* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Isosceles, Equilateral and Right Triangles
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
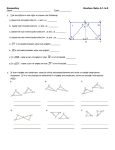
Isosceles, Equilateral and Right Triangles November 7, 2012 By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: • Use properties of isosceles and equilateral triangles to show angle measures, side lengths and prove triangle congruence. • Use properties of right triangles to show angle measures, side lengths and prove triangle congruence. • Prove triangle congruence using the Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Theorem Draw and label an ISOSCELES triangle with the following: • • • • • Vertices A, B & C Legs Base Base Angles Vertex Angle • Base Angles Theorem: If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite them are congruent. If 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝐴𝐶, then 𝐵 ≅ 𝐶 • Base Angles Theorem: If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite them are congruent. • Converse of the Base Angles Theorem: If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite them are congruent. If 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝐴𝐶, then 𝐵 ≅ 𝐶 If 𝐵 ≅ 𝐶, then 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝐴𝐶 • Base Angles Theorem: If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite them are congruent. • Converse of the Base Angles Theorem: If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite them are congruent. If 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝐴𝐶, then 𝐵 ≅ 𝐶 If 𝐵 ≅ 𝐶, then 𝐴𝐵 ≅ 𝐴𝐶 Both of these statements are TRUE, so we can write this in the form of a BICONDITIONAL STATEMENT. Both of these statements are TRUE, so we can write this in the form of a BICONDITIONAL STATEMENT. Two angles of a triangle are congruent if and only if the sides opposite them are congruent. An EQUILATERAL triangle is a special type of triangle. An EQUILATERAL triangle is a special type of triangle. If a triangle is EQUIANGULAR, then it is EQUILATERAL. An EQUILATERAL triangle is a special type of triangle. If a triangle is EQUIANGULAR, then it is EQUILATERAL. If a triangle is EQUILATERAL, then it is EQUIANGULAR. So far we have learned about four ways to prove that triangles are congruent. SSS ( ) Congruence Postulate SAS ( ) Congruence Postulate ( ) Congruence Postulate ( ) Congruence Postulate ASA AAS There is ONE MORE WAY to prove triangle congruence. This way is SPECIAL because it can only be used when working with RIGHT triangles. There is ONE MORE WAY to prove triangle congruence. This way is SPECIAL because it can only be used when working with RIGHT triangles. HYPOTENUSE-LEG (HL) CONGRUENCE THEOREM: If the hypotenuse and a leg of a right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and a leg of a second right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. If 𝐵𝐶 ≅ 𝐸𝐹 and 𝐴𝐶 ≅ 𝐷𝐹, then ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF