* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORMS!!!!!
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
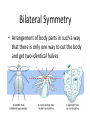
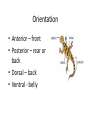
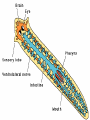
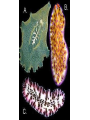
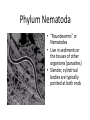
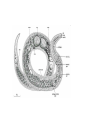
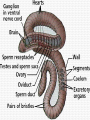
WORMS!!!!! Phylum Platyhelminthes Phylum Nemertea Phylum Nematoda Phylum Annelida Bilateral Symmetry • Arrangement of body parts in such a way that there is only one way to cut the body and get two identical halves Orientation • Anterior – front • Posterior – rear or back • Dorsal – back • Ventral - belly Bilateral Charact. Bilateral symmetry allows for the following: - A head with a brain - More active pursuit of prey - Body has specialized tissues and organs - More sophisticated behaviors Phylum Platyhelminthes • “Flatworms” • Dorsoventrally flattened (flat backs and bellies) • Simplest organisms whose tissues are organized into real organs and organ systems Phylum Platyhelminthes • Has a central nervous system with a simple brain and nerve cords along the body • There is a well developed muscular system, reproductive, and digestive system Phylum Platyhelminthes a) Can be carnivorous b) Can live inside or on the surface of organisms c) Parasites such as flukes and tapeworms Phylum Nemertea • “Ribbon worms” • Look like long flat worms • One measured at 30m long Phylum Nemertea • Defining characteristics: – Complete digestive tract: mouth, gut, anus – Presence of a circulatory system – Most distinctive feature is a proboscis – All predators that feed on worms and crustaceans Proboscis • A long, fleshy tube used to entangle prey • Everted from a cavity above the mouth like a finger in a glove Phylum Nematoda • “Roundworms” or Nematodes • Live in sediments or the tissues of other organisms (parasites) • Slender, cylindrical bodies are typically pointed at both ends Phylum Nematoda • Hydrostatic skeleton that provides support and locomotion • Larva can be found in raw fish which is in turn ingested by humans Phylum Annelida • “Segmented Worms” • Body consists of a series of segments (think earthworm) • Gut goes through all segments • Contain a central cavity known as a coelom Phylum Annelida • Closed circulatory system – blood always stays in blood vessels • Typically burrowers • Includes Leeches