* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transformer - Hafiz Physics
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Single-wire earth return wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
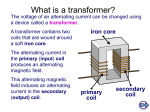
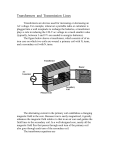
Transformer • • A transformer transforms (change) an alternating p.d. (voltage) from one value to another of greater or smaller value. It has primary and secondary coils wound on a complete soft iron core Primary coil (the input coil) – the incoming voltage, Vp Iron core – link the two coils Secondary coil (the output coil) – provide the voltage Vs to the external circuit How does the transformer induce an alternating voltage in the secondary coil? When the alternating current flows through the primary coil, it sets up an alternating magnetic field in the core and in the secondary coil. This changing field induces an alternating voltage in the secondary coil. Why don’t we use direct current (d.c.) instead of alternating current (a.c.) in the primary coil? Unless there is a changing current in the primary coil, no voltage is induced in the secondary coil. Connecting a d.c. supply to the transformer can damage the transformer. High current flows through the primary coil which can make it overheat. A simple transformer. AC voltages can be increased or decreased using a transformer. Suppose that the field lines pass through both coils, and the coils waste no energy because of the heating effects, therefore the equation applies: secondary voltage secondary turns primary voltage primary turns Vs N s Vp N p 1 STEP-UP AND STEP-DOWN TRANSFORMERS (a) Step-up Transformer A ‘step-up’ transformer has more turns on the secondary than the primary and Vs is greater than Vp. (b) Step-down transformer A ‘step-down’ transformer has fewer turns on the secondary than the primary and Vs is less than Vp. DESIGNS OF TRANSFORMER Both methods are design to trap the magnetic field in the core so that all the field lines from one coil pass through the other. All transformer waste some energy because of the heating effects. 2 Why there is a heating effect and how to reduce this heating effect? The coils are not perfect electrical conductors and heat up because of resistance. To keep the resistance low, thick copper wire is used where possible. The core is itself a conductor, so the changing magnetic field induces currents in it. These circulating currents have heating effect. To reduce them, the core is laminated (layered): it is made from thin, insulated sheets of iron rather than a solid block. Large, well designed transformers can have efficiencies as high as 99%. In other words, their useful power output is 99% of their power input. Power Assume that all electrical energy given to the primary is conserved and transform to secondary, then Power in primary = power in secondary VpIp= VsIs Exercise: 1. How does a step-up transformer differ from the step-down transformer? 2. Explain each of the following: (a) the transformer will not work on DC (b) the core of the transformer need to be laminated (c) If the transformer increase voltage, it reduces current. Prepared by Cikgu Muhd Hafizuddin@ SMSB2006 3