* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 32-honors
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Systolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
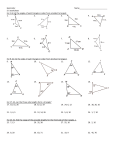
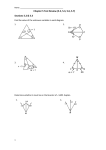
LESSON PLAN Kiea Brown Geometry (5.6/5.7) Objective: SWBAT use and apply inequalities involving angles and sides of triangles. Application of SAS inequality and SSS inequality to form conclusions about two triangles. (day 32-HONORS) Warm-Up: SOL and review questions/attendance/check hw Presentation: “Triangle Inequalities”……….Storytime Theorem: The ⊥ segment from a point to a line is the shortest segment. Draw a picture. Activity: Protractor, Ruler, Notebook paper (Work together in pairs) 1. Draw a scalene triangle on a sheet of paper or on the dry erase board. Label the triangle as ∆𝐶𝐴𝑇. 2. Each side of the triangle is measure in _________(what units) and each angle in ___________(what units). Now name each side of the triangle: __________, __________, _________ Now name each angle of the triangle: _________, __________, _________ 3. Draw a square around the measure of the longest side. Draw a square around the angle that lies opposite the longest side. Make a conjecture about the measures of the angles based upon the measure of the opposite sides. 4. Raise your hand when you have finished for your classgrade Theorem- In a , if two angles are not congruent then larger side is opposite the larger angle. (The converse is also true) In a , if two sides are not congruent then the larger angle is opposite the longer side. (The converse is also true) Ex: Name in descending order. 1. 2. A A 3. A 50𝑜 𝑜 30 19 17 60𝑜 B C B B C 20 C Theorem- in a , the lengths of any two sides must be larger than the third side to form a triangle. Example-Can the 4. 7, 7 , 9 be formed? 5. 6, 4, 2 Between what two values must the third side lie? 8. 8 and 9 9. 6 and 15 6. 11, 5, 8 7. 4, 10, 6 10. 12 and 7 11. 2.3 and 9.2 SAS inequality- if 2 sides of one be greatest. 11. are D 12. A 7 to 2 sides of another and the included angles are not 30𝑜 10 15 𝑜 80 80𝑜 B 11 E 12 14. the side opposite the largest < will N P 50𝑜 53𝑜 12 50𝑜 F Q M G C J 13. L R K X 10 27𝑜 15 Z Y 85𝑜 7 SSS inequality- if 2 sides of one the larger side is larger. to 2 sides of another, but the third side of one A 15. C 11 G E 10 12 N SAS inequality draw conclusions about sides Class Exercises: use power point examples Homework: worksheet rd 4 Y 11 15 I SSS inequality side the angle opposite R 15 2 1 H 7 F 18 10 4 7 M is greater than the 3 17. 3 L B 15 D 16. 12 10 H 11 I draw conclusions about angles I 3 K 12 SAS and SSS Inequality Practice Problems (CW day____) 1-7. Highlight those that form a triangle. If a triangle can be formed, list the angles in descending order. (Diagrams not drawn to scale) E 13 D P T 12 14 F 13.5 W 17 3 S U 14 10.5 R ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶: ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 = 𝑥, ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐶 = 𝑥 + 2, ̅̅̅̅ 𝐵𝐶 = 𝑥 + 3 4 Q V 6.5 ∆𝑇𝑂𝑃: ̅̅̅̅ 𝑇𝑂 = 4 ̅̅̅̅ 𝑃𝑂 = 12, ̅̅̅̅ 𝑃𝑇 = 10 X ∆𝑆𝑈𝑁 ℎ𝑎𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟 86. ̅̅̅̅ 𝑆𝑈 = 2𝑥 + 8, ̅̅̅̅ 𝑈𝑁 = 4𝑥, ̅̅̅̅ 𝑆𝑁 = 3𝑥 + 6 8-16. Highlight those that form a triangle. If a triangle can be formed, list the sides in ascending order. (Diagrams not drawn to scale) E B 65𝑜 H 𝑜 36 I K K 75𝑜 75.5𝑜 70𝑜 A C F D D J I L ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶: ∡𝐵 = 92𝑜 , ∡𝐴 = 41𝑜 10𝑜 M M L H J ∆𝑆𝑅𝑇: ∡𝑆 = 75𝑜 , 𝑒𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑟 ∡𝑆𝑅𝑀 = 107𝑜 120𝑜 E F 17. List the sides of ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 in descending order, given: 𝑚∠𝐴 = (8𝑥 − 3)𝑜 , 𝑚∠𝐵 = (3𝑥 − 8)𝑜 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑚∠𝐶 = (74 − 2𝑥)𝑜 18. Given ∆𝐶𝐴𝑇 with ̅̅̅̅ 𝐶𝐴 = 25 𝑐𝑚, ̅̅̅̅ 𝑇𝐴 = 23 𝑐𝑚 𝑎𝑛𝑑 ̅̅̅̅ 𝐶𝑇 = 24 𝑐𝑚. Highlight the true statement(s). ̅̅̅̅ ̅̅̅̅ ∠𝐴 < ∠𝑇 < ∠𝐶 ∠𝐶 < ∠𝐴 < ∠𝑇 𝐶𝐴 > ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝑇 > ̅̅̅̅ 𝐶𝑇 𝐴𝑇 < ̅̅̅̅ 𝐶𝑇 > ̅̅̅̅ 𝐶𝐴 ̅̅̅̅ ̅̅̅̅ ̅̅̅̅ ∠𝐴 < ∠𝐶 < ∠𝑇 ∠𝑇 > ∠𝐶 > ∠𝐴 𝑇𝐴 < 𝐶𝑇 < 𝐶𝐴 ∆𝐶𝐴𝑇 𝑖𝑠 𝑎𝑛 𝑎𝑐𝑢𝑡𝑒 𝑡𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 19-25. Determine which side measures will form a triangle. Underline those that form a right triangle. Highlight those that form a obtuse triangle. Put a rectangle around those that form an acute triangle. 2, 3 and 4 9, 10 and 20 14, 17 and 31 3, 4 and 5 15, 17 and 19 (3, 5), (4, 7) and (7, 6) (1, -5), (-3, 0) and (-1, 0) 26-27. For each of the problems below, highlight the possible values for the third side of the triangle(s).. side lengths 5 and 9: 4, 7.8, 10, 12.9 side lengths 7 and 14: 5, 11, 15, 18, 22 28-29. For each of the problems below, highlight the values that will not form triangle(s). side lengths 1 and 1: 0.5, 1.9, 2, 8 side lengths 18 and 22: 2, 4, 17, 25, 39, 40, 45 30. Find the two longest sides of ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 𝑤𝑖𝑡ℎ 𝑚∡𝐶 = 67𝑜 and 𝑒𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝑚∡𝐵𝐴𝐺 = 108𝑜 31. Find the two shortest sides of ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 𝑤𝑖𝑡ℎ 𝑚∡𝐵 = 67𝑜 and 𝑒𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝑚∡𝐵𝐶𝐾 = 114𝑜 32-34. Name the shortest length. 36-38. What can be concluded for each of the three pairs? 35. Using the diagram, which must be true? 𝐴𝑆 < 𝑌𝑈 𝑆𝐾 > 𝑌𝑈 𝑆𝐾 < 𝑌𝑈 𝐴𝐾 = 𝑂𝑈 Honors Geometry: Triangle Inequalities HW (day _____) Name _____________ Block _____