* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Deficits and Debt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
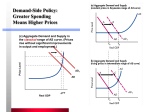
THE ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF PUBLIC SECTOR BORROWING McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Deficits and Debt • The core critique of fiscal stimulus focuses on the budget consequences of government pumppriming – How do deficits arise? – What harm, if any, do deficits cause? – Who will pay off the accumulated national debt? 12-2 Budget Effects of Fiscal Policy • Keynesian theory highlights the potential of fiscal policy to solve macro problems – Fiscal policy: The use of government taxes and spending to alter macroeconomic outcomes • Use of the budget to stabilize the economy implies that federal expenditures and receipts won’t always be equal 12-3 Budget Surpluses and Deficits • Deficit spending: The use of borrowed funds to finance government expenditures that exceed tax revenues • Budget deficit: Amount by which government spending exceeds government revenue in a given time period Budget government tax – 0 deficit spending revenues 12-4 Budget Surpluses and Deficits • If the government spends less than its tax revenues, a budget surplus is created • Budget surplus: An excess of government revenues over government expenditures in a given time period 12-5 Keynesian View • Budget deficits and surpluses are a routine feature of counter-cyclical fiscal policy • The goal of macro policy is not to balance the budget but to balance the economy at fullemployment 12-6 Economic Effects of Deficits • Crowding out: A reduction in private-sector borrowing (and spending) caused by increased government borrowing • Crowding out reminds us that there is an opportunity cost to government spending • Government borrowing to finance deficits puts upward pressure on interest rates 12-7 Public-sector output Crowding Out g2 g1 b Increase in government spending . . . a c Crowds out private spending h2 h1 Private-sector output 12-8 Economic Effects of Surpluses • Four potential uses for a budget surplus: – – – – Spend it on goods and services Cut taxes Increase income transfers Pay off old debt (“save it”) • The economic effects are the mirror image of those for deficits 12-9 Crowding In • Crowding in: An increase in private-sector borrowing (and spending) caused by decreased government borrowing • When the government reduces borrowing, it takes pressure off market interest rates • As interest rates drop, consumers will be more willing and able to purchase big-ticket items 12-10 Crowding Out Hypothesis • Real Source (direct) crowding out • Financial (indirect) crowding out – Disincentive-to work – Disincentive-to-invest • Higher interest rates • Inflation 12-11