* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multiplexer - dhimas ruswanto
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
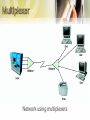
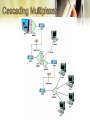
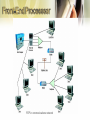
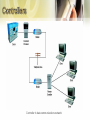
• • • • • • • Multiplexer Multiplexing FDM TDM WDM Front-End Processor Controllers • A device that combines data from several devices into a single stream • Multiplexers are used in pairs (multiplexer and demultiplexer) • Increases efficiency, reduces cost • Idle time is reduced Network using multiplexers • Used in WANS, LANs, wireless networks – In WANs, used on point-to-point, multipoint lines – Connection multiplexer in LANs – Multiple radio signals combined on wireless networks Corporate Network using multiplexers • Connect communications lines to another multiplexer • Using several levels of multiplexers at several sites • Reduces costs • Many types of multiplexing techniques employed: – Frequency Division Multiplexing – Time Division Multiplexing • Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing • Statistical Time Division Multiplexing – Wave Division Multiplexing • FDM is used with analog signals. • Used in television and radio transmission. • Bandwidth divided into narrow bandwidths • How it works? – A multiplexer accepts analog signals from multiple sources, each of which has a specified bandwidth. – Guard bands (unused parts of the frequency range It acts as a buffer between adjacent channels to avoid one channel’s data from crossing over into another channel) used to separate the signals. – The signals then are combined in to another, more complex signal with a much larger bandwidth. – The resulting signal is transmitted over some medium to its destination, where demultiplexer extracts and separates the individual components Frequency Division Multiplexing • • • • TDM is used with digital signals. Many input signals are combined and transmitted together. The technique interleaves more than one individual digital signal into another channel by giving each original signal time a slot in the multiplexed channel. TDM has split into two separate technologies; - synchronous time division multiplexing - statistical time division multiplexing • • • • • Each incoming source gets a turn to transmit, proceeding through the sources in roundrobin fashion The demultiplexor on the receiver end of the high speed link must disassemble the incoming bit stream and deliver each bit (or byte) to the appropriate destination A precise order must be maintained so that the demultiplexor can disassemble and deliver the bits to the respective owners Must maintaining synchronization between the receiver and transmitter Must transmit empty slot and cannot take advantage of the empty slot. • Transmit data only from active users i.e. no empty time slots • Multiplexer scan the buffers and create a variable-size frame depending on how many buffers contain data. • Frame is created that contains data and address of data to identify who sent the data and for whom it is intended • Examples - data entry systems, point of sale systems • Advantage : – – Does not need a line as high speed as synchronous time division multiplexing for transferring the same amount of data Good for connecting a number of lower speed devices that do not transmit data on a continuous basis to a remote computer system • Disadvantage: – increased level of complexity. • Used for analog and digital transmission over fiber optic cables • Optical signals from light sources consists of different wavelengths • The simultaneous transmission of these light sources over a single fiber-optic channel • Light sources of different wavelengths are combined by a WDM multiplexor before transmission • A WDM demultiplexor separates them and Beneficial from cost and performance – it increases bandwidth without requiring the installation of additional fiber, (cost) – WDM consolidates data from separate channels onto a single line (performance) Multiplexing Technique Advantages Disadvantages Frequency Division Multiplexing -Simple -Popular with Radio, TV, cable TV, local telephone exchange -Analog signals only -Limited by frequency ranges Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing -Digital Signals -Wastes bandwidth -Relatively simple -Commonly used with T1 and ISDN Statistical Time Divison Multiplexing -More efficient use of bandwidth -Packets can be various sizes -Frame can contain control and error information -More complex than synchronous time division multiplexing Wavelength Divison Multiplexing -Very high capacities over fiber -Scalable -Signals can have varying speeds -Cost -Complexity • FEP is a small-sized computer which interfaces to the host computer a number of networks, such as peripheral devices (terminals, disk units, printers and tape units) • Data is transferred between the host computer and the FEP using a high-speed parallel interface. • The FEP communicates with peripheral devices using slower serial interfaces. • The purpose is to off-load from the host computer the work of managing the peripheral devices, transmitting and receiving messages, packet assembly and disassembly, error detection and error correction FEP in communications network • Scaled-down version of an FEP – Handles up to 64 devices – Cluster controller • Specifically used with IBM servers – Remote controller • Located a distance from the server – Local controller • Located near the server Controller in data communications network