* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Network Devices
Parallel port wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Nonblocking minimal spanning switch wikipedia , lookup
Spanning Tree Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
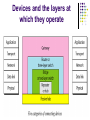
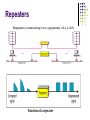
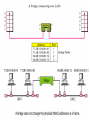
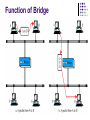
2.2 Network Devices Connectors, Repeaters, Hubs, Bridges, Switches, Routers, NIC’s Network Devices Network is interconnection of devices. For these connection we need to use the connecting devices. Also called as Network Control Devices. The purpose Allow a greater number of nodes to be connected to the network. Extend the distance over which a network can extend. Localize traffic on the network. Can merge existing networks. Isolate network problems so that they can be diagnosed more easily. Devices and the layers at which they operate Connectors To connect cable between two computers. Connectors are of different type such as – Twisted Pair cable Co-axial Cable Fibre optic cable. Connectors are type such as Jacks Plugs Sockets and ports Connectors Example: RS232 and V35 for serial interface RJ45 and BNC connectors for Ethernet. SC or ST connectors for fibre optic Repeaters Signal attenuation or signal loss – signal degrades over distance Repeaters clean, amplify, and resend signals that are weakened by long cable length. Built-in to hubs or switches A repeater operates only at the PHYSICAL layer. It connects two segments of the same network. Single port, multi-port repeaters. Repeaters Function of a repeater HUB A hub is used as a central device. Connects the computers in star topology. Hubs are simple devices that direct data packets to all devices connected to the hub. Hubs regenerate and retime network signals hubs work at the OSI physical layer They cannot filter network traffic. They cannot determine best path They are really multi-port repeaters Types of Hub Passive hub 1. 2. Active hubs or Multiport repeaters 3. is just a connector - connects the wires coming from different branches. The signal pass through a passive hub without regeneration or amplification. (distance 300 feet) They regenerate or amplify the signal before they are retransmitted (distance -2000 feet). Intelligent Hub Regenerate the signals and perform network management and intelligent path selection. Bridges Operates in both the PHYSICAL and the data link layer. As a PHYSICAL layer device, it regenerates the signal it receives. As a data link layer device, the bridge can check the PHYSICAL/MAC addresses (source and destination) contained in the frame. Bridge Bridges A bridge has a table used in filtering decisions. It can check the destination address of a frame and decide if the frame should be forwarded or dropped. For frame to be forwarding, it specify the port. Limit or filter traffic - keeps local traffic local yet allow connectivity to other parts (segments). Function of Bridge Characteristics of Bridges Routing Tables – Contains one entry per station of network. – Is used to determine the network of destination. Filtering – Packets are filtered with respect to their destination and multicast addresses. Forwarding – the process of passing a packet from one network to another. Learning Algorithm – the process by which the bridge learns how to reach stations on the internetwork. Types of Bridges Transparent Bridge Also called learning bridges Build a table of MAC addresses as frames arrive. Ethernet networks use transparent bridge Duties are : Filtering frames, forwarding and blocking Source Routing Bridge Used in Token Ring networks Frame contains not only the source and destination address but also the bridge addresses. Advantages And Disadvantages Advantages of using a bridge – Extend physical network – Reduce network traffic with minor segmentation – Reduce collisions – Connect different architecture Disadvantages of using bridges – Slower than repeaters due to filtering – Do not filter broadcasts – More expensive than repeaters Differences Between Bridges and Repeaters Repeaters Bridges OSI layer Physical layer Data link layer Data regeneration Regenerate data at the signal level Regenerate data at the packet level Yes Reduce network No traffic Switched networks Shared ethernet networks perform best when kept to 30-40 percent full capacity This is a result of CSMA/CD A LAN switch is a high-speed multiport bridge which segments each port into its own collision domain and can access the full bandwidth Devices and the layers at which they operate Layer Name of Layer Device 3 Network Routers, layer 3 switches 2 Data Link Switches, bridges, NIC’s 1 Physical Hubs Switches Each port is a simulated segment to itself Store and Forward Switches Do error checking on each frame after the entire frame has arrived into the switch If the error checking algorithm determines there is no error, the switch looks in its MAC address table for the port to which to forward the destination device Highly reliable because doesn’t forward bad frames Slower than other types of switches because it holds on to each frame until it is completely received to check for errors before forwarding Cut Through Switch Faster than store and forward because doesn’t perform error checking on frames Reads address information for each frame as the frames enter the switch After looking up the port of the destination device, frame is forwarded Forwards bad frames Performance penalty because bad frames can’t be used and replacement frames must be sent which creates additional traffic Fragment free cut through switch Combines speed of cut through switch with error checking functionality Forwards all frames initially, but determines that if a particular port is receiving too many bad frames, it reconfigures the port to store and forward mode Preferred switching solution Unmanaged/Intelligent switches Unmanaged – provides LAN’s with all the benefits of switching Fine in small networks Intelligent switches tracks and reports LAN performance statistics Have a database ASIC (application specific integrated circuit) on board to collect and store data which you view through a software interface Layer 3 switch By definition a switch filters or forwards frames based on MAC addresses. This makes a switch a layer 2 device. Now we have layer 3 switches which have routing capability. If a data frame can’t be switched it is routed. Each port is a separate LAN port, but the forwarding engine actually calculates and stores routes based on IP addresses, not MAC addresses Usually support only IP or IP and IPX VLAN Switches Virtual local area network Each port on a switch defines a collision domain The entire switch forms a single broadcast domain VLANs can define multiple broadcast domains Network traffic that is directed to all computers on the network can be segmented to transmit only on a specific VLAN. Improves bandwidth on a the VLAN’s because each VLAN filters the network-to-network broadcast traffic as well as the collision traffic from other VLAN’s Physical Layer Broadcast Physical layer broadcasts – implemented by non-switched Ethernet networks through shared cabling and hubs Each bit that is transmitted is physically received by every station Switches and VLAN’s don’t do physical layer broadcasts MAC-level broadcast MAC-level broadcast – deal with how to handle MAC level broadcast frames; that is the data frames that have a broadcast destination MAC address MAC-level broadcast frames are addressed to all MAC addresses on a given network (not a network segment, but an actual network as defined by its network address) A regular switch forwards all broadcast frames out all ports, but a VLAN switch forwards broadcast frames only to ports that are part of the same VLAN Multiple switches can be part of the same VLAN VLAN Switches None of the VLAN’s can communicate unless each VLAN is connected to a router or layer 3 switch Each VLAN is separating collision traffic associated with MAC Addresses (layer 2) and each VLAN is separating the network-tonetwork broadcast traffic. In other words each VLAN is acting as a separate network so a layer 3 device is necessary for them to communicate