* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fertilization and Development in Humans
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
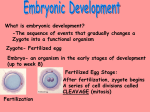
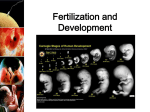
Fertilization and Development in Humans Fertilization • • • • Fertilization the ______________ Fusion (joining) of the sperm and egg ______________ nuclei Oviducts or fallopian tubes ______________ in the ____________________________ Fertilization and ______________ development is In humans, ______________ Internal female ______________ in the body of the ______________. At the moment of fertilization, the egg develops a Protective membrane ____________________________ around itself to prevent other sperm ______________ from penetrating. zygote A fertilized egg is called a ______________ Name: egg ______________ + sperm ______________ = zygote ______________ 23 23 46 Chromosome ______________ ______________ ______________ Number FERTILIZATION RESTORES THE SPECIES NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES As the Egg Travels Fraternal Twins 2 • Fertilization of _____ 2 sperm eggs by ___ • Female releases more than one __________ egg during ovulation Identical Twins • Fertilized zygote splits into 2 __________ identical embryos One egg was • Only __________ fertilized by One sperm _______________ Advantages / Disadvantages of Internal Fertilization Advantages 1. Avoid hazards of the environment _______________ 2. Eggs are well protected _______________ Disadvantages 1. Sperm can only fertilize an egg for a short _______________ period of time 2. Sperm live a short _______________ time because they store little _______________ food. Animal Development (A) (B) 2 cell embryo egg zygote 4) __________ sperm 1) __________ 2) __________ 3) __________ Mesoderm 11)__________ (C) endoderm ectoderm 10)__________ 9) __________ cell embryo 5) __________ 4 cell embryo blastula gastrula 8) __________ 7) __________ 6) 8__________ Fertilization A. _____________________________________ Cleavage by mitosis B. _____________________________________ Gastrulation and differentiation C. _____________________________________ Cleavage cleavage - after fertilization, the __________ zygote divides • __________ mitosis to produce __________ two by __________ cells growth • Cell division continues without __________ embryo • Once cleavage begins, the zygote is called an __________ blastula - hollow ball formed by the embryo • __________ • implantation __________ - when the embryo attaches to the Uterine lining ____________________ Gastrulation • • • different from one another differentiation - embryo cells become __________ _______________ • • job or function PROTEINS A CELL MAKES, DETERMINE ITS _______________ THE _____________ tissues and __________ organs of the new organism They form __________ GENES TURN ON OR OFF IN CERTAIN CELLS TO DIFFERENT __________ PRODUCE DIFFERENT PROTEINS __________ Three embryonic germ layers of the embryo • • • ectoderm - develops into __________ skin Nervous system __________ and ____________________ endoderm - develops into __________ digestive andrespiratory __________ __________ systems mesoderm all __________ - develops into __________ other systems like the reproductive __________ and circulatory __________ systems ectoderm mesoderm endoderm Growth in the Uterus • • • surrounds the embryo amnion - __________ __________ protects the embryo, holds in a and__________ Amniotic fluid fluid called ____________________ placenta - organ responsible for the __________ diffusion of passage by __________, __________, oxygen from the nutrients and __________ __________ blood to the fetus. mother’s __________ wastes from the fetus __________ diffuse to __________ the mother’s blood through the placenta The mother’s and fetus’ __________. Never mix blood ____________________ Umbilical chord ____________________ - attaches the embryo to the __________. placenta Contains __________ Blood vessels ____________________ that connect the circulatory system to the embryo’s __________ capillaries of the placenta __________ Reproductive Technology Reproductive technology has greatly changed the way we can deal with reproduction of humans as well as other plants problems involving _______________ and organisms. • Agriculture scientists have produced plants resistant to __________, insects Weed killers or even __________ _______________, frost • • cloned to produce more resistant crops Resistant plants can be __________ • • Hormone therapy - enables infertile women to become pregnant ____________________ • Fertilized eggs are implanted into the woman’s uterus, The ____________________ and a _______________pregnancy may result. successful • ultrasound and ____________________ Miniature cameras allow doctors to view _______________ ovaries __________, oviducts and other reproductive structures __________, Artificial insemination - used to reproduce farm animals that _________________________ exhibit genetic advantages Invitro fertilization - eggs are extracted from an infertile woman ____________________ and __________ fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish. Invitro Fertilization Amniocentesis amniocentesis - procedure to extract fluid from • _______________ around the developing fetus amniotic fluid • Doctors analyze the cells in the __________ Chromosomal abnormalities and • _________________________ Biochemical deficiencies can be detected that may ____________________ threaten the health of the developing fetus • • • • • • • • Dangers that face a Fetus placenta prevents most infections that make the The __________ mother ill from passing to the fetus radiation - passes through the tissues of the mother and __________ may affect the fetus X-rays - damages the dividing __________ cells __________ of the fetus Infectious microorganisms - found within the mother can _________________________ enter the fetus Cigarette smoking by the mother affects development in ____________________ the fetus and may produce underweight babies toxins or __________ chemicals are also harmful to the Exposure to __________ fetus alcohol during heroine __________, cocaine LSD, and __________ Use of __________, pregnancy can cause serious results addiction Mental retardation can result ____________________ and ____________________ drugs and __________ alcohol passing from the mother’s from __________ blood to the fetus Fertilization & Development in Other Organisms Fish and Amphibians • Fertilization is __________ external large • Females lay __________ numbers of eggs in the water • This ensures the __________ survival of the species deposit sperm over the eggs in the water • Males will __________ to fertilize them Advantages Disadvantages 1. Moist surroundings 1. Egg and sperm may not __________ meet 2. Eggs may be __________ eaten 3. Changes in environment may _________________ destroy the eggs and sperm water (__________, temperature and ________________, Oxygen concentration _________________________ Fertilization & Development in Other Organisms Birds and Reptiles internal within • In birds and reptiles, fertilization is __________, the female’s reproductive tract reptiles produce a __________ leathery shell around the egg • __________ development is external – outside the female’s body and ____________ birds hard • __________ produce a __________ shell around the egg development is external – outside the female’s body and ____________ Fertilization & Development in Other Organisms Non-placental Mammals – Egg Laying Mammals internal fertilization Egg laying mammals - have __________ • ____________________ Soft shell • Lay ____________________ eggs hatched the young are nourished by the • When __________, Mammory glands mother’s ____________________ • Examples of egg laying mammals are: Duck billed platypus • ____________________ Spiny anteater • ____________________ Fertilization & Development in Other Organisms Non-placental Mammals – Marsupials • • • • marsupials internal fertilization ____________________ - have __________ • pouch the __________ embryo will receive nourishment from Once in the __________, Mammary glands the mother’s ____________________ • inside the female Fertilized egg ____________________ - begin development __________ yolk of the egg is used for __________ food The __________ embryo leaves the mother’s body and crawls across the A tiny __________ pouch mother’s fur into a __________ Examples of marsupials are: • kangaroo koalas ____________________, ____________________, wombats possums ____________________, and ____________________,