* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download basic-facts-on
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
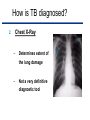
TB 101 “Basic Facts on Tuberculosis” What we should know… The TB Scenario Defining TB: Cause, Transmission, and Manifestations Risk of TB infection Diagnosing Pulmonary Tuberculosis TB Treatment and Cure Preventing transmission Proper Management of TB cases TB Burden in the World 1/3 of the World Population is Infected 1 Person is Infected per Second 1.9 Million People Die of TB each Year Philippines is 1 of the world’s 22 high-burden countries for Tuberculosis TB Burden in the Philippines 22 million reported infections TB kills 75 Filipinos per day TB is the 6th leading cause of Mortality and Morbidity Undiagnosed TB cases remain high in local communities What is Tuberculosis? TUBERCULOSIS is an infectious disease caused by a micro bacteria called “Tubercle bacilli”. It is airborne. It usually affects the lungs but may also affect other organs in the body like the meninges, bones, kidneys etc. The Tubercle Bacilli Characteristics: • slow growing • can survive inside cells of the human body Other Names: Mycobacterium tuberculosis TB germ • exposure to direct sunlight can kill the bacteria in sputum How is it transmitted? The TB Bacilli spreads through airborne inhalation of droplets of infection coming from a TB patient whenever a person coughs or sneezes, without covering his mouth. How does PTB develop? 1. TB bacilli enters the body and lodges in the lungs (TB Infection). 2. In the lungs, they multiply and slowly eat the cells and the body begins to experience A person is infected after inhaling droplets from a symptoms (TB Disease) person with TB 3. If undiagnosed, lungs cells are eaten up leading that may lead death. What are the signs and symptoms of TB? Persistent cough for at least 2 weeks Chest pains/ Back Pains (breathlessness) Persistent low grade fever for more than a month Significant weight loss with or with out loss of appetite Hemoptysis (Blood-tinged sputum) Feeling of weakness (tiredness) Night Sweats Who are at risk of getting TB? People who share the same breathing space with someone who has infectious TB Health workers, specially those working in longterm facilities (prison, sanitariums, etc.) People whose immune systems are compromised (People with HIV infection, Pneumonia, Chronic lung disease, etc) Who are at risk… People exposed to silica and those with jobs that compromise the respiratory system (mine workers) People underweight and malnourished (esp. Children) Alcoholics and IV drug users Others How is TB diagnosed? 1. Sputum Microscopy – It shows the TB bacilli in the sputum – It is the most definitive diagnostic tool of Tuberculosis How is TB diagnosed? 2. Chest X-Ray – Determines extent of the lung damage – Not a very definitive diagnostic tool How is TB cured? TB can be cured. DOTS (Directly-Observed Treatment Short Course) is the recommended strategy to cure TB. It ensures the right combination and dosage of anti-TB drugs. It ensures regular and complete intake of antiTB drugs. Patient takes drugs every day with the help of a treatment partner. With proper treatment… We want to treat patients with DOTS: 1. To make them get well as soon as possible 2. To make them stop spreading the disease onto others in the community 3. To avoid complications and multi-drug resistance (MDR) How can TB be prevented? 1. BCG vaccination for infants (newborn to 1 year old). This gives 80-85% protection against development of complicated TB among children; 2. Hygienic practices like covering the mouth when coughing and sneezing; and 3. Early diagnosis and treatment of TB infectious cases to stop transmission Other Preventive Measures… Maintain open air circulation inside the house Have enough sleep Eat nutritious food that boost the immune system Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol, and use of prohibited drugs What are some misconception about TB? Misconceptions Facts TB is mana-mana TB is hawa-hawa TB results from “Pasma” and “naulanan” TB is due a bacteria known as the “Tubercle bacilli” TB is transmitted through sharing utensils with a person with TB TB is transmitted through inhalation of the droplet nuclei from a person with TB TB is not curable. One should be ashamed of his disease. TB can be cured. The patient’s commitment is important. Everyone’s support is important in fighting TB. REMINDER If you experience the signs and symptoms of TB, do not be ashamed. Immediately visit our clinic for proper diagnosis and treatment