* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faults - Geology
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Igneous rock wikipedia , lookup
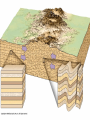
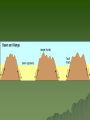
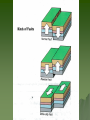
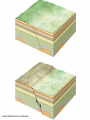
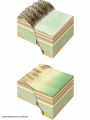
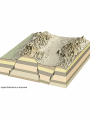
Mountains Part II Domed and FaultBlock Dome Mountains Created when magma pushes up from underneath existing strata and cools. Associated features: A sill is an igneous intrusion that squeezes in between existing rock layers – Goes parallel to the layers – The cliff band on Triangle Mtn is a sill A dike is similar but cuts across the existing rock strata – The belt on Mt Daly is a dike Intrusive Magma: Batholiths are large bubbles of magma (usually felsic) that cool underground. –Forms Tectonic Domes Smaller bubbles are called Laccoliths- usually a sill that has bulged upwards. –Forms Plutonic Domes Stock> Domed mountains create: Cuestas Hogback ridges Flatirons Watergaps Stocks Dike Dike Mtn Sopris = Stock Flat Irons- Boulder Hogback- front range - closest = Grand Hogback near Rifle Cuesta- Horse tooth Reservoir Historic photo of the Grand HogbackNew Castle How to tell the difference between a folded and a domed mountain? If the mountain is folded, the underlying rocks will be either sedimentary or metamorphic If the mountain is domed, then the rocks below will be igneous (intrusive/plutonic) FaultBlock Mountain Fault Block Mtns Formed from blocks of crust that have been faulted and tilted at the same time. Red Butte Sangre De Cristos Tetons Sierra Nevada Wasatch Mountains Joints Rock layers may rupture from pressure applied. Fractures where no movement has occurred are called joints, Faults Faults are fractures in the earth’s crust where movement has occurred. There are three types: normal, reverse or thrust, and strike-slip (also called transcurrent). Teton Mountains The Tetons in Wyoming have been uplifted along a fault plane. Mountain Ranges Mountain ranges are formed when long belts of the earth’s crust are folded and/or faulted then are uplifted and eroded. The Rockies are an example. Erosion When a section of the earth’s crust is elevated, streams begin to erode deep channels. Can form mountains also. Capstones Resistant layers help to produce mesas, buttes, and pinnacles. Earthquakes Earthquakes occur due to movement along faults. Lake Baikal-deepest lake in the world -5,315 feet deep -contains 1/5 of all the world’s freshwater Lake Tahoe