* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Media Access and Internet Working
Low Pin Count wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
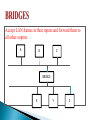
MEDIA ACCESS AND INTERNETWORKING BY SUBASHINI.G Sub layer of datalink layer. Provides addressing and channel access control mechanism. IEEE 802.3 formed a standard technology called Ethernet. Uses CSMA/CD technology. Ethernet standard found in 1972. 802.3 extended for 100 Mbps called fast ethernet. 1000 Mbps- GigaBit Ethernet Carrier Sense Multiple Access. Set of nodes send and receive frames. Nodes can distinguish between an idle and busy link. Uses packet radio network as a rout protocol. Implemented on a coaxial cable of 500 metres. Host connect to an ethernet. Transceiver- device attached to the tape. It receives incoming signal. It connected to ethernet adapter which is plugged into the host. transceiver ethernet cable adapter Multiple ethernet segment can be joined by repeaters. Device that follows signals in all outgoing segments. Signal is propagated in both directions. Manchester encoding is used here. Several point to point segments coming out of a multiwave repeater. HUB HUB HOST ETHERNET HUB Algorithm that controls access to a shared ethernet link. Implemented as hardware in the network adapter. 64 48 48 preamble Dest add Src add 16 46-1500 32 type body CRC Preamble(64 bits): allows receiver to synchronize the signal. Host and destination address(48 bits). Packet type(16 bits):acts as demux key and identify the higher level protocol. Each host on the ethrnet has a unique ethernet address. Address belongs to the adapter not the host. A sequence of six number separated by colon(ie) 6*1/2 Ex 8:0:2b:e4:b1:2 Every adapter has a unique address . Unicast – frame is transmitted to the ethernet. Broadcast - we are going to set all the bits as 1. Multicast – the first bit set to 1. Ethernet adapter accepts all frames and accepts. Frames address to its own address Frames address to the broadcast address Frames address to the multicast address if it has been instructed Wireless signal uses electromagnetic signals. Use of particular frequency allocated by FCC-Federal Communication Commission- USA Three categories: Some bands for government use. Some bands for AM Radio,FM Radio, telivision,satellite communication. Some bands for individual organization in certain area. BLUETOOTH WI-FI WI MAX 3G CELLULAR NETWORKS Nodes are peers. Designed for limited geographical area. Signal propagation through space. 802.11 using two technologies Frequency hopping- MHz(or)GHz Direct sequence- MHz A and c are said to be hiden nodes because they re not aware of collision B A C is called exposed node to B C D 802.11 packet format 16 16 48 48 48 16 48 0-18496 32 control dest add1 add2 add3 seq add4 Pay CRC load Used for short range communication inbetween mobile phones, PDA Going to operate on 2.45 GHz Distance is 10 meters Speed is 2.1 Mbps Based on piconet We have advanced technology called Zigbee HUB REPEATER SWITCH BRIDGE ROUTER GATEWAY - PHYSICAL LAYER - PHYSICAL LAYER - DATA LINK LAYER - DATA LINK LAYER - NETWORK LAYER - TRANSPORT LAYER DATAGRAM APPROACH(OR) CONNECTIONLESS VIRTUAL CIRCUIT(OR) CONNECTION ORIENTED SOURCE ROUTING Host can send packet anywhere at anytime Does not care the delivery of data To decide how to forward a packet a routing table is used TWO STAGES Connection setup Data transfer Also called packet switching or virtual circuit Virtual circuit making virtual connection in between sender and receiver Accept LAN frames in their inputs and forward them to all other outputs A B C BRIDGE X Y Z Keeps all the vertices of the original graph but throws some of the edge Sub graph that covers all the vertices but contains no cycle No cycle is formed Minimum cost and covers all the vertices IP PACKET FORMAT VERSION HLEN TOS FLAGS IDENT TTL LENGTH PROTOCOL OFFSET CHECKSUM SOURCE ADDRESS DESTINATION ADDRESS OPTIONS(VARIABLE) PAD(VARIABLE) DATA VERSION- 4 HLEN- HEADER LEN-4 BITS TOS- TYPE OF SERVICE LENGTH-16 BIT-NO OF BYTES IN THE DATAGRAM IDENT- 16 BITS USED FOR FRAGMENTATION FLAGS/OFFESET- THERE ARE 16 BITS USED BY FRAGMENTATION TTL- NO OF HOPS PROTOCOL- 8 BITS-DEMUX KEY CHECKSUM-16 BITS DESTINAION/SOURCE ADDRESS-32 BITS EACH OPTIONS& PAD- 16 BITS(VARYING FROM PACKET TO PACKET) PACKET DELIVERY MODEL Each network has some MTU(Maximum Transmission Unit) ex, Ethernet FDDI- Fibre Distributed Data Interface GLOBAL ADDRESSING SCHEME Global unique address Combination of network and host IP address The division of network into smaller network called subnet IP Address is 32 bit LAN One portion indicates a networlk ID and other portion indicates host or router To connect more host we need subnet 16 1 0 Ex:class B 141.14.0.0 NET 16 H H Delivery to the site Delivery to the sub-net Delivery to the host MASKING: It is a process that extracts the address of physical network from an IP address Masking can be done whether we have subnet or not MASK WITHOUT SUBNETTING 141.14.2.21 IP ADDRESS N/w ADDRESS 141.14.0.0 MASK 255.255.0.0 • MASK WITH SUBNETTING 141.14.2.21 MASK 255.255.255.0 141.14.2.0 Also called supernetting Allocate and specify the internet address used in inter domain routing Consists of two groups ◦ To identify a network/subnetwork ◦ To identify a host ARP PACKET FORMAT HARDWARE TYPE H LEN P LEN PROTOCOL TYPE OPERATION SOURCE HARDWARE ADDRS(BYTE 0-3) SOURCE HARDWARE ADDRESS (BYTE 4-5) SOURCE PROTOCOL ADDRESS(BYTE 0-1) SOURCE PROTOCOL ADDRESS (BYTE 2-3) TARGET HARDWARE ADDRESS (BYTE 0-1) TARGET HARDWARE ADDRESS(BYTE 2-5) TARGET PROTOCOL ADDRESS(BYTE 0-3) UNICAST TO SERVER DHCP RELAY HOST OTHER N/W DHCP SERVER It is responsible for providing configufration information to host There is atleast one DHCP server for an administrative domain It maintains a pool of available devices DHCP relay unicast the message to the DHCP server and waits for response Defines collection of error messages that are send back to the source host whenever the router is unable to crosses an IP datagram ERRORS: ◦ Destination host unreachable due to link or node failure ◦ Reassembling process failed