* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Low Pass Filter
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Multidimensional empirical mode decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Sound level meter wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
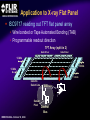
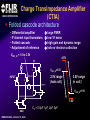
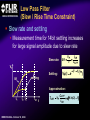
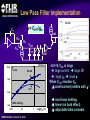
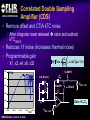
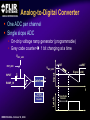
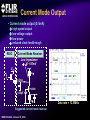
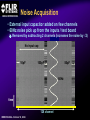
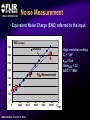
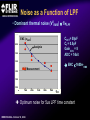
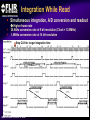
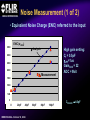
A High Performance, Low Noise, 128Channel Readout Integrated Circuit for Instrumentation and X-Ray Applications E.Beuville, M.Belding, A.Costello, R.Hansen, S.Petronio Operation Indigo Systems Background INDIGO OPERATIONS (Merged with FLIR, January 2004) Infra-Red Systems Manufacturer Imaging and Thermography Surveillance, Firefighting, Industrial, Military… • IR sensor fabrication facility (GaAs, InSb, mBolo) • Readout Integrated Circuit (ROIC) Core Capability • Large 2D ROIC pixel arrays (1k x 1k at 15um pixel size) • Custom IC (mixed signal) IR applications X-ray and mammography applications Implantable devices Space applications Instrumentation IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 INDIGO OPERATIONS ISC9717 ROIC Description Design 128 Channels, Low-Noise ROIC for Flat Panel Array and Instrumentation • • • • • 80um channel pitch Low noise charge amplifier (programmable gain) Low Pass Filter (programmable time constant) Correlated Double Sampling (programmable gain) On-Chip ADC (programmable 9 to 14 bits gray-code output) Charge Integrator Gain Gain Low Pass Filter Time TimeConstant Constant 2 Integrator IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 LPF C.D.S. Amplifier Track-and-Hold 9-14 Bit ADC Gain Gain Resolution Resolution 4 CDS 4 T/H ADC 9 to 14bit 9 to 14bit INDIGO OPERATIONS Applications and Detectors Compatibility Wide Range of Applications Wide Range of Detectors Digital X-ray Medical Imaging Flat Panel X-ray Sensors (TFT) - Radiography - Fluoroscopy - Mammography - Angiography - Tomography Instrumentation - Airport screening - Non-Destructive Testing - CT scan, PET imaging - Astrophysics applications - Nuclear Science - Industrial Instrumentation IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 - Cesium Iodide (CsI) or other scintillators - Selenium (Se) - Amorphous Silicon - Photodiode Solid-State Detectors - Silicon Detectors (Si) - Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CdZnTe) - Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) - Germanium (Ge) - Photodiode INDIGO OPERATIONS Application to X-ray Flat Panel ISC9717 reading out TFT flat panel array • Wire bonded or Tape Automated Bonding (TAB) • Programmable readout direction TFT Array (split in 2) Gate Driver Gate Driver 14 bits 14 bits 14 bits 14 bits Column Select Line DATA Line + Sensor Pixel IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 Detector Bias INDIGO OPERATIONS ISC9717 Serial Command Register Gain Control (Integrator and CDS) • Full dynamic range from 48fC (3x105 e-/hole) to 12pC (75x106 e-/hole) Integration While Read mode • Higher readout rate Integration Then Read mode • Lower noise Integration time control • Integration time adjusted by controlling the clock (24us to few ms) Readout direction (left or right) • Allows the readout IC to be connected on both sides of 2D sensors Averaging mode (two adjacent channels averaged) • Improved signal-to-noise ratio • Higher readout rates ADC resolution (9 to 14 bit) • Higher readout rate for lower ADC resolution • Current mode output (reduced clock feedthrough) IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 Charge TransImpedance Amplifier (CTIA) Folded cascode architecture INDIGO OPERATIONS • Differential amplifier • P channel input transistors • Folded cascode • Adjustment of reference large PSRR low 1/f noise high gain and dynamic range hole or electron collection VREF_IN = 1.5 to 3.5V 4.5V 5V 6 5 VREF_IN INPUT 2.5V range (hole coll.) 2 1 VREF_IN=3.5V 3.0V range (e- coll.) VREF_IN=1.5V 3 4 1.0V GND IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 CF = 0.5pF, 1pF, 2pF, 4pF INDIGO OPERATIONS Low Pass Filter (LPF) Simple first order low pass filter Limit the bandwidth (f-3dB from 32 to 200kHz) • Noise attenuation RC filter implementation • RC=1us with Resistor (1Meg) and Capacitor (1pF) • Resistor can be too large to implement (HiRes poly=1k/SQ) Using transistor’s transconductance gm • Time constant = CLPF/gm Programmable time constant • 0.8us, 1.3us, 2.8us, 3.3us • 1us, 2us, 4us, 5us with external voltage adjustment IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 INDIGO OPERATIONS Low Pass Filter (Slew / Rise Time Constraint) Slew rate and settling • Measurement time for 14bit settling increases for large signal amplitude due to slew rate Slew rate: SR I VP SR t CLPF VP settling SR Settling: VP (1 e (t t1 ) Approximation: t1 t2 t3 IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 TM t TSET VP CLPF N.ln(2) 1 ISR ) INDIGO OPERATIONS Low Pass Filter Implementation RC+SR = CLPF/gm Cf out VIN gm VGS 1.0E-05 10us LPF VLPF CLPF RST SPICE sim. Tsettle RC+SR 8.0E-06 8us LPF • At t=0, VGS is large large current large SR large gm small When VLPF reaches VIN small current (settles with ) 6us 6.0E-06 10bit settling 4us 4.0E-06 0.01 0.01 0.1 0.1 IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 11 10 Log(VIN) 10 non-linear settling linear (no bulk effect) adjustable time constant INDIGO OPERATIONS Correlated Double Sampling Amplifier (CDS) Remove offset and CTIA kTC noise • After integrator reset released store and subtract kTCINTEG Reduces 1/f noise (increases thermal noise) Programmable gain 2 C 2 H (f ) CDS 1 4 Sin 2 ( f TS ) C2 • X1, x2, x4, x8, x32 1.E+01 CLAMP2 V2/Hz C2 CDS_BIT[0-3] 1.E+00 CLAMP1 1.E-01 TRACK VREF_CDS 1.E-02 1.E-03 1.E-04 1.E+02 C1 1.E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 1.E+06 f(Hz) + VREF_CDS Gain =C1/C2 INDIGO OPERATIONS Analog-to-Digital Converter One ADC per channel Single slope ADC • On-chip voltage ramp generator (programmable) • Grey code counter 1 bit changing at a time VREF_ADC RST RST_ADC VREF_ADC Cc RAMP_IN Latches 14 Signal (held) Input INPUT RST 14 IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 Latch 9-14bit Gray Code Counter t Gray Code Counter INDIGO OPERATIONS ADC Ramp Generator • Charge pump architecture • Programmable ramp for 9 to 14 bit conversion Clock = 40ns (twice Master clock) VPOS VLSB = VADJ_RAMP C2 RST_ADC RAMP_OUT C1 C2+CL CL 40ns VADJ_RAMP C1 f f f Non-overlapping clock f GND IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 VLSB C1 • Slope controlled by VADJ_RAMP and the C1/(C2+CL) ratio Adjustment of the LSB level from 9bit to 14bit Current Mode Output INDIGO OPERATIONS • Current mode output (0.5mA) high speed output low voltage output low power reduced clock feedthrough ROIC Current Mode Receiver Low Impedance DV < 50mV VPD CLOCK SYNC 10k BIT9 . BIT8 BIT7 Data Out 0.5mA PN3640 CL<30pF 1V 700 Suggested current mode receiver IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 Data rate = 12.5MHz ISC9717 Noise Analysis and Measurements All noise sources taken into account INDIGO OPERATIONS RST CF 1 (2 f CLPF gm )2 VkTCf VkTCcds CC2 Detector Noise SELECT 1 2 H (f ) LPF vLine v1/f CLAMP vAmp CC1 + CINT T/H LPF + CT/H BWAmp VkTC INT VkTC T H (f ) INTEG S CF 2 2 Sin 2 ( f TS ) ( f TS )2 For detector current integration IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 H (f ) 2 2 CDS Vout T/H C 1 4 Sin 2 ( f TS ) C2 +Quantization Noise + INDIGO OPERATIONS Noise Acquisition • External input capacitor added on few channels • 60Hz noise pick up from the inputs / test board Removed by subtracting 2 channels (increases the noise by √2) No input cap 10pF 100pF 50pF 60Hz time 128 channel IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 INDIGO OPERATIONS Noise Measurement • Equivalent Noise Charge (ENC) referred to the input 4000 ENC (e-RMS) 3500 Analysis High resolution setting: ■ ▲ 3000 2500 2000 ■ ▲ 1500 ■▲ Measurement ■ ▲ ■ ▲ 500 1000 00 00 2E-11 20pF IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 4E-11 40pF 6E-11 60pF 8E-11 80pF 1E-10 100pF 1.2E-10 CDET Cf = 1pF LPF=1us GainCDS = 32 ADC = 14bit Noise as a Function of LPF INDIGO OPERATIONS • Dominant thermal noise (V2RMS) 1/LPF 2200 CDET= 50pF Cf = 0.5pF GainCDS = 8 ADC = 14bit ENC (e-RMS) ■ 2000 2000 ▲ 1800 1800 Analysis ▲ ■ 1600 1600 ■ ■ ▲Measurement 1400 1400 ENC 1600e-RMS ■ ▲ 1200 1200 1000 1000 0 0.00E+00 1us 1.00E-06 2us 2.00E-06 3us 3.00E-06 4us 4.00E-06 5us 5.00E-06 LPF 6.00E-06 Optimum noise for 5us LPF time constant IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 INDIGO OPERATIONS ISC9717 Averaging Mode Averaging mode • SNR improvement • Increase readout rate by a factor 2 T/H VAVG = (V1 + V2) / 2 V1 To ADC Odd channel SNR = CHOLD AVG T/H Even channel V2 CHOLD IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 (V1 + V2) 2√ (V2n1 + V2n2) √2 SNR improvement INDIGO OPERATIONS ISC9717 Performance Summary Specifications Nominal Comments Number of channel 128 channel/chip 80um Input bonding pad pitch Clock frequency 12.5MHz Low voltage differential clock Integrator gain control CF=0.5pF, 1pF, 2pF, 4pF 2BIT gain control Charge collection Electrons (≤ 75x106 e-) Hole (≤ 62x106 hole) VREF_INTEG = 1.5V for e- collection VREF_INTEG = 3.0V for hole collection Low-Pass-Filter time constant 0.8us, 1.3us, 2.8us, 3.3us (1us, 2us, 4us, 5us) 2BIT (2 capacitors selectable) 10% tolerance With external voltage adjustment Correlated Double Sampling Gain = x1, x2, x4, x8, x32 Removes the ROIC kTC and 1/f noise Crosstalk 0.25% (internal to ROIC) Total power dissipation 220mW 200mW nominal ADC resolution 9 to 14 bits (gray code output) Programmable ADC resolution (ADC frequency=25MHz) Current mode output 9 to14 output used Parallel output (single ended 0.5mA 20%) ENC (GINTEG =2mV/fC, GCDS=32, ADC=9bit) 1200 e-RMS referred to input Measured noise with 50pF input capacitor Noise depends on systems noise performance ENC (GINTEG =2mV/fC, GCDS=8, ADC=14bit) 1400 e-RMS referred to input Measured noise with 50pF input capacitor Noise depends on systems noise performance ENC (GINTEG =2mV/fC, GCDS=1, ADC=14bit) 2300 e-RMS referred to input Measured noise with 50pF input capacitor Noise depends on systems noise performance IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 INDIGO OPERATIONS Standard ASIC Product Package ISC9717 ROIC USER MANUAL DOC # 400-9717-10 VERSION 2.3 October 14, 2003 Copyright Indigo Systems Corporation 2003 Information furnished by Indigo Systems Corporation is believed to be accurate. However, no responsibility is assumed by Indigo Systems Corporation for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Indigo Systems Corporation. Standard ASICs • By the die in fully tested wafer form • 487 die / wafer AMI 0.5um process Typical yield is above 90% IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 Each wafer: Complete set of documentation • Design and Users Guide complete test data on CD• Technical Application Notes ROM • Physical Interface Drawings CD-ROM contains PRISM test Applications engineering data explorer software support Physical database in GDSII successful integration of format provided on CD-ROM sensor with ROIC Integration While Read INDIGO OPERATIONS Simultaneous integration, A/D conversion and readout Higher frame rate 28.6kHz conversion rate at 9 bit resolution (Clock = 12.5MHz) 1.49kHz conversion rate at 14 bit resolution Stop CLK for longer integration time tINTEG=11.68us + 2(N-1)/fCLK IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 Integration Then Read INDIGO OPERATIONS Integration, ADC and readout performed sequentially Lower Noise 15.1kHz conversion rate at 9 bit ADC resolution (Clock = 12.5MHz) 1.42kHz conversion rate at 14 bit ADC resolution Stop CLK for longer integration time tINTEG=34.4us IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 INDIGO OPERATIONS Noise Measurement (1 of 2) • Equivalent Noise Charge (ENC) referred to the input 4000 3500 3500 ENC (e-RMS) Analysis ▲ High gain setting: Cf = 0.5pF LPF=1us GainCDS = 32 ADC = 9bit 3000 3000 ■ 2500 2500 2000 2000 ▲ ■ ■▲ Measurement 1500 1500 1000 1000 ▲ ■ ■ ▲ 500 500 00 00 2E-11 20pF 4E-11 40pF IEEE NSS N8-4– October 18, 2004 6E-11 60pF 8E-11 80pF 1E-10 100pF 1.2E-10 CDET CBOARD 4.0pF