* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPTX
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
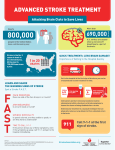
Cardiovascular Disease Project: Stroke Drew, Bruce, Guy, Nick Stroke A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is severely slowed by a blockage or blocked entirely. These blockages cause cells in the brain due to lack of oxygen and other key nutrients that are necessary for brain function. Diagnosis & Symptoms The symptoms ranges based on severity but the overall symptoms are loss of balance, slurred speech, drooping of face, numbness to left side, and trouble understanding. Diagnosing after the fact includes a CT scan of the brain and spinal cord. Causes of Strokes occurs when the blood supply to your brain is interrupted or reduced This deprives your brain of oxygen and nutrients, which can cause your brain cells to die may be caused by a blocked artery (ischemic stroke) or the leaking or bursting of a blood vessel (hemorrhagic stroke) may experience only a temporary disruption of blood flow to their brain (transient ischemic attack, or TIA) About 85 percent of strokes are ischemic stroke Categories of ischemic strokes Thrombotic stroke. A thrombotic stroke occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one of the arteries that supply blood to your brain. A clot may be caused by fatty deposits (plaque) that build up in arteries and cause reduced blood flow (atherosclerosis) or other artery conditions. Embolic stroke. An embolic stroke occurs when a blood clot or other debris forms away from your brain — commonly in your heart — and is swept through your bloodstream to lodge in narrower brain arteries. This type of blood clot is called an embolus. Ways it can be prevented Eating a healthy diet Working out 2 or more days a week Restrict tobacco use Restrict alcohol use Controlling other diseases Be aware of age, family history, race, ethnicity, and previous stroke history Treatments -Anticoagulant medicines such as warfarin, prevents blood clots and current clots from getting bigger -Antiplatelet medication, such as aspirin (keeps platelets from sticking together) -Thins out the blood -Mechanical devices, surgical clips, or coils References "Mayo Clinic." Mayo Clinic. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2015. "MedicineNet - Health and Medical Information Produced by Doctors." MedicineNet - Health and Doctors. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2015. "Menu." National Stroke Association. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2015 "WebMD - Better Information. Better Health." WebMD. WebMD, n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2015. "Welcome." AHA Media Player. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Oct. 2015. Medical Information Produced by