Workers’ abilities/skills don’t match employers needs. • Cyclical unemployment: The unemployment resulting from business-cycles. • Natural rate of unemployment (U*): The frictional and structural components. Aka, the “full employment” level of unemployment. Cycles in Economic Activity • Business cycles: • • • • Real GDP varies around its long-run growth path. Recession: The decline in real GDP. lasting at least two consecutive quarters. Trough: Low point in real GDP. Expansion: The growth phase. Peak: High point of real GDP. Business Cycles - Theories • External shocks. • Population pressures. [Malthus vs. Simon] • Schumpeter – innovation. • Marx – underconsumption. • “Classical school” – erratic anomalies. • Keynesian – W&P rigidity leads to overproduction. • Austrian School - Induced by policy/credit. Macroeconomic Fundamentals ECO 473 - Money & Banking - Dr. D. Foster